Abstract
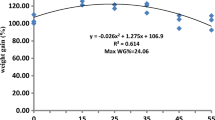
A feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effects of different levels (0%, 16.67%, 33.33%, 50%, and 66.67%) of fish meal replacement by protein mixtures on the growth, body composition, and physiological metabolism of juvenile swimming crabs, Portunus trituberculatus. The results showed that the final body weight (FBW), weight gain rate (WGR), specific growth rate (SGR), intermolt duration (ID), and hepatosomatic index (HSI) initially increased and then decreased with increasing dietary fish meal replacement levels, and the highest FBW, WGR, and SGR values were found in crabs fed Diet 3. The crude protein content in the body significantly decreased, whereas the moisture and ash contents increased significantly with increasing fish meal replacement levels. The digestive enzyme activity of crabs was significantly affected by different levels of fish meal replacement with protein mixtures. The highest glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT) levels in the hepatopancreas were detected in crabs fed Diet 5. The serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity increased significantly with increasing fish meal replacement levels. In conclusion, the results of this study indicated that the appropriate dietary fish meal replacement level is approximately 33% with no significant negative effects on the growth performance of juvenile P. trituberculatus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand PSS, Kohli MPS, Roy SD et al (2013) Effect of dietary supplementation of periphyton on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities in Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 392-395:59–68
Andersen F, Lygren B, Maage A, Waagbø R (1998) Interaction between two dietary levels of iron and two forms of ascorbic acid and the effect on growth, antioxidant status and some non-specific immune parameters in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolts. Aquaculture 161:437–451
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, AOAC International, Arlington
Barnes ME, Brown ML, Neiger R (2015) Comparative performance of two rainbow trout strains fed fermented soybean meal. Aquac Int 23:1227–1238
Catacutan MR (2002) Growth and body composition of juvenile mud crab, Scylla serrata, fed different dietary protein and lipid levels and protein to energy ratios. Aquaculture 208:113–123
Chang GL, Wu XG, Cheng YX et al (2008) Effect of lipid nutrition on hepatosomatic index and biochemical composition of juvenile Eriocheir sinensis. Oceanol Limnol Sin 39:276–283. https://doi.org/10.11693/hyhz20080348048
Chen LQ, Du NS, Lai W (1994) Evaluation of soybean cake as a substitute for partial fish meal in formulated diets for Chinese mitten-handed crab (Eriocheir sinensis) juvenile. J Fish China 18:24–31
Chien YH, Pan CH, Hunter B (2003) The resistance to physical stresses by Penaeus monodon juveniles fed diets supplemented with astaxanthin. Aquaculture 216:177–191
Cortés-jacinto E, Villarreal-colmenares H, Cruz-suárez LE, Civera-cerecedo R, Nolasco-soria H, Hernandez-llamas A (2005) Effect of different dietary protein and lipid levels on growth and survival of juvenile Australian redclaw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens). Aquac Nutr 11:283–291
Dai WW, Mai KS, Xu W et al (2016) Effects of replacing fish meal with plant-based protein on growth, physiological and biological indices, and intestinal histology in tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis Güntuer. J Fish Sci China 23:125–137. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1118.2016.15106
Fisheries Bureau of Ministry of Agriculture, China (2018) China fishery statistical yearbook. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Food and Agriculture Organization (2012) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. http://www.fao.org/fishery/sofia/en. Accessed 28 April 2019
Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227
Gamboa-Delgado J, Rojas-Casas MG, Nieto-López MG, Cruz-Suárez LE (2013) Simultaneous estimation of the nutritional contribution of fish meal, soy protein isolate and corn gluten to the growth of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) using dual stable isotope analysis. Aquaculture 380-383:33–40
Gao F (2017) Discriminant analysis of animal-derived feedstuffs of different species by spectroscopy based on lipid characteristics. Dissertation, China Agricultural University
Jin M, Zhou QC, Zhang W, Xie FJ, Shentu JK, Huang XL (2013) Dietary protein requirements of the juvenile swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Aquaculture 414-415:303–308
Li EC, Chen LQ, Zeng C, Yu N, Xiong ZQ, Chen XF, Qin JG (2008) Comparison of digestive and antioxidant enzymes activities, haemolymph oxyhemocyanin contents and hepatopancreas histology of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, at various salinities. Aquaculture 274:80–86
Li ZS, Wu LX, Li SM, Peng BW, Zhao BW (2016) Effects of replacing fish meal with poultry by-product meal on growth performance and body composition of juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Fish Sci 35:486–491. https://doi.org/10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2016.05.005
Li N, Zheng YH, Wu XF et al (2017) Tolerance of selenium-yeast in diets of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Chin J Anim Nutr 29:1949–1960. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2017.06.016
Lin S, Li L (2011) Effects of different levels of soybean meal inclusion in replacement for fish meal on growth, digestive enzymes and transaminase activities in practical diets for juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus. Anim Feed Sci Technol 168:80–87
