Abstract
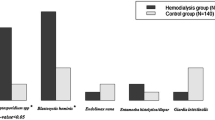
Intestinal parasitic infections (IPIs) can be a severe threat to immunocompromised patients. This is particularly true for those undergoing chemotherapy and hemodialysis. The present research is aimed at identifying intestinal parasites that might be present in immunocompromised patients. In this cross-sectional study 1040 stool samples were collected from March to September 2017. Six hundred and forty-one stool samples from immunocompromised patients (279 samples from hemodialysis patients and 362 samples from chemotherapy patients) and 399 samples from the control group were collected in Guilan province, Iran. The samples were tested by direct, formalin-ether methods for protozoa and ova of intestinal parasites and Ziehl-Neelsen staining methods for coccidian parasites such as Cryptosporidium species. The overall parasitic infection rate was highest (15%) in hemodialysis patients and 11.3% in chemotherapy patients, whereas the lowest rate was observed (7.3%) in the control group. The infectivity rates were statistically significant (P = 0.008) when compared with the control group. The parasites found were Blastocystis hominis (8.9% of the cases), Entamoeba coli (1.6%), Iodamoeba butschlii (0.8%), Endolimax nana (0.6%), Chilomastix mesnili (0.5%), Strongyloides stercoralis (0.5%), and Taenia species (0.15%), whereas Giardia lamblia was detected only in the control group. There was not a correlation between prevalence of parasites with age or education levels of the infected individuals. Results of the present study suggest that periodic stool examinations in special parasitological laboratories should be included as part of routine and general medical care.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hameed DM, Hassanin OM (2011) Proteaese activity of Blastocystis hominis subtype 3 in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Parasitol Res 109(2):321–327
Al-Megrin W (2010) Intestinal parasites infection among immunocompromised patients in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Pakistan J Biol Sci 13:390–394
Al-Qobati SA, Al-Maktari MT, Derhim M (2012) Intestinal parasitosis among Yemeni patients with cancer, Sana’a, Yemen. J Egyptian Soc Parasitol 240:1–8
Alter M J, Arduino MJ, Lyerla H C, Miller E R, Tokars JI (2001) Recommendations for preventing transmission of infections among chronic hemodialysis patients. MMWR Recommend Rep 50 (RR-5):1–43; quiz CE1
Ashrafi K, Tahbaz A, Rahmati B (2010) Strongyloides stercoralis: the most prevalent parasitic cause of eosinophilia in Guilan Province, northern Iran. Iranian J Parasitol 5:40
Azizian M, Basati G, Abangah G, Mahmoudi MR, Mirzaei A (2016) Contribution of Blastocystis hominis subtypes and associated inflammatory factors in development of irritable bowel syndrome. Parasitol Res 115:2003–2009
Baiomy AMS, Mohamed KAAH, Ghannam MAM, Al-Razek SA (2010) Opportunistic parasitic infections among immunocom-promised patients. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 40:797–807
Barazesh A, Fouladvand M, Tahmasebi R, Heydari A, Fallahi J (2015) The prevalence of intestinal parasites in hemodialysis patients in Bushehr, Iran. Hemodial Internat 19:447–451
Bloom BR, Murray CJ (1992) Tuberculosis: commentary on a reemergent killer. Sci 257:1055–1064
Bora I, Dutta V, Lyngdoh WV, Khyriem AB, Durairaj E, Phukan AC (2016) Study of intestinal parasites among the immunosuppressed patients attending a tertiary-care center in Northeast India. Int J Med Sci Pub Health 5:924–929
Botero JH, CastañoA MMN, OcampoNE HMI, Lopera MM (2003) A preliminary study of the prevalence of intestinal parasites in immunocompromised patients with and without gastrointestinal manifestations. Rev Instituto Med Trop S Paulo 45:197–200
