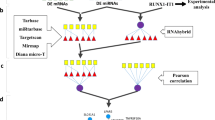
Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can not only regulate gene transcription and translation, but also participate in the development of central nervous system diseases as epigenetic modification factors. However, their functional significance in atherosclerosis-induced ischemic stroke (AIIS) is unclear. The study aimed to screen out differentially expressed lncRNAs (delncRNAs), and to elucidate their potential regulatory mechanisms in the pathophysiology of AIIS. Based on the clinicopathological features and clinical images, we screened out 10 patients with AIIS and recruited 10 healthy volunteers. Then we used microarray to detect the whole blood RNA of subjects, and explored the biological functions of delncRNAs by GO and KEGG analysis. After further analyzing the delncRNAs of THP-1 stimulated with ox-LDL, selective lncRNAs were screened and a corresponding lncRNA–mRNA interaction network was constructed through co-expression analysis. We yielded 180 delncRNAs (44 up-regulated and 136 down-regulated) and 218 demRNAs (45 up-regulated and 173 down-regulated). Lnc-SCARNA8 and lnc-SNRPN-2 are the most significant elevated and decreased lncRNA in AIIS, respectively. The delncRNAs may play a significant role in ubiquitination-mediated protein degradation signaling pathways. According to lncRNA–mRNA network, the expression of vacuolar protein sorting 13 homolog B (VPS13B) and biliverdin reductase B (BLVRB) were significantly regulated. Our findings suggest that the ubiquitinated proteasome pathway, VPS13B and BLVRB may play a fundamental role in the pathological process of AIIS.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIIS:
-
Atherosclerosis-induced ischemic stroke
- BLVRB:
-
Biliverdin reductase B
- CTA:
-
CT angiography
- delncRNAs:
-
Differentially expressed lncRNAs
- demRNAs:
-
Differentially expressed mRNAs
- GO:
-
Geneontology
- HECTD1:
-
HECT domain E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1
- ICA:
-
Intracranial atherosclerosis
- KEGG:
-
Kyotoencyclopedia of genes and genomes
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- MAT2A:
-
Methionine adenosyltransferase 2A
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- ncRNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- OGD:
-
Oxygen and glucose deprivation
- ox-LDL:
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- qRT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SLC38A2:
-
Solute carrier family 38 member 2
- VPS13B:
-
Vacuolar protein sorting 13 homolog B
References
Banerjee C, Chimowitz MI (2017) Stroke caused by atherosclerosis of the major intracranial arteries. Circ Res 120(3):502–513. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308441
Bao MH, Szeto V, Yang BB, Zhu SZ, Sun HS, Feng ZP (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 9(3):281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0282-x
Bhattarai S, Pontarelli F, Prendergast E, Dharap A (2017) Discovery of novel stroke-responsive lncRNAs in the mouse cortex using genome-wide RNA-seq. Neurobiol Dis 108:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.08.016
Chamorro A, Dirnagl U, Urra X, Planas AM (2016) Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol 15(8):869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(16)00114-9
Chandra D, Londino J, Alexander S, Bednash JS, Zhang Y, Friedlander RM et al (2019) The SCFFBXO3 ubiquitin E3 ligase regulates inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell 126:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.11.006
Chaudhry FA, Schmitz D, Reimer RJ, Larsson P, Gray AT, Nicoll R et al (2002) Glutamine uptake by neurons: interaction of protons with system a transporters. J Neurosci 22(1):62–72. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-01-00062.2002
Dharap A, Nakka VP, Vemuganti R (2012) Effect of focal ischemia on long noncoding RNAs. Stroke 43(10):2800–2802. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.669465
Dolati S, Ahmadi M, Khalili M, Taheraghdam AA, Siahmansouri H, Babaloo Z et al (2018) Peripheral Th17/Treg imbalance in elderly patients with ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci 39(4):647–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3250-4
Donkor ES (2018) Stroke in the 21(st) century: a snapshot of the burden, epidemiology, and quality of life. Stroke Res Treat 2018:3238165. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3238165
Doyle KP, Quach LN, Sole M, Axtell RC, Nguyen TV, Soler-Llavina GJ et al (2015) B-lymphocyte-mediated delayed cognitive impairment following stroke. J Neurosci 35(5):2133–2145. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4098-14.2015
Duplomb L, Riviere J, Jego G, Da Costa R, Hammann A, Racine J et al (2019) Serpin B1 defect and increased apoptosis of neutrophils in Cohen syndrome neutropenia. J Mol Med 97(5):633–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01754-4
Dykstra-Aiello C, Jickling GC, Ander BP, Shroff N, Zhan X, Liu D et al (2016) Altered expression of long noncoding RNAs in blood after ischemic stroke and proximity to putative stroke risk loci. Stroke 47(12):2896–2903. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013869
Fernandez DM, Rahman AH, Fernandez NF, Chudnovskiy A, Amir ED, Amadori L et al (2019) Single-cell immune landscape of human atherosclerotic plaques. Nat Med 25(10):1576–1588. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0590-4
Forstermann U, Xia N, Li H (2017) Roles of vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 120(4):713–735. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.116.309326
