Abstract
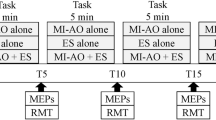
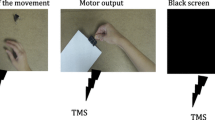
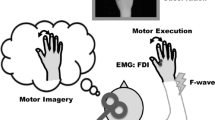
Action observation (AO) and motor imagery (MI) are potential methods to improve various motor functions. AO and MI facilitate corticospinal excitability. Additionally, the combination of AO and MI (AO + MI) facilitates greater corticospinal excitability than AO alone. However, it is unclear whether AO + MI facilitates the excitability of spinal motor neurons better than AO alone. Thus, in this study, we compared the excitability of spinal motor neurons between AO + MI and AO conditions using F-waves. We recruited healthy adult volunteers (n = 31) for F-wave analysis. We recorded F-waves during relaxation to determine the baseline level (Rest), followed by measurement during AO and AO + MI. To counterbalance the order effect, 15 participants performed AO first, while the others performed AO + MI first. F-wave persistence was significantly increased during AO and AO + MI compared to Rest. The F-wave/M-wave amplitude ratio was significantly increased during AO + MI compared to Rest. The present results suggest that the combination of AO and MI facilitates the excitability of spinal motor neurons compared to Rest, whereas AO alone does not.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abe M, Hanakawa T, Takayama Y, Kuroki C, Ogawa S, Fukuyama H (2007) Functional coupling of human prefrontal and premotor areas during cognitive manipulation. J Neurosci 27:3429–3438. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4273-06.2007
Baldissera F, Cavallari P, Craighero L, Fadiga L (2001) Modulation of spinal excitability during observation of hand actions in humans. Eur J Neurosci 13:190–194. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0953-816X.2000.01368.x
Berends HI, Wolkorte R, Ijzerman MJ, Van Putten MJAM (2013) Differential cortical activation during observation and observation-and-imagination. Exp Brain Res 229:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3571-8
Borra E, Belmalih A, Gerbella M, Rozzi S, Luppino G (2010) Projections of the hand field of the macaque ventral premotor area F5 to the brainstem and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 518:2570–2591. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.22353
Borroni P, Montagna M, Cerri G, Baldissera F (2005) Cyclic time course of motor excitability during the observation of a cyclic hand movement. Brain Res 1065:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.10.034
Buccino G, Binkofski F, Fink GR, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Gallese V, Seitz RJ, Zilles K, Rizzolatti G, Freund HJ (2001) Action observation activates premotor and parietal areas in a somatotopic manner: an fMRI study. Eur J Neurosci 13:400–404. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2001.01385.x
Bunno Y, Yurugi Y, Onigata C, Suzuki T, Iwatsuki H (2014) Influence of motor imagery of isometric opponens pollicis activity on the excitability of spinal motor neurons: a comparison using different muscle contraction strengths. J Phys Ther Sci 26:1069–1073. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.26.1069
Bunno Y, Onigata C, Suzuki T (2015) Excitability of spinal motor neurons during motor imagery of thenar muscle activity under maximal voluntary contractions of 50% and 100%. J Phys Ther Sci 27:2775–2778. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.2775
Bunno Y (2018) Does the duration of motor imagery affect the excitability of spinal anterior horn cells? Somatosens Mot Res 35:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/08990220.2018.1538963
Bunno Y (2019) Imagery strategy affects spinal motor neuron excitability: using kinesthetic and somatosensory imagery. NeuroReport 30:463–467. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000001218
Caspers S, Zilles K, Laird AR, Eickhoff SB (2010) ALE meta-analysis of action observation and imitation in the human brain. Neuroimage 50:1148–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.112
Cheng YW, Tzeng OJL, Hung D, Decety J, Hsieh JC (2005) Modulation of spinal excitability during observation of bipedal locomotion. NeuroReport 16:1711–1714. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wnr.0000183325.13618.5f
Clark S, Tremblay F, Ste-Marie D (2004) Differential modulation of corticospinal excitability during observation, mental imagery and imitation of hand actions. Neurophychologia 42:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(03)00144-1
Coleman ER, Moudgal R, Lang K, Hyacinth HI, Awosika OO, Kissela BM, Feng W (2017) Early rehabilitation after stroke: a narrative review. Curr Atheroscler Rep 19:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-017-0686-6
