Abstract
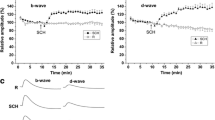
The high functional plasticity of the glutamatergic synapse of the vestibular epithelium is supported by a delicate balance of excitatory and inhibitory interactions. One of the peptides co-localized with acetylcholine (ACh) in the efferent fibers is dopamine. Using external perfusion of the synaptic zone and multiunit recording of an afferent fibers activity the effect of dopamine antagonists on the background firing rate of the semicircular canal sensory fibers was studied on the isolated frog vestibular. The present research revealed that the dopamine receptor antagonist (D1) SCH-23390 significantly reduced the level of background activity at high concentrations. In contrast, D2 antagonist eticlopride caused positive-negative answer of the background activity of the sensory fibers in dose-depending manner. The data confirm the hypothesis that dopamine, being tonic released from the efferent fibers, realizes neuroprotective inhibitory control over the afferent glutamatergic synapse activity in the vestibular epithelium via D1 and D2 receptors.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Guth, P.S., Perin, P., Norris, C.H., et al., The vestibular hair cells: post-transductional signal processing, Prog. Neurobiol., 1998, vol. 54, pp. 193–247.
De Mei, C., Ramos, M., Iitaka, C., et al., Getting specialized: presynaptic and postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2009, vol. 9, pp. 53–58.
Beaulieu, J.-M. and Gainetdinov, R.R., The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors, Pharmacol. Rev., 2011, vol. 63, pp. 182–217.
Usiello, A., Baik, J.H., Rougé-Pont, F., et al., Distinct functions of the two isoforms of dopamine D2 receptors, Nature, 2000, vol. 408, pp. 199–203.
Andrianov, G.N., Ryzhova, I.V., and Tobias, T.V., Dopaminergic modulation of afferent synaptic transmission in the semicircular canals of frogs, Neurosignals, 2009, vol. 17, pp. 222–228.
Bonsacquet, J., Brugeaud, A., Compan, V., et al., AMPA type glutamate receptor mediates neurotransmission at turtle vestibular calyx synapse, J. Physiol., 2006, vol. 576, pp. 63–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryzhova, I.V., Tobias, T.V. & Nozdrachev, A.D. Antagonists D1 and D2 of Dopamine Receptors Determine Different Mechanisms of Neuroprotective Action in the Frog Vestibular. Dokl Biochem Biophys 492, 139–141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672920030084
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672920030084