Abstract
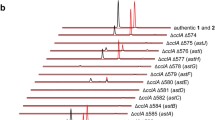
FR901533 (1, also known as WS79089B), WS79089A (2), and WS79089C (3) are polycyclic aromatic natural products with promising inhibitory activity to endothelin-converting enzymes. In this work, we isolated five tridecaketide products from Streptosporangium roseum No. 79089, including 1–3, benaphthamycin (4) and a novel FR901533 analogue (5). The structure of 5 was characterized based on spectroscopic data. Compared with the major product 2, the new compound 5 has an additional hydroxyl group at C-12 and an extra methyl group at the 13-OH. The configuration of C-19 of these compounds was determined to be R using Mosher’s method. A putative biosynthetic gene cluster for compounds 1–5 was discovered by analyzing the genome of S. roseum No. 79089. This 38.6-kb gene cluster contains 38 open reading frames, including a minimal polyketide synthase (wsaA-C), an aromatase (wsaD), three cyclases (wsaE, F, and W), and a series of tailoring enzymes such as monooxygenases (wsaO1-O7) and methyltransferases (wsaM1 and M2). Disruption of the ketosynthase gene (wsaA) in this gene cluster abolished the production of 1–5, confirming that this gene cluster is indeed responsible for the biosynthesis of 1–5. A type II polyketide biosynthetic pathway was proposed for this group of natural endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
Key points
• Five aromatic tridecaketides were isolated from Streptosporangium roseum No. 79089.
• A novel FR901533 analogue, 12-hydroxy-13-O-methyl-WS79089A, was characterized.
• The absolute configuration of C-19 of FR901533 and analogues was determined.
• The biosynthetic gene cluster of FR901533 and analogues was discovered.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnato A, Spinella F, Rosano L (2008) The endothelin axis in cancer: the promise and the challenges of molecularly targeted therapy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 86(8):473–484. https://doi.org/10.1139/Y08-058
Bierman M, Logan R, O'Brien K, Seno ET, Nagaraja Rao R, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(92)90627-2
Cheng Y, Li W, Dou X, Jia R, Yang H, Liu X, Xu C, Liu J, Cao Y, Luo G (2018) Role of endothelin-1 and its receptors in cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol Med Rep 18(6):5229–5236. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9513
Coelho SC, Berillo O, Caillon A, Ouerd S, Fraulob-Aquino JC, Barhoumi T, Offermanns S, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL (2018) Three-month endothelial human endothelin-1 overexpression causes blood pressure elevation and vascular and kidney injury. Hypertension 71(1):208–216. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.09925
Davenport AP, Hyndman KA, Dhaun N, Southan C, Kohan DE, Pollock JS, Pollock DM, Webb DJ, Maguire JJ (2016) Endothelin. Pharmacol Rev 68(2):357–418. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.115.011833
De Lombaert S, Blanchard L, Stamford LB, Tan J, Wallace EM, Satoh Y, Fitt J, Hoyer D, Simonsbergen D, Moliterni J, Marcopoulos N, Savage P, Chou M, Trapani AJ, Jeng AY (2000) Potent and selective non-peptidic inhibitors of endothelin-converting enzyme-1 with sustained duration of action. J Med Chem 43(3):488–504. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm990507o
Dhaun N, Webb DJ (2019) Endothelins in cardiovascular biology and therapeutics. Nat Rev Cardiol 16(8):491–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-019-0176-3
Doggrell SA (2004) Endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitors and their potential for cardiovascular and renal therapeutics. Expert Opin Ther Pat 14(5):655–665. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543776.14.5.655
Emoto N, Yanagisawa M (1995) Endothelin-converting enzyme-2 is a membrane-bound, phosphoramidon-sensitive metalloprotease with acidic pH optimum. J Biol Chem 270(25):15262–15268. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.25.15262
Fidan O, Yan R, Zhu D, Zhan J (2019) Improved production of antifungal angucycline Sch47554 by manipulating three regulatory genes in Streptomyces sp. SCC-2136. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 66(4):517–526. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1748
Hitzerd E, Neuman RI, Broekhuizen M, Simons SHP, Schoenmakers S, Reiss IKM, Koch BCP, van den Meiracker AH, Versmissen J, Visser W, Danser AHJ (2020) Transfer and vascular effect of endothelin receptor antagonists in the human placenta. Hypertension 75(3):877–884. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.119.14183
Ishikawa J, Hotta K (1999) FramePlot: a new implementation of the frame analysis for predicting protein-coding regions in bacterial DNA with a high G+C content. FEMS Microbiol Lett 174(2):251–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13576.x
Jaeger RJR, Spiteller P (2010) Mycenaaurin a, an antibacterial polyene pigment from the fruiting bodies of Mycena aurantiomarginata. J Nat Prod 73(8):1350–1354. https://doi.org/10.1021/np100155z