Davare M, Lemon R, Olivier E (2008) Selective modulation of interactions between ventral premotor cortex and primary motor cortex during precision grasping in humans. J Physiol 586:2735–2742. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.152603
De Luca CJ, LeFever RS, McCue MP, Xenakis AP (1982) Behavior of human motor units in different muscles during linearly varying contractions. J Physiol 329:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014293
Di Pellegrino G, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Gallese V, Rizzolatti G (1992) Understanding motor events: a neurophysiological study. Exp Brain Res 91:176–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230027
Drory VE, Neufeld MY, Korczyn AD (1993) F-wave characteristics following acute and chronic upper motor neuron lesions. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 33:441–446
Dum RP, Strick PL (2002) Motor areas in the frontal lobe of the primate. Physiol Behav 77:677–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9384(02)00929-0
Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Pavesi G, Rizzolatti G (1995) Motor facilitation during action observation: a magnetic stimulation study. J Neurophysiol 73:2608–2611. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1995.73.6.2608
Fierro B, Raimondo D, Modica A (1990) Analysis of F response in upper motoneurone lesions. Acta Neurol Scand 82:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb03311.x
Fisher MA (2002) H reflexes and F waves fundamentals, normal and abnormal patters. Neurol Clin 20:339–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-8619(01)00004-4
Fisher MA (2007) F-waves-physiology and clinical uses. Sci World J 7:144–160. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2007.49
Fogassi L, Ferrari PF, Gesierich B, Rozzi S, Chersi F, Rizzolatti G (2005) Parietal lobe: from action organization to intention understanding. Science 308:662–667. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1106138
Foltys H, Krings T, Meister IG, Sparing R, Boroojerdi B, Thron A, Töpper R (2003) Motor representation in patients rapidly recovering after stroke: a functional magnetic resonance imaging and transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Clin Neurophysiol 114:2404–2415. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2457(03)00263-3
Fourkas AD, Ionta S, Aglioti SM (2006) Influence of imagined posture and imagery modality on corticospinal excitability. Behav Brain Res 168:190–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2005.10.015
Gallese V, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, Rizzolatti G (1996) Action recognition in the premotor cortex. Brain 119:593–609. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/119.2.593
Guillot A, Di Rienzo F, Maclntyre T, Moran A, Collet C (2012) Imagining is not doing but involves specific motor commands: a review of experimental data related to motor inhibition. Front Hum Neurosci 6:247. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00247
Han CE, Arbib MA, Schweighofer N (2008) Stroke rehabilitation reaches a threshold. PLoS Comput Biol 4:e1000133. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000133
Hanakawa T, Dimyan MA, Hallett M (2008) Motor planning, imagery, and execution in the distributed motor network: a time-course study with functional MRI. Cereb Cortex 18:2775–2788. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhn036
Hara M, Kimura J, Walker DD, Taniguchi S, Ichikawa H, Fujisawa R, Shimizu H, Abe T, Yamada T, Kayamori R, Mizutani T (2010) Effect of motor imagery and voluntary muscle contraction of the F-wave. Muscle Nerve 42:208–212. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.21667
Hardwick RM, Caspers S, Eickhoff SB, Swinnen SP (2018) Neural correlates of action: comparing meta-analyses of imagery, observation, and execution. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 94:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.08.003
Hashimoto R, Rothwell JC (1999) Dynamic changes in corticospinal excitability during motor imagery. Exp Brain Res 125:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050660
Heffner RS, Masterton RB (1983) The role of the corticospinal tract in the evolution of human digital dexterity. Brain Behav Evol 23:165–183. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121494
Henneman E, Somjen G, Carpenter DO (1965) Functional significance of cell size in spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 28:560–580. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.560
Horn SD, DeJong G, Smout RJ, Gassaway J, James R, Conroy B (2005) Stroke rehabilitation patients, practice, and outcomes: is earlier and more aggressive therapy better? Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:S101–S114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2005.09.016