Fu X, Li X, Xiong L, Li X, Huang R, Gao Q (2019) Cerebral arterial stiffness as a new marker of early stage atherosclerosis of the cerebral large artery in acute stroke. J Atheroscler Thromb 26(9):783–791. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.46573
He W, Wei D, Cai CS, Li S, Chen W (2018) Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in ischemic stroke. Hum Gene Ther 29(6):719–732. https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2017.064
Hochrainer K (2018) Protein modifications with ubiquitin as response to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transl Stroke Res 9(2):157–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-017-0567-x
Hoffmann TM, Cwiklinski E, Shah DS, Stretton C, Hyde R, Taylor PM et al (2018) Effects of sodium and amino acid substrate availability upon the expression and stability of the SNAT2 (SLC38A2) amino acid transporter. Front Pharmacol 9:63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00063
Jones KA, Maltby S, Plank MW, Kluge M, Nilsson M, Foster PS et al (2018) Peripheral immune cells infiltrate into sites of secondary neurodegeneration after ischemic stroke. Brain Behav Immun 67:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.09.006
Kamimura T, Okazaki S, Morimoto T, Kobayashi H, Harada K, Tomita T et al (2019) Prevalence of RNF213 p.R4810K variant in early-onset stroke with intracranial arterial stenosis. Stroke 50(6):1561–1563. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.118.024712
Katan M, Luft A (2018) Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol 38(2):208–211. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1649503
Li G, Morris-Blanco KC, Lopez MS, Yang T, Zhao H, Vemuganti R et al (2018) Impact of microRNAs on ischemic stroke: from pre- to post-disease. Prog Neurobiol 163–164:59–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.08.002
Li P, Mao L, Zhou G, Leak RK, Sun BL, Chen J et al (2013) Adoptive regulatory T-cell therapy preserves systemic immune homeostasis after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 44(12):3509–3515. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.002637
Li Z, Li J, Tang N (2017) Long noncoding RNA Malat1 is a potent autophagy inducer protecting brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-26b and upregulating ULK2 expression. Neuroscience 354:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.04.017
Lin CH, Liao LY, Yang TY, Chang YJ, Tung CW, Hsu SL et al (2019) Microglia-derived adiposomes are potential targets for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39(5):591–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00665-9
Liu D, Ding Z, Wu M, Xu W, Qian M, Du Q et al (2017) The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, D-4F, alleviates ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress and promotes endothelial repair through the eNOS/HO-1 pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol 105:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.01.017
Lorenzen JM, Martino F, Thum T (2012) Epigenetic modifications in cardiovascular disease. Basic Res Cardiol 107(2):245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-012-0245-9
Lorenzen JM, Thum T (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in kidney and cardiovascular diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol 12(6):360–373. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.51
Mazidi M, Penson P, Gluba-Brzozka A, Rysz J, Banach M (2017) Relationship between long noncoding RNAs and physiological risk factors of cardiovascular disease. J Clin Lipidol 11(3):617–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacl.2017.03.009
Mehta SL, Kim T, Vemuganti R (2015) Long noncoding RNA FosDT promotes ischemic brain injury by interacting with REST-associated chromatin-modifying proteins. J Neurosci 35(50):16443–16449. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2943-15.2015
Morotti M, Bridges E, Valli A, Choudhry H, Sheldon H, Wigfield S et al (2019) Hypoxia-induced switch in SNAT2/SLC38A2 regulation generates endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(25):12452–12461. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818521116
Paukovich N, Xue M, Elder JR, Redzic JS, Blue A, Pike H et al (2018) Biliverdin reductase B dynamics are coupled to coenzyme binding. J Mol Biol 430(18 Pt B):3234–3250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2018.06.015
Ruan W, Li J, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhao F, Yang X et al (2019) MALAT1 up-regulator polydatin protects brain microvascular integrity and ameliorates stroke through C/EBPbeta/MALAT1/CREB/PGC-1alpha/PPARgamma pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39(2):265–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-00646-4
Rust R, Hofer AS, Schwab ME (2018) Stroke promotes systemic endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Trends Mol Med 24(7):593–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2018.04.008
Selvaraj UM, Poinsatte K, Torres V, Ortega SB, Stowe AM (2016) Heterogeneity of B cell functions in stroke-related risk, prevention, injury, and repair. Neurotherapeutics 13(4):729–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-016-0460-4
Shearman JR, Wilton AN (2011) A canine model of Cohen syndrome: trapped neutrophil syndrome. BMC Genomics 12:258. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-258
