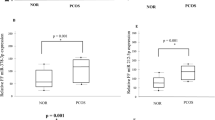
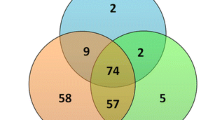
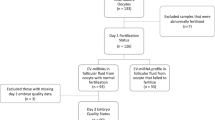
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, about 22 nucleotides, non-coding RNAs which regulate a wide range of gene expression during post-transcriptional stage. They are released into intra- and extracellular microenvironments and play vital roles in different physiological and pathological pathways. Due to easy accessibility, detection of extracellular miRNAs in body fluids, e.g. serum, plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and follicular fluid, has been explored in recent years. Since miRNAs are stable at unsuitable conditions, scientists have been investigating to use them as biomarkers in different fields of medicines. It goes without saying that experienced biomarkers would be required in reproductive medicine as well. Biomarkers can help clinicians and embryologists to diagnose disorders and assess the embryo quality via molecular pattern which is more reliable than nowadays routine methods. Follicular fluid as a noninvasive fluid in assisted reproductive techniques (ART) has attracted researchers as a rich pool for biomarkers, and miRNAs are not exception. Although miRNA biomarkers in reproduction field are located on their initial stage and there is a long path to move forward, several meticulous studies have been performed and discovered their associations with various conditions. In this regard, we summarize the reported miRNAs in follicular fluid and their correlations with female infertility and ART success rate, while subsequent investigations are required.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tesfaye D, Salilew-Wondim D, Gebremedhn S, Sohel MMH, Pandey HO, Hoelker M, et al. Potential role of microRNAs in mammalian female fertility. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2017;29(1):8–23.
da Silveira JC, de Andrade GM, Nogueira MFG, Meirelles FV, Perecin F. Involvement of miRNAs and cell-secreted vesicles in mammalian ovarian antral follicle development. Reprod Sci. 2015;22(12):1474–83.
Tesfaye D, Gebremedhn S, Salilew-Wondim D, Hailay T, Hoelker M, Grosse-Brinkhaus C, et al. MicroRNAs: tiny molecules with a significant role in mammalian follicular and oocyte development. Reproduction. 2018;155(3):R121–35.
Sohel MMH, Hoelker M, Noferesti SS, Salilew-Wondim D, Tholen E, Looft C, et al. Exosomal and non-exosomal transport of extra-cellular microRNAs in follicular fluid: implications for bovine oocyte developmental competence. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e78505.
Salilew-Wondim D, Gebremedhn S, Hoelker M, Tholen E, Hailay T, Tesfaye D. The role of microRNAs in mammalian fertility: from gametogenesis to embryo implantation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):585.
Kropp J, Salih SM, Khatib H. Expression of microRNAs in bovine and human pre-implantation embryo culture media. Front Genet. 2014;5:91.
Andronico F, Battaglia R, Ragusa M, Barbagallo D, Purrello M, di Pietro C. Extracellular vesicles in human oogenesis and implantation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2162.
Scalici E, Traver S, Mullet T, Molinari N, Ferrières A, Brunet C, et al. Circulating microRNAs in follicular fluid, powerful tools to explore in vitro fertilization process. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24976.
Martinez RM, Liang L, Racowsky C, Dioni L, Mansur A, Adir M, et al. Extracellular microRNAs profile in human follicular fluid and IVF outcomes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17036.
Machtinger R, Rodosthenous RS, Adir M, Mansour A, Racowsky C, Baccarelli AA, et al. Extracellular microRNAs in follicular fluid and their potential association with oocyte fertilization and embryo quality: an exploratory study. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017;34(4):525–33.
Imbar T, Eisenberg I. Regulatory role of microRNAs in ovarian function. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(6):1524–30.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843–54.
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol. 2018;9:402.
MacFarlane L-A. and P. R Murphy, MicroRNA: biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics. 2010;11(7):537–61.
Sohel MH. Extracellular/circulating microRNAs: release mechanisms, functions and challenges. Achiev Life Sci. 2016;10(2):175–86.
Gu W, Xu Y, Xie X, Wang T, Ko JH, Zhou T. The role of RNA structure at 5′ untranslated region in microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Rna. 2014;20(9):1369–75.
Ender C, Meister G. Argonaute proteins at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(11):1819–23.
Broughton JP, Lovci MT, Huang JL, Yeo GW, Pasquinelli AE. Pairing beyond the seed supports microRNA targeting specificity. Mol Cell. 2016;64(2):320–33.
Vasudevan S. Posttranscriptional upregulation by microRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012;3(3):311–30.