Jiang D, Xin K, Yang B, Chen Y, Zhang Q, He H, Gao S (2020) Total synthesis of three families of natural antibiotics: anthrabenzoxocinones, fasamycins/naphthacemycins, and benastatins. CCS Chem 2:800–812. https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.020.202000151
Johnson GD, Stevenson T, Ahn K (1999) Hydrolysis of peptide hormones by endothelin-converting enzyme-1. A comparison with neprilysin. J Biol Chem 274(7):4053–4058. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.7.4053
Kaburagi S, Hasegawa K, Morimoto T, Araki M, Sawamura T, Masaki T, Sasayama S (1999) The role of endothelin-converting enzyme-1 in the development of α1-adrenergic-stimulated hypertrophy in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Circulation 99(2):292–298. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.99.2.292
Kotha S, Cheekatla SR, Fatma A (2019) Synthetic approach to the ABCD ring system of anticancer agent fredericamycin A via Claisen rearrangement and ring-closing metathesis as key steps. ACS Omega 4(17):17109–17116. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b01178
Liu M, Jia Y, Xie Y, Zhang C, Ma J, Sun C, Ju J (2019) Identification of the actinomycin D biosynthetic pathway from marine-derived Streptomyces costaricanus SCSIO ZS0073. Mar Drugs 17(4):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040240
Löffler BM (2000) Endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitors: current status and perspectives. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 35(4 Suppl 2):S79–S82. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-200000002-00018
Lu F, Hou Y, Zhang H, Chu Y, Xia H, Tian Y (2017) Regulatory genes and their roles for improvement of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. 3 Biotech 7(4):250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0875-6
Maglangit F, Fang Q, Leman V, Soldatou S, Ebel R, Kyeremeh K, Deng H (2019) Accramycin A, a new aromatic polyketide, from the soil bacterium, Streptomyces sp. MA37. Molecules 24(18):3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183384
Martin P, Tzanidis A, Stein-Oakley A, Krum H (2000) Effect of a highly selective endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitor on cardiac remodeling in rats after myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 36(5, Suppl. 1):S367–S370. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-200036051-00106
Martínez-Miguel P, Raoch V, Zaragoza C, Valdivielso JM, Rodríguez-Puyol M, Rodríguez-Puyol D, López-Ongil S (2009) Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 increases in atherosclerotic mice: potential role of oxidized low density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res 50(3):364–375. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M800215-JLR200
Martínez-Miguel P, Valdivielso JM, Medrano-Andrés D, Román-García P, Cano-Peñalver JL, Rodríguez-Puyol M, Rodríguez-Puyol D, López-Ongil S (2014) The active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, induces a complex dual upregulation of endothelin and nitric oxide in cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 307(12):E1085–E1096. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00156.2014
Miyagawa K, Emoto N (2014) Current state of endothelin receptor antagonism in hypertension and pulmonary hypertension. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 8(5):202–216. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753944714541511
Nakagawa Y, Doi T, Taketani T, Takegoshi K, Igarashi Y, Ito Y (2013) Mannose-binding geometry of pradimicin a. Chem Eur J 19(32):10516–10525. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201301368
Napan K, Zhang S, Morgan W, Anderson T, Takemoto JY, Zhan J (2014) Synergistic actions of tailoring enzymes in pradimicin biosynthesis. ChemBioChem 15(15):2289–2296. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201402306
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2020) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J Nat Prod 83(3):770–803. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
Nolan M, Sikorski J, Jando M, Lucas S, Lapidus A, Glavina DRT, Chen F, Tice H, Pitluck S, Cheng J-F, Chertkov O, Sims D, Meincke L, Brettin T, Han C, Detter JC, Bruce D, Goodwin L, Land M, Hauser L, Chang Y-J, Jeffries CD, Ivanova N, Mavromatis K, Mikhailova N, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Chain P, Rohde M, Goker M, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Kyrpides NC, Klenk H-P (2010) Complete genome sequence of Streptosporangium roseum type strain (NI 9100). Stand Genomic Sci 2(1):29–37. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.631049
Overbeek R, Olson R, Pusch GD, Olsen GJ, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Parrello B, Shukla M, Vonstein V, Wattam AR, Xia F, Stevens R (2013) The SEED and the rapid annotation of microbial genomes using subsystems technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D206–D214. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1226