Cancer Research UK (2019) Can parasites cause cancer? Retrieved from https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/causes-of-cancer/infections-eg-hpv-and-cancer/can-parasites-cause-cancer
Chandramathi S, Suresh K, Anita ZB, Kuppusamy UR (2012) Infections of Blastocystis hominis and microsporidia in cancer patients: are they opportunistic? TRSTMH 106:267–269
Chieffi PP, Sens YA, Paschoalotti MA, Miorin LA, Silva HGC, Jabur P (1998) Infection by Cryptosporidium parvum in renal patients submitted to renal transplant or hemodialysis. Rev Soc Brasil Med Trop 31:333–337
Choy SH, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Mahdy MA, Nasr NN, Sulaiman M, Lim YA, Surin J (2014) Prevalence and associated risk factors of Giardia infection among indigenous communities in rural Malaysia. Sci Rep 4:6909
Daryani A, Sharif M, Nasrolahei M, Khalilian A, Mohammadi A, Barzegar G (2012) Epidemiological survey of the prevalence of intestinal parasites among schoolchildren in Sari, northern Iran. TRSTMH 106:455–459
De Martel C, Georges D, Bray F, Ferlay J, Clifford GM (2020) Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: a worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet GlobHealth 8:e180–e190
Ferreira MS, Borges AS (2002) Some aspects of protozoan infections in immunocompromised patients: a review. Mem Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 97:443–457
Garcia LS (2007) Diagnostic Medical Parasitology, 5th edn. Asm Press, Washington DC, pp 850–858
Garcia LS, Bruckner DA, Brewer TC, Shimizu RY (1983) Techniques for the recovery and identification of Cryptosporidium oocysts from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 18:185–190
Iguchi A, Yoshikawa H, Yamada M, Kimata I, Arizono N (2009) Expression of interferon gamma and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the cecal mucosa of rats experimentally infected with Blastocystis sp. strain RN94-9. Parasitol Res 105:135
Karadag G, Tamer GS, Dervisoglu E (2013) Investigation of intestinal parasites in dialysis patients. Saudi Med J 34:714–718
Kazemi E, Tavalla M, Maraghi S, Sharafkhani R (2014) Frequency of intestinal parasites among immunosuppressed patients undergoing chemotherapy in Khuzestan province, southwest Iran. Int J Anal Pharmac Biomed Sci 3(4):42–46
Kia EB, Hosseini M, Nilforoushan MR, Meamar AR, Rezaeian M (2008) Study of intestinal protozoan parasites in rural inhabitants of Mazandaran province. Northern Iran Iran J Parasitol 12:21–25
Koivusalo R, Hietanen S (2004) The cytotoxicity of chemotherapy drugs varies in cervical cancer cells depending on the p53 status. Cancer Biol Ther 3:1177–1183
Kulik RA, Falavigna DLM, NishiL Araujo SM (2008) Blastocystis sp. and other intestinal parasites in hemodialysis patients. Brazil. J Inf Dis 12:338–341
Mahmoudi M, Ashrafi K, Abedinzadeh H, Tahvildar-Bideruni F, Haghighi A, Bandehpour M, Taghipour Lailabadi N, Kazemi B (2011) Development of sensitive detection of Cryptosporidium and Giardia from surface water in Iran. Iran J Parasitol 6:43–51
Mahmoudi MR, Kazemi B, Mohammadiha A, Mirzaei A, Karanis P (2013) Detection of Cryptosporidium and Giardia (oo)cysts by IFA, PCR and LAMP in surface water from Rasht, Iran. TRSTMH 107:511–517
Mahmoudi MR, Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E, Kazemi B, Haghighi A, MirzaeiA MA, Karanis P (2015a) Cryptosporidium genotypes and subtypes distribution in river water in Iran. J Wat Health 13:600–606
Mahmoudi MR, Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E, Karanis P (2015b) Genotyping of Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba spp from river waters in Iran. Parasitol Res 114:4565–4570
Mahmoudi MR, Ongerth JE, Karanis P (2017) Cryptosporidium and cryptosporidiosis: the Asian perspective. Int J Hyg Environ Health 220:1098–1109