Li G, Wu X, Qian W, Cai H, Sun X, Zhang W, et al. CCAR1 5′ UTR as a natural miRancer of miR-1254 overrides tamoxifen resistance. Cell Res. 2016;26(6):655–73.
Geekiyanage H, Jicha GA, Nelson PT, Chan C. Blood serum miRNA: non-invasive biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Exp Neurol. 2012;235(2):491–6.
Shiino S, Matsuzaki J, Shimomura A, Kawauchi J, Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, et al. Serum miRNA–based prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(6):1817–27.
Caglar O, Cayir A. Total circulating cell-free miRNA in plasma as a predictive biomarker of the thyroid diseases. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):9016–22.
Mitchell AJ, Gray WD, Hayek SS, Ko YA, Thomas S, Rooney K, et al. Platelets confound the measurement of extracellular miRNA in archived plasma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32651.
Hicks SD, Johnson J, Carney MC, Bramley H, Olympia RP, Loeffert AC, et al. Overlapping microRNA expression in saliva and cerebrospinal fluid accurately identifies pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(1):64–72.
Rapado-González Ó, Majem B, Álvarez-Castro A, Díaz-Peña R, Abalo A, Suárez-Cabrera L, et al. A novel saliva-based miRNA signature for colorectal cancer diagnosis. J Clin Med. 2019;8(12):2029.
Pelloni M, Coltrinari G, Paoli D, Pallotti F, Lombardo F, Lenzi A, et al. Differential expression of miRNAs in the seminal plasma and serum of testicular cancer patients. Endocrine. 2017;57(3):518–27.
Radtke A, Dieckmann KP, Grobelny F, Salzbrunn A, Oing C, Schulze W, et al. Expression of miRNA-371a-3p in seminal plasma and ejaculate is associated with sperm concentration. Andrology. 2019;7(4):469–74.
Marí-Alexandre J, et al. Micro-RNA profile and proteins in peritoneal fluid from women with endometriosis: their relationship with sterility. Fertil Steril. 2018;109(4):675–684.e2.
Ohzawa, Hideyuki, et al. Exosomal microRNA profiles in peritoneal fluids as a therapeutic biomarker for peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. 2018;5393–5393
Royo F, Diwan I, Tackett M, Zuñiga P, Sanchez-Mosquera P, Loizaga-Iriarte A, et al. Comparative miRNA analysis of urine extracellular vesicles isolated through five different methods. Cancers. 2016;8(12):112.
Catapano F, Domingos J, Perry M, Ricotti V, Phillips L, Servais L, et al. Downregulation of miRNA-29,-23 and-21 in urine of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Epigenomics. 2018;10(7):875–89.
Müller M, Jäkel L, Bruinsma IB, Claassen JA, Kuiperij HB, Verbeek MM. MicroRNA-29a is a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease in cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(5):2894–9.
Akers JC, Hua W, Li H, Ramakrishnan V, Yang Z, Quan K, et al. A cerebrospinal fluid microRNA signature as biomarker for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):68769–79.
da Silveira JC, Veeramachaneni DN, Winger QA, Carnevale EM, Bouma GJ. Cell-secreted vesicles in equine ovarian follicular fluid contain miRNAs and proteins: a possible new form of cell communication within the ovarian follicle. Biol Reprod. 2012;86(3):71 1-10.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(30):10513–8.
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–9.
Van der Pol E, et al. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64(3):676–705.
Beyer C, Pisetsky DS. The role of microparticles in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(1):21–9.
Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Tréguer K, Boettger T, Horrevoets AJG, Zeiher AM, et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(3):249–56.
Turiák L, Misják P, Szabó TG, Aradi B, Pálóczi K, Ozohanics O, et al. Proteomic characterization of thymocyte-derived microvesicles and apoptotic bodies in BALB/c mice. J Proteome. 2011;74(10):2025–33.
Akao Y, Iio A, Itoh T, Noguchi S, Itoh Y, Ohtsuki Y, et al. Microvesicle-mediated RNA molecule delivery system using monocytes/macrophages. Mol Ther. 2011;19(2):395–9.
Jaiswal R, Gong J, Sambasivam S, Combes V, Mathys JM, Davey R, et al. Microparticle-associated nucleic acids mediate trait dominance in cancer. FASEB J. 2012;26(1):420–9.
Shantsila E, Kamphuisen P, Lip G. Circulating microparticles in cardiovascular disease: implications for atherogenesis and atherothrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(11):2358–68.
Aharon A, et al. Microparticles bearing tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in gestational vascular complications. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7(6):1047–50.
Lee Y, El Andaloussi S, Wood MJ. Exosomes and microvesicles: extracellular vesicles for genetic information transfer and gene therapy. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(R1):R125–34.
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteome. 2010;73(10):1907–20.