Pavkov-Keller T, Steiner K, Faber M, Tengg M, Schwab H, Gruber-Khadjawi M, Gruber K (2017) Crystal structure and catalytic mechanism of CouO, a versatile C-methyltransferase from Streptomyces rishiriensis. PLoS One 12(2):e0171056. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171056
Qin Z, Devine R, Hutchings MI, Wilkinson B (2019) A role for antibiotic biosynthesis monooxygenase domain proteins in fidelity control during aromatic polyketide biosynthesis. Nat Commun 10(1):3611. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11538-6
Ritzau M, Vettermann R, Fleck WF, Gutsche W, Dornberger K, Gräfe U (1997) Benaphthamycin, a new dihydrobenzo[α]naphthacenequinone antibiotic from Streptomyces sp. HKI-0057. J Antibiot 50(9):791–793. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.50.791
Rodríguez-Pascual F, Busnadiego O, Lagares D, Lamas S (2011) Role of endothelin in the cardiovascular system. Pharmacol Res 63(6):463–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2011.01.014
Shao L, Zi J, Zeng J, Zhan J (2012) Identification of the herboxidiene biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces chromofuscus ATCC 49982. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(6):2034–2038. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06904-11
Smith TP, Haymond T, Smith SN, Sweitzer SM (2014) Evidence for the endothelin system as an emerging therapeutic target for the treatment of chronic pain. J Pain Res 7:531–545. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S65923
Sun L, Zeng J, Cui P, Wang W, Yu D, Zhan J (2018) Manipulation of two regulatory genes for efficient production of chromomycins in Streptomyces reseiscleroticus. J Biol Eng 12:9/1–9/11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-018-0103-x
Takahashi T, Kanda T, Inoue M, Sumino H, Kobayashi I, Iwamoto A, Nagai R (1998) Endothelin converting enzyme inhibitor protects against development of right ventricular overload and medial thickening of pulmonary arteries in rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Life Sci 63(10):PL137–PL143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(98)00347-6
Tian J, Chen H, Guo Z, Liu N, Li J, Huang Y, Xiang W, Chen Y (2016) Discovery of pentangular polyphenols hexaricins A–C from marine Streptosporangium sp. CGMCC 4.7309 by genome mining. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(9):4189–4199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7248-z
Tsurumi Y, Ohhata N, Iwamoto T, Shigematsu N, Sakamoto K, Nishikawa M, Kiyoto S, Okuhara M (1994) WS79089A, B and C, new endothelin converting enzyme inhibitors isolated from Streptosporangium roseum no. 79089: taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological activities. J Antibiot 47(6):619–630. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.47.619
Tsurumi Y, Fujie K, Nishikawa M, Kiyoto S, Okuhara M (1995) Biological and pharmacological properties of highly selective new endothelin converting enzyme inhibitor WS79089B isolated from Streptosporangium roseum no. 79089. J Antibiot 48(2):169–174. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.48.169
Wada A, Tsutamoto T, Ohnishi M, Sawaki M, Fukai D, Maeda Y, Kinoshita M (1999) Effects of a specific endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitor on cardiac, renal, and neurohumoral functions in congestive heart failure: comparison of effects with those of endothelin a receptor antagonism. Circulation 99(4):570–577. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.99.4.570
Wada A, Ohnishi M, Tsutamoto T, Fujii M, Matsumoto T, Yamamoto T, Wang X, Kinoshita M (2002) Chronic effects of an endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitor on cardiorenal and hormonal function in heart failure. Clin Sci 103(Suppl):254S–257S. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS103S254S
Whyteside AR, Turner AJ, Lambert DW (2014) Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) is post-transcriptionally regulated by alternative polyadenylation. PLoS One 9(1):e83260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083260
Zhan J, Watanabe K, Tang Y (2008) Synergistic actions of a monooxygenase and cyclases in aromatic polyketide biosynthesis. ChemBioChem 9(11):1710–1715. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200800178
Funding
The Bruker Avance III HD Ascend-500 NMR instrument used in this research was funded by the National Science Foundation Award CHE–1429195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FX and JZ conceived and designed research. FX, YL, JR, and SW conducted experiments. FX, YL, JR, SW, and JZ analyzed data. FX and JZ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 778 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Liang, Y., Ren, J. et al. Discovery of a novel analogue of FR901533 and the corresponding biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptosporangium roseum No. 79089. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 7131–7142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10765-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10765-y