Abstract
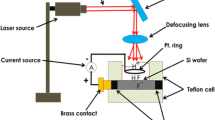
This work discusses the preparation and formation of macro porous silicon (PSi) with silicon nano pillars; synthesized via laser–induced etching. The role of laser pulse duty cycle (10–100%) was investigated for silicon nano pillars samples creation using laser diode; characterized by its short wavelength (405 nm) and high laser intensity (500 mW/cm2). Morphological and spectroscopic aspects of the Si nanocrystallite sizes and plasmonic Au–NP, surface topography, roughness and thickness of the created layer were investigated by the scanning probe microscopy, photoluminescence measurements, the analysis of (FESEM) images and (XRD) patterns. The results revealed well-regulated Si nano pillars layers after adjusting the laser duty cycle under the same laser intensity and etching time. The histogram of Si nano pillars sizes, surface roughness and altitude of nano pillars within macro PSi created at 20% laser duty cycle showed specific characteristics; due to the minimal heat accumulation within the pillars and limited probability of damaging the pillars’ morphological aspects. The Si nano pillars were employed to synthesize and control the plasmonic features of Au-NPs. The histogram of hotspot regions and plasmonic Au-NPs sizes and their specific surface areas and grain size showed well-controlled structures after adjusting the laser pulse duty cycle.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexis, L., Victoire, A., Boitel-Aullen, G., Mylan, L., Michèle, S., Souhir, B.: Silver-based plasmonic nanoparticles for and their use in biosensing. Biosensors 9, 1–39 (2019)
Alwan, A.M., Dheyab, A.B.: Room temperature CO2 gas sensors of AuNPs/mesoPSi hybrid structures. Appl. Nanosci. 7, 335–341 (2017)
Alwan, A.M., Hayder, A.J., Jabbar, A.A.: Study on morphological and structural properties of silver plating on laser etched silicon. Surf. Coat. Techbol. 283, 22–28 (2015)
Alwan, A.M., Yousif, A.A., Wali, L.A.: A study on the morphology of the silver nanoparticles deposited on the n-type porous silicon prepared under different illumination types. Plasmonics (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0620-3
Alwan, A.M., Rashid, R.B., Dheyab, A.B.: Morphological and electrical properties of gold nanoparticles/macro porous silicon for CO2 gas. Iraqi J. Sci. 59(1), 57–66 (2018)
Chalhoub, A.E., Semmar, N., Coudron, L., Gautier, G., Boulmer-Leborgne, C., et al.: Thermal conductivity measurement of porous silicon by the pulsed-photothermal method. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44, 1–16 (2011)
Hayder, A.J., Alwan, A.M., Jabbar, A.A.: Optimizing of porous silicon morphology for synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 227, 152–160 (2016)
Huang, A.P., Uti, X.Y.J., Paul, K.C.: Surface modification of Si-based materials by plasma gas treatments. In: Research Signpost, pp. 335–387 (2009)
Kaganer, V.M., Bernd, J., Roman, S., Wolfgang, B., Henning, R.: Kinetic optimum of volmer-weber growth. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 1–14 (2009)
Kucherik, A., Kutrovskaya, S., Osipov, A., Gerke, M., Chestnov, I., Arakelian, S., Shalin, A.S., Evlyukhin, A.B., Kavokin, A.V.: Nano-antennas based on silicon gold nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–6 (2019)
Kumar, V., Saxena, K., Shukla, A.K.: Size-dependent photoluminescence in silicon nanostructures: quantum confinement effect. Micro Nano Lett. 8(6), 311–314 (2013)
Lannoo, M.: The role of dangling bonds in the properties of surfaces and interfaces of semiconductors. Rev. Phys. Appl. 25, 887–894 (1990)
Makarov, V.V., Love, A.J., Sinitsyna, O.V., Makarova, S.S., Yaminsky, I.V., Taliansky, M.E., Kalinina, N.O.: “Green” nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 6, 35–44 (2014)
Pohl, U.W.: Low-Dimensional Semiconductors. Springer Handbook of Materials Data, pp. 1081–1104 (2018)
Spinelli, P., Polman, A.: Prospects of near-field plasmonic absorption enhancement in semiconductor materials using embedded Ag nanoparticles. Opt. Express 20, 1–14 (2012)
Sychugov, I., Juhasz, R., Linnros, J., Valenta, J.: Luminescence blinking of a Si quantum dot in a SiO2 shell. Phys. Rev. B 71, 115331–115335 (2005)
Xiong, Z.H., Yuan, S., Jiang, Z.M., Qin, J., Peil, C.W., Liao, S., Ding, X.M., Hou, X.Y., Xun, W.: Photoluminescence studies of porous silicon microcavities. J. Lumin. 80, 137–140 (1998)
Xu, S.H., Xiong, Z.H., Gu, L.L., Liu, Y., Ding, X.M., Zi, J., Hou, X.Y.: Photon confinement in one-dimensional photonic quantum-well structures of nanoporous silicon. Solid State Commun. 126, 125–128 (2003a)
Xu, S.H., Xiong, Z.H., Gu, L.L., Liu, Y., Ding, X.M., Zi, J., Hou, X.Y.: Preparation of one-dimensional porous silicon photonic quantum-well structures. Appl. Phys. A 76, 589–592 (2003b)
Yang, L., Minnich, A.J.: Thermal transport in nanocrystalline Si and SiGe by ab initio based Monte Carlo simulation. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44254
Zayer, M.Q., Alwan, A.M., Dheyab, A.B.: Optimizing of gold nanoparticles on porous silicon morphologies for a sensitive carbon monoxide gas sensor device. Plasmonics 14(2), 501–509 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamoudi, W.K., Alwan, A.M. & Sulaiman, D. Controllable formation of plasmonic gold nanoparticles by pulsed laser–induced etching. Opt Quant Electron 52, 351 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02466-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02466-7