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Cantaluppi V, Biancone L. Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int. 2010;78(9):838–48.
Simpson RJ, Kalra H, Mathivanan S. ExoCarta as a resource for exosomal research. Journal of extracellular vesicles. 2012;1(1):18374.
Cheng L, Sharples RA, Scicluna BJ, Hill AF. Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(1):23743.
Buck AH, Coakley G, Simbari F, McSorley HJ, Quintana JF, le Bihan T, et al. Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5488.
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A, Burwinkel B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(16):7223–33.
Babin PJ, Gibbons GF. The evolution of plasma cholesterol: direct utility or a “spandrel” of hepatic lipid metabolism? Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48(2):73–91.
Niculescu LS, Simionescu N, Sanda GM, Carnuta MG, Stancu CS, Popescu AC, et al. MiR-486 and miR-92a identified in circulating HDL discriminate between stable and vulnerable coronary artery disease patients. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140958.
Tabet F, Vickers KC, Cuesta Torres LF, Wiese CB, Shoucri BM, Lambert G, et al. HDL-transferred microRNA-223 regulates ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3292.
Sørensen AE, Wissing ML, Englund ALM, Dalgaard LT. MicroRNA species in follicular fluid associating with polycystic ovary syndrome and related intermediary phenotypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(4):1579–89.
Hossain M, et al. Characterization and importance of microRNAs in mammalian gonadal functions. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;349(3):679–90.
Kenigsberg S, Wyse BA, Librach CL, da Silveira JC. Protocol for exosome Isolation from small volume of ovarian follicular fluid: Evaluation of ultracentrifugation and commercial kits. InExtracellular Vesicles 2017 (pp. 321-341). Humana Press, New York, NY.
Duy J, Koehler JW, Honko AN, Minogue TD. Optimized microRNA purification from TRIzol-treated plasma. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):95.
Tan GW, Khoo ASB, Tan LP. Evaluation of extraction kits and RT-qPCR systems adapted to high-throughput platform for circulating miRNAs. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9430.
Wright K, et al. Comparison of methods for miRNA isolation and quantification from ovine plasma. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1–11.
Mariani G, Bellver J. Proteomics and metabolomics studies and clinical outcomes. InReproductomics 2018 Jan 1 (pp. 147-170). Academic Press.
Sang Q, Yao Z, Wang H, Feng R, Wang H, Zhao X, et al. Identification of microRNAs in human follicular fluid: characterization of microRNAs that govern steroidogenesis in vitro and are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(7):3068–79.
Santonocito M, et al. Molecular characterization of exosomes and their microRNA cargo in human follicular fluid: bioinformatic analysis reveals that exosomal microRNAs control pathways involved in follicular maturation. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(6):1751–1761. e1.
Battaglia R, Vento ME, Borzì P, Ragusa M, Barbagallo D, Arena D, et al. Non-coding RNAs in the ovarian follicle. Front Genet. 2017;8:57.
Mencaglia L, Cerboneschi M, Ciociola F, Ricci S, Mancioppi I, Ambrosino V, et al. Characterization of microRNA in the follicular fluid of patients undergoing assisted reproductive technology. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2019;33(3):946–56.
Moreno JM, et al. Follicular fluid and mural granulosa cells microRNA profiles vary in in vitro fertilization patients depending on their age and oocyte maturation stage. Fertil Steril. 2015;104(4):1037–1046. e1.
Butler AE, Ramachandran V, Hayat S, Dargham SR, Cunningham TK, Benurwar M, et al. Expression of microRNA in follicular fluid in women with and without PCOS. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16306.
Feng R, Sang Q, Zhu Y, Fu W, Liu M, Xu Y, et al. MiRNA-320 in the human follicular fluid is associated with embryo quality in vivo and affects mouse embryonic development in vitro. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8689.
Mulner-Lorillon O, Chassé H, Morales J, Bellé R, Cormier P. MAPK/ERK activity is required for the successful progression of mitosis in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 2017;421(2):194–203.
Fu J, Qu RG, Zhang YJ, Gu RH, Li X, Sun YJ, et al. Screening of miRNAs in human follicular fluid reveals an inverse relationship between microRNA-663b expression and blastocyst formation. Reprod BioMed Online. 2018;37(1):25–32.
Zhang X-D, Zhang YH, Ling YH, Liu Y, Cao HG, Yin ZJ, et al. Characterization and differential expression of microRNAs in the ovaries of pregnant and non-pregnant goats (Capra hircus). BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):157.
Xia HF, Jin XH, Cao ZF, Hu Y, Ma X. Micro RNA expression and regulation in the uterus during embryo implantation in rat. FEBS J. 2014;281(7):1872–91.
