Abstract
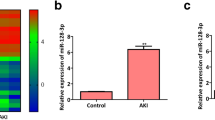
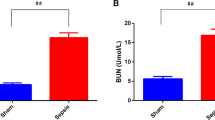
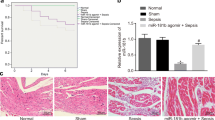
Pediatric sepsis has become the leading cause of death in pediatric intensive care units (PICU). The regulation of target genes may be the key to the treatment of pediatric sepsis. The expression of miR-210 in rat serum was detected by RT-qPCR. The serum BUN, Scr, and CysC were detected by an automatic biochemical analyzer. The expression of inflammatory factors was detected by ELISA. The apoptosis level of the cells was detected by TUNEL staining. The expression of apoptotic proteins Bcl2, Bax, Cleaved caspase3, caspase3, and JAK/STAT3 pathway-related proteins were detected by western blot. The expression of miR-210 was abnormally elevated in sepsis pups. Interfering with the expression of miR-210 in rats could reduce the degree of renal injury and inhibit the inflammatory response in sepsis pups. In addition, interference with miR-210 could inhibit the apoptosis level of renal tissue cells, and the expression of apoptosis-related proteins was also significantly decreased. During this process, we found that after interfering with the expression of miR-210, the expression of the JAK/STAT pathway was inhibited. Then, pathway agonist SC-39100 can reverse the inhibitory effects of interfering with miR-210 on renal tissue damage, inflammatory response, and apoptosis. Interference with miR-210 alleviated renal injury in septic rats by inhibiting JAK-STAT pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rittirsch, D., M.S. Huber-Lang, M.A. Flierl, and P.A. Ward. 2009. Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Nature Protocols 4 (1): 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.214.
Jawad, I., I. Luksic, and S.B. Rafnsson. 2012. Assessing available information on the burden of sepsis: global estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality. Journal of Global Health 2 (1): 010404. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.02.010404.
Marx, G., and SepNet Critical Care Trials G. 2018. Correction to: Incidence of severe sepsis and septic shock in German intensive care units: the prospective, multicentre INSEP study. Intensive Care Medicine 44 (1): 153–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4980-0.
Prusakowski, M.K., and A.P. Chen. 2017. Pediatric Sepsis. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America 35 (1): 123–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emc.2016.08.008.
Hunt, A. 2019. Sepsis: an overview of the signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. Emergency Nurse 27 (5): 32–41. https://doi.org/10.7748/en.2019.e1926.
Huang, M., S. Cai, and J. Su. 2019. The pathogenesis of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20 (21): 5376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215376.
Venet, F., and G. Monneret. 2018. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nature Reviews. Nephrology 14 (2): 121–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.165.
Wu, R., J. Zeng, J. Yuan, X. Deng, Y. Huang, L. Chen, et al. 2018. MicroRNA-210 overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 128 (6): 2551–2568. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI97426.
Xie, W., W. Su, H. Xia, Z. Wang, C. Su, and B. Su. 2019. Synovial fluid microRNA-210 as a potential biomarker for early prediction of osteoarthritis. BioMed Research International 2019: 7165406. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7165406.
Lin, Y., Y. Ding, S. Song, M. Li, T. Wang, and F. Guo. 2019. Expression patterns and prognostic value of miR-210, miR-494, and miR-205 in middle-aged and old patients with sepsis-induced acute renal injury. Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 19 (3): 249–256. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4131.
Yue, J.N., W.M. Li, W.Z. Hong, J. Yang, T. Zhu, Y. Fang, et al. 2019. MiR-210 inhibits apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells via JAK-STAT in arteriosclerosis obliterans. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 23 (3 Suppl): 319–326. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201908_18663.
Cai, B., J.P. Cai, Y.L. Luo, C. Chen, and S. Zhang. 2015. The specific roles of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in sepsis. Inflammation. 38 (4): 1599–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0135-z.
Keir, I., and J.A. Kellum. 2015. Acute kidney injury in severe sepsis: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations. Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care (San Antonio, Tex.) 25 (2): 200–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/vec.12297.
Chen, Y., J. Qiu, B. Chen, Y. Lin, Y. Chen, G. Xie, J. Qiu, H. Tong, and D. Jiang. 2018. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 plays an important role in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by targeting miR-204 and modulating the NF-kappaB pathway. International Immunopharmacology 59: 252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.023.
An, R., J. Feng, C. Xi, J. Xu, and L. Sun. 2018. miR-146a Attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by suppressing IRAK1 and TRAF6 via targeting ErbB4 expression. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2018: 7163057. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7163057.
Qiao, X.R., L. Wang, M. Liu, Y. Tian, and T. Chen. 2020. MiR-210-3p attenuates lipid accumulation and inflammation in atherosclerosis by repressing IGF2. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 84 (2): 321–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2019.1685370.
Chang, X., L.F. Hu, X.J. Ma, J. Yin, X.Y. Liu, and J.B. Li. 2019. Influence of roflumilast on sepsis mice through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 23 (3): 1335–1341. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201902_17028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the People’s Hospital of Longhua, Shenzhen. All animal experiments comply with the ethical requirements of the animal council.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Guo, Z., Lai, S. et al. Interference with miR-210 Alleviated Renal Injury in Septic Rats by Inhibiting JAK-STAT Pathway. Inflammation 43, 2156–2165 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01283-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01283-0