Shekhar S, Cunningham MW, Pabbidi MR, Wang S, Booz GW, Fan F (2018) Targeting vascular inflammation in ischemic stroke: recent developments on novel immunomodulatory approaches. Eur J Pharmacol 833:531–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.06.028
Shimada K (2009) Immune system and atherosclerotic disease: heterogeneity of leukocyte subsets participating in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ J 73(6):994–1001. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-09-0277
Solanki A, Bhatt LK, Johnston TP (2018) Evolving targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Ther 187:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.02.002
Stohr R, Mavilio M, Marino A, Casagrande V, Kappel B, Mollmann J et al (2015) ITCH modulates SIRT6 and SREBP2 to influence lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis in ApoE null mice. Sci Rep 5:9023. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09023
Szczesniak MW, Makalowska I (2016) lncRNA-RNA interactions across the human transcriptome. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150353. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150353
Thakkar M, Edelenbos J, Dore S (2019) Bilirubin and ischemic stroke: rendering the current paradigm to better understand the protective effects of bilirubin. Mol Neurobiol 56(8):5483–5496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1440-y
Wang Y, Yang T, Zhang Z, Lu M, Zhao W, Zeng X et al (2017) Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes migration and invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-335-5p in osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Sci 108(5):859–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13201
Wu S, Li Z, Gnatenko DV, Zhang B, Zhao L, Malone LE et al (2016) BLVRB redox mutation defines heme degradation in a metabolic pathway of enhanced thrombopoiesis in humans. Blood 128(5):699–709. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-02-696997
Wu Z, Wu P, Zuo X, Yu N, Qin Y, Xu Q et al (2017) LncRNA-N1LR enhances neuroprotection against ischemic stroke probably by inhibiting p53 phosphorylation. Mol Neurobiol 54(10):7670–7685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0246-z
Xu Q, Deng F, Xing Z, Wu Z, Cen B, Xu S et al (2016) Long non-coding RNA C2dat1 regulates CaMKIIdelta expression to promote neuronal survival through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway following cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Dis 7:e2173. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.57
Yan H, Yuan J, Gao L, Rao J, Hu J (2016) Long noncoding RNA MEG3 activation of p53 mediates ischemic neuronal death in stroke. Neuroscience 337:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.09.017
Yang J, Gu L, Guo X, Huang J, Chen Z, Huang G et al (2018) LncRNA ANRIL expression and ANRIL gene polymorphisms contribute to the risk of ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han population. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(6):1253–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-0593-6
Ye J, Das S, Roy A, Wei W, Huang H, Lorenz-Guertin JM et al (2019) Ischemic injury-induced CaMKIIdelta and CaMKIIgamma confer neuroprotection through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Neurobiol 56(3):2123–2136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1198-2
Yin KJ, Hamblin M, Chen YE (2014) Non-coding RNAs in cerebral endothelial pathophysiology: emerging roles in stroke. Neurochem Int 77:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.03.013
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2013) Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA. J Mol Biol 425(19):3723–3730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.024
Zhang J, Yuan L, Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Zhu T, Meng F et al (2016) Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 277:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.014
Zhang X, Tang X, Liu K, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ (2017) Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci 37(7):1797–1806. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3389-16.2017
Zhou Z, Lu J, Liu WW, Manaenko A, Hou X, Mei Q et al (2018) Advances in stroke pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther 191:23–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.05.012
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571134, 81973512), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160032), the Opening Project of Zhejiang Provincial Preponderant and Characteristic Subject of Key University (Traditional Chinese Pharmacology), Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (No. ZYAOX2018001), and Double First-Class Project of China Pharmaceutical University (CPU2018GY06, CPU2018GY20). This work was also supported by the Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province to Tao Pang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed contributed immensely to this study. WR and JW performed the experiments and wrote the paper. WR, JW, JS, and YJ collected the samples, performed molecular biology experiments, in vitro experiments, and analyzed the data. TP and JL designed the research, discussed the results, and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, China Pharmaceutical University and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, W., Wu, J., Su, J. et al. Altered lncRNAs Transcriptomic Profiles in Atherosclerosis-Induced Ischemic Stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 265–278 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00918-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00918-y