Karakas SE. New biomarkers for diagnosis and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2017;471:248–53.
Broekmans F, Knauff EAH, Valkenburg O, Laven JS, Eijkemans MJ, Fauser BCJM. PCOS according to the Rotterdam consensus criteria: change in prevalence among WHO-II anovulation and association with metabolic factors. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;113(10):1210–7.
Xu T, Fang Y, Rong A, Wang J. Flexible combination of multiple diagnostic biomarkers to improve diagnostic accuracy. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2015;15(1):94.
Naji M, Nekoonam S, Aleyasin A, Arefian E, Mahdian R, Azizi E, et al. Expression of miR-15a, miR-145, and miR-182 in granulosa-lutein cells, follicular fluid, and serum of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018;297(1):221–31.
Long W, Zhao C, Ji C, Ding H, Cui Y, Guo X, et al. Characterization of serum microRNAs profile of PCOS and identification of novel non-invasive biomarkers. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(5):1304–15.
Chen B, Xu P, Wang J, Zhang C. The role of MiRNA in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Gene. 2019 Jul 20;706:91–6.
Shi Y, Zhao H, Shi Y, Cao Y, Yang D, Li Z, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight new risk loci for polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Genet. 2012;44(9):1020–5.
Roth LW, McCallie B, Alvero R, Schoolcraft WB, Minjarez D, Katz-Jaffe MG. Altered microRNA and gene expression in the follicular fluid of women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31(3):355–62.
Naji M, Aleyasin A, Nekoonam S, Arefian E, Mahdian R, Amidi F. Differential expression of miR-93 and miR-21 in granulosa cells and follicular fluid of polycystic ovary syndrome associating with different phenotypes. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14671.
Xue Y, Lv J, Xu P, Gu L, Cao J, Xu L, et al. Identification of microRNAs and genes associated with hyperandrogenism in the follicular fluid of women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(5):3913–21.
Cirillo F, Catellani C, Lazzeroni P, Sartori C, Nicoli A, Amarri S, et al. MiRNAs regulating insulin sensitivity are dysregulated in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) ovaries and are associated with markers of inflammation and insulin sensitivity. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:879.
Jirge PR. Poor ovarian reserve. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2016;9(2):63–9.
Luo H, Han Y, Liu J, Zhang Y. Identification of microRNAs in granulosa cells from patients with different levels of ovarian reserve function and the potential regulatory function of miR-23a in granulosa cell apoptosis. Gene. 2019;686:250–60.
Zhang K, Zhong W, Li WP, Chen ZJ, Zhang C. miR-15a-5p levels correlate with poor ovarian response in human follicular fluid. Reproduction. 2017;154(4):483–96.
Bjorkman S, Taylor HS. microRNAs in endometriosis: biological function and emerging biomarker candidates. Biol Reprod. 2019;100(5):1135–46.
Li X, Zhang W, Fu J, Xu Y, Gu R, Qu R, et al. MicroRNA-451 is downregulated in the follicular fluid of women with endometriosis and influences mouse and human embryonic potential. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2019;17(1):96.
Piotrowska H, Kempisty B, Sosinska P, Ciesiolka S, Bukowska D, Antosik P, Rybska M, Brussow KP, Nowicki M, Zabel M. The role of TGF superfamily gene expression in the regulation of folliculogenesis and oogenesis in mammals: a review. Veterinarni Medicina. 2013 Oct 1;58(10).
Raja-Khan N, Urbanek M, Rodgers RJ, Legro RS. The role of TGF-β in polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Sci. 2014;21(1):20–31.
Li Y, Xiang Y, Song Y, Wan L, Yu G, Tan L. Dysregulated miR-142, -33b and -423 in granulosa cells target TGFBR1 and SMAD7: a possible role in polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Hum Reprod. 2019;25(10):638–46.
Conti M, Hsieh M, Musa Zamah A, Oh JS. Novel signaling mechanisms in the ovary during oocyte maturation and ovulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;356(1-2):65–73.
Russell DL, Robker RL. Molecular mechanisms of ovulation: co-ordination through the cumulus complex. Hum Reprod Update. 2007;13(3):289–312.
Zhang M, Ouyang H, Xia G. The signal pathway of gonadotrophins-induced mammalian oocyte meiotic resumption. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009;15(7):399–409.
Guo Z, Yu Q. Role of mTOR signaling in female reproduction. Frontiers in endocrinology. 2019;10.
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Janic A, Herold MJ, Strasser A. How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(1):104–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qasemi, M., Amidi, F. Extracellular microRNA profiling in human follicular fluid: new biomarkers in female reproductive potential. J Assist Reprod Genet 37, 1769–1780 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01860-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01860-0