Kasai T, Kawai S, Kawanishi M, Yahagi S (1997) Evidence for facilitation of motor evoked potentials (MEPs) induced by motor imagery. Brain Res 744:147–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(96)01101-8
Kimura J (1974) F-wave velocity in the central segment of the median and ulnar nerves. A study in normal subjects and in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neurology 24:539–546. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.24.6.539
Kreisei SH, Hennerici MG, Bäzner H (2007) Pathophysiology of stroke rehabilitation: the natural course of clinical recovery, use-dependent plasticity and rehabilitative outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis 23:243–255. https://doi.org/10.1159/000098323
Leisman G, Braun-Benjamin O, Melillo R (2014) Cognitive-motor interactions of the basal ganglia in development. Front Syst Neurosci 8:16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2014.00016
Lemon RN, Griffiths J (2005) Comparing the function of the corticospinal system in different species: organization differences for motor specialization? Muscle Nerve 32:261–279. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.20333
Liepert J, Bauder H, Miltner WHR, Taub E, Weiller C (2000) Treatment-induced cortical reorganization after stroke in humans. Stroke 31:1210–1216. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.31.6.1210
Lorey B, Pilgramm S, Bischoff M, Stark R, Vaitl D, Kindermann S, Munzert J, Zentgraf K (2011) Activation of the parieto-premotor network is associated with vivid motor imagery -a parametric fMRI study. PLoS ONE 6:e20368. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020368
Lu MT, Preston JB, Strick PL (1994) Interconnections between the prefrontal cortex and the premotor areas in the frontal lobe. J Comp Neurol 341:375–392. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903410308
Maier MA, Armand J, Kirkwood PA, Yang HW, Davis JN, Lemon RN (2002) Differences in the corticospinal projection from primary motor cortex and supplementary motor area to macaque upper limb motoneurons: an anatomical and electrophysiological study. Cereb Cortex 12:281–296. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/12.3.281
Mercuri B, Wassermann EM, Manganotti P, Ikoma K, Samii A, Hallett M (1996) Cortical modulation of spinal excitability: an F-wave study. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Electromyogr Mot Control 101:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(95)00164-6
Mesrati F, Vecchierini MF (2004) F-waves: neurophysiology and clinical value. Neurophysiol Clin 34:217–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2004.09.005
Milner-Brown HS, Stein RB, Yemm R (1973a) The contractile properties of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol 228:285–306. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010087
Milner-Brown HS, Stein RB, Yemm R (1973b) The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol 230:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192
Montagna M, Cerri G, Borroni P, Baldissera F (2005) Excitability changes in human corticospinal projections to muscles moving hand and fingers while viewing a reaching and grasping action. Eur J Neurosci 22:1513–1520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04336.x
Mouthon A, Ruffieux J, Wälchli M, Keller M, Taube W (2015) Task-dependent changes of corticospinal excitability during observation and motor imagery of balance tasks. Neuroscience 303:535–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.031
Nakayama H, Jørgensen HS, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS (1994) Recovery of upper extremity function in stroke patients: the Copenhagen stroke study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 75:394–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9993(94)90161-9
Nedelko V, Hassa T, Hamzei F, Schoenfeld MA, Dettmers C (2012) Action imagery combined with action observation activates more corticomotor regions than action observation alone. J Neurol Phys Ther 36:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1097/NPT.0b013e318272cad1
Nojima I, Koganemaru S, Kawamata T, Fukuyama H, Mima T (2015) Action observation with kinesthetic illusion can produce human motor plasticity. Eur J Neurosci 41:1614–1623. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12921
Oishi K, Kimura M, Yasukawa M, Yoneda T, Maeshima T (1994) Amplitude reduction of H-reflex during mental movement simulation in elite athletes. Behav Brain Res 62:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(94)90037-X
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4
