Abstract
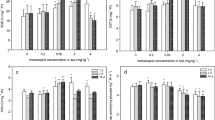
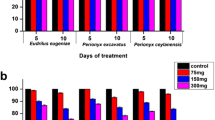
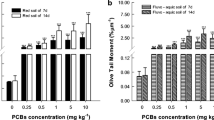
The present study investigated the biochemical toxicity and potential detoxification mechanisms in earthworms Eisenia fetida exposed to sulfamethazine (SMZ) (7.5, 15 and 30 mg kg−1) either alone or in combination with Copper (Cu) (100 mg kg−1) in soil. The results showed that increasing concentrations of SMZ in soil activated superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase isozymes, suggesting reactive oxygen species (ROS) burst in earthworms. Treatment with SMZ and Cu separately or in combination caused protein oxidation and damage, elevating the synthesis of ubiquitin, the 20S proteasome, cytochrome P450 (CYP450), and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). Such treatments also induced the activities of proteases, endoproteinase (EP) and glutathione S-transferases (GSTs). The results suggested that the ubiquitin-20S proteasome, proteases, EP and HSP70 were involved in degradation or remediation of oxidatively damaged proteins. Elevated levels of CYP450 and GSTs also participated in the detoxification of the earthworms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
An J, Chen HW, Wei SH, Gu J (2015) Antibiotic contamination in animal manure, soil, and sewage sludge in Shenyang, northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 74:5077–5086
Awali S, Abdulelah SA, Crile KG, Yacoo KE, Almouseli A, Torres VC, Dayfeld DJ, Evans KR, Belanger RM (2019) Cytochrome P450 and glutathione-S-transferase activity are altered following environmentally relevant atrazine exposures in Crayfsh (Faxonius virilis). B Environ Contam Tox 103:579–584
Book AJ, Yang P, Scalf M, Smith LM, Vierstra RD (2005) Tripeptidyl peptidase II. An oligomeric protease complex from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138:1046–1057
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Davies KJ, Shringarpure R (2006) Preferential degradation of oxidized proteins by the 20S proteasome may be inhibited in aging and in inflammatory neuromuscular diseases. Neurology 66:S93–S96
Gajewska E, Skłodowska M (2010) Differential effect of equal copper, cadmium and nickel concentration on biochemical reactions in wheat seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe 73:996–1003
García-Limones C, Hervás A, Navas-Cortés JA, Jiménez-Diaz RM, Tena M (2002) Induction of an antioxidant enzyme system and other oxidative stress markers associated with compatible and incompatible interactions between chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Ciceris. Physiol Mol Plant P 61:325–337
Glickman MH, Ciechanover A (2002) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev 82:373–428
Grune T, Merker K, Jung T, Sitte N, Davies KJ (2005) Protein oxidation and degradation during postmitotic senescence. Free Radical Bio