Monsef AR, Hashemi SH, Abbasi M, Taherkhani H, Shalchi Z, Eliasi A (2008) Frequency of intestinal parasites in patients with malignancy, admitted in oncology ward of Sina Hospital, Hamadan, Iran. J Gorgan Univ Med Sci 9:51–55
Motta MEFA, Silva GAP (2002) Parasites induced diarrheas. Rev Bras Saúde Matern Infant 2:117–127
Naeini AE, Sharifi M, Shahidi S, Taheri S, Seirafian S, Taheri D, Harandi AA (2012) Intestinal fungal and parasitic infections in kidney transplant recipients: a multi-center study. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 23:677
Omrani VF, Fallahi S, Rostami A, Siyadatpanah A, Barzgarpour G, Mehravar S, Joneidi Z (2015) Prevalence of intestinal parasite infections and associated clinical symptoms among patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis. Infect 43:537–544
Rao K, Sekar U, Iraivan KT, Abraham G, Soundararajan P (2003) Blastocystis hominis—an emerging cause of diarrhoea in renal transplant recipients. J Assoc Physicians India 51:719–721
Rasti S, Hassanzadeh M, Hooshyar H, Momen-Heravi M, Mousavi SGA, Abdoli A (2017) Intestinal parasitic infections in different groups of immunocompromised patients in Kashan and Qom cities, central Iran. Scand J Gastroenterol 52:738–741
Samaras V, Petros I, Rafailidis PI, Mourtzoukou EG, Peppas G, Falagas ME (2010) Chronic bacterial and parasitic infections and cancer: a review. J Infect Dev Ctries 4:267–281
Sayyari AA, Imanzadeh F, Bagheri Yazdi SA, Karami H, Yaghoobi M (2005) Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in the Islamic Republic of Iran. Int J Inf Control 4:e15593
Seyrafian S, Pestehchian N, Kerdegari M, Yousefi HA, Bastani B (2006) Prevalence rate of Cryptosporidium infection in hemodialysis patients in Iran. Hemodial Int 10:375–379
Sharifdini M, Keyhani A, Eshraghian MR, Kia EB (2018) Molecular diagnosis of strongyloidiasis in a population of an endemic area through nested-PCR. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 11:68
Solomayer EF, Feuerer M, Bai L, Umansky V, Beckhove P, Meyberg GC, Diel IJ (2003) Influence of adjuvant hormone therapy and chemotherapy on the immune system analysed in the bone marrow of patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:174–180
Stensvold CR, Suresh GK, Tan KS, Thompson RA, Traub RJ, Viscogliosi E, Clark CG (2007) Terminology for Blastocystis subtypes–a consensus. Trends Parasitol 23:93–96
Togeh GR, Keihani M, Athari A, Sadafi H (2000) Parasitic infestation in cancer patients chemotherapy. Tehran University MedJ TUMS Pub 58:52–58
Turkcapar N, Kutlay S, Nergizoglu G, Atli T, Duman N (2002) Prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection in hemodialysis patients. Nephron 90:344–346
World Health Organisation (2020). Cancer retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
Zabolinejad N, Berenji F, Eshkaftaki EB, Badeii Z, Banihashem A, Afzalaqaei M (2013) Intestinal parasites in children with lymphohematopoietic malignancy in Iran, Mashhad. Jundishapur J Microbiol 6:e7765
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to Vice Chancellor for Research and Technology in Guilan University of Medical Sciences. Also, we are very grateful to the respected staff of the laboratory, hemodialysis, and oncology departments of Razi hospital of Rasht, Guilan Oncology Center, Kianmehr Hemodialysis Center, and all of those who helped us in conducting and performing this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Una Ryan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, M.R., Hasani, H., Tsiami, A. et al. Intestinal protozoan and helminthic infections among hemodialysis and cancer patients. Parasitol Res 119, 3053–3059 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06774-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06774-5