Patten JP (1996) The extrapyramidal system and the cerebellum. In: Patten JP (ed) Neurological differential diagnosis, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 178–212
Peioglou-Harmoussi S, Fawcett PRW, Howel D, Barwick DD (1985) F-responses: a study of frequency, shape and amplitude characteristics in healthy control subjects. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:1159–1164. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.48.11.1159
Rizzolatti G, Fadiga L, Gallese V, Fogassi L (1996) Premotor cortex and the recognition of motor actions. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 3:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-6410(95)00038-0
Rizzolatti G, Fogassi L, Gallese V (2001) Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying the understanding and imitation of action. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:661–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/35090060
Sakamoto M, Muraoka T, Mizuguchi N, Kanosue K (2009) Combining observation and imagery of an action enhances human corticospinal excitability. Neurosci Res 65:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2009.05.003
Skoff HD (1998) The role of the abductor pollicis brevis in opposition. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 27:369–370
Stinear CM, Byblow WD (2004) Modulation of corticospinal excitability and intracortical inhibition during motor imagery is task-dependent. Exp Brain Res 157:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-1851-z
Stinear CM, Fleming MK, Byblow WD (2006) Lateralization of unimanual and bimanual motor imagery. Brain Res 1095:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.04.008
Strafella AP, Paus T (2000) Modulation of cortical excitability during action observation: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. NeuroReport 11:2289–2292. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200007140-00044
Suzuki T, Bunno Y, Onigata C, Tani M, Uragami S (2013) Excitability of spinal neural function during several motor imagery tasks involving isometric opponens pollicis activity. Neurorehabilitation 33:171–176. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-130942
Taniguchi S, Kimura J, Yamada T, Ichikawa H, Hara M, Fujisawa R, Shimizu H, Tani T (2008) Effect of motion imagery to counter rest-induced suppression of F-wave as a measure of anterior horn cell excitability. Clin Neurophysiol 119:1346–1352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2007.11.179
Taube W, Mouthon M, Leukel C, Hoogewoul HM, Annoni JM, Keller M (2015) Brain activity during observation and motor imagery of different balance task: an fMRI study. Cortex 64:102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.09.022
Triggs WJ, Calvanio R, Levine M (1997) Transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals a hemispheric asymmetry correlate intermanual differences in motor performance. Neurophychologia 35:1355–1363. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(97)00077-8
Villiger M, Estévez N, Hepp-Reymond MC, Kiper D, Kollias SS, Eng K, Hotz-Boendermaker S (2013) Enhanced activation of motor execution networks using action observation combined with imagination of lower limb movements. PLoS ONE 8:e72403. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072403
Vogt S, Di Rienzo F, Collet C, Collins A, Guillot A (2013) Multiple roles of motor imagery during action observation. Front Hum Neurosci 7:807. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00807
Williams J, Pearce AJ, Loporto M, Morris T, Holmes PS (2012) The relationship between corticospinal excitability during motor imagery and motor imagery ability. Behav Brain Res 226:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.09.014
Wright DJ, Williams J, Holmes PS (2014) Combined action observation and imagery facilitates corticospinal excitability. Front Hum Neurosci 8:951. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00951
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YB: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, visualization, writing-original draft. TS: validation, writing-review and editing, supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Kansai University of Health Sciences (approval number: 16-42).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in this study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Winston D. Byblow.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunno, Y., Suzuki, T. Motor imagery while viewing self-finger movements facilitates the excitability of spinal motor neurons. Exp Brain Res 238, 2077–2086 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05870-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05870-3