Liu YZ, He G, Wang QC, Mai KS, Xu W, Zhou HH (2014) Hydroxyproline supplementation on the performances of high plant protein source based diets in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 433:476–480
Millamena OM (2002) Replacement of fish meal by animal by-product meals in a practical diet for grow-out culture of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 204:75–84
Mu YY, Shim KF, Guo JY (1998) Effects of protein level in isocaloric diets on growth performance of the juvenile Chinese hairy crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquaculture 165:139–148
Nandeesha MC, De Silva SS, Murthy DK, Dathatri K (1994) Use of mixed feeding schedules in fish culture: field trials on catla, Catla catla (Hamilton-Buchanan), rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton), and common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Aquac Res 25:659–670
Nandeesha MC, Gangadhara B, Varghese TJ, Keshavanath P (1998) Effect of feeding Spirulina platensis on the growth, proximate composition and organoleptic quality of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Aquac Res 29:305–312
Ross SW, Dalton DA, Kramer S, Christensen BL (2001) Physiological (antioxidant) responses of estuarine fishes to variability in dissolved oxygen. Comp Biochem Physiol C 130:289–303
Shen YC, Chen ZZ, Liu L, Li ZL, Wu ZH (2012) The effects of salinity and nutrition on molt and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei. J Fish China 36:290–299
Skalli A, Hidalgo MC, Abellán E, Arizcun M, Cardenete G (2004) Effects of the dietary protein/lipid ratio on growth and nutrient utilization in common dentex (Dentex dentex L.) at different growth stages. Aquaculture 235:0–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.01.014
Wang P, Zhu JQ, Feng J, He JJ, Lou YD, Zhou QC (2017) Effects of dietary soy protein concentrate meal on growth, immunity, enzyme activity and protein metabolism in relation to gene expression in large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 477:15–22
Ward LR, Carter CG, Crear BJ, Smith DM (2003) Optimal dietary protein level for juvenile southern rock lobster, Jasus edwardsii, at two lipid levels. Aquaculture 217:483–500
Watanabe T, Pongmaneerat J, Sato S, Takeuchi T (1993) Replacement of fishmeal by alternative protein sources in rainbow trout diets. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 59:1573–1579
Webster CD, Thompson KR, Morgan AM, Grisby EJ, Gannam AL (2000) Use of hempseed meal, poultry by-product meal, and canola meal in practical diets without fish meal for sunshine bass (Morone chrysops × M. saxatilis). Aquaculture 188:299–309
Winston GW, Giulio RTD (1991) Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 19:137–161
Wu XG, Chang GL, Cheng YX, Zeng CS, Southgate PC, Lu JF (2010) Effects of dietary phospholipid and highly unsaturated fatty acid on the gonadal development, tissue proximate composition, lipid class and fatty acid composition of precocious Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquac Nutr 16:25–36
Xie SW, Liu YJ, Zeng S, Jin N, Tian LX (2016) Partial replacement of fish-meal by soy protein concentrate and soybean meal based protein blend for juvenile Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 464:296–302
Zhang L (2007) The study of effect of dietary protein sources and anti-nutritional factors on physiology and chemistry in the Chinese mitten-handed crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Dissertation, East China Normal University
Zhang L, Chen LQ, Hong ML et al (2007) Apparent digestibility of crude protein and amino acids of 11 feed ingredients for Eriocheir sinensis. J Fish China 31:116–121. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0615.2007.z1.021
Zhang L, Mai KS, Ai QH, Duan QY, Zhang CX, Li HT, Tan BP (2010) Use of a compound protein source as a replacement for fish meal in diets of large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea R. J World Aquacult Soc 39:83–90
Zhao ZX, Song CY, Xie J, Ge XP, Liu B, Xia SL, Yang S, Wang Q, Zhu S (2016) Effects of fish meal replacement by soybean peptide on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, and immune responses of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Fish Sci 82:665–673
Zhou PP, Wang MQ, Xie FJ, Deng DF, Zhou QC (2016) Effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratios on growth performance, digestive enzyme and hepatic carbohydrate metabolic enzyme activities of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea). Aquaculture 452:45–51
Zhu SC, Long XW, Xiang CL, Zhang JB, Deng D, Zhou YC, Cheng YX, Wu XG (2019) Effects of dietary fishmeal replacement with protein mixtures on growth performance, physiological metabolism and biochemical composition of juvenile Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). South China Fish Sci 15:83–92. https://doi.org/10.12131/20180168
Funding
This study was supported by an extension project (no. 2016-1-18) from the Shanghai Agriculture Committee and Research Project for High Level University in Shanghai (no. A1-2801-18-1003) from the Shanghai Education Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Zhu, S., Long, X. et al. Effects of dietary fish meal replacement with protein mixtures on growth performance, biochemical composition, and physiological metabolism of juvenile swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Aquacult Int 28, 1531–1545 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00541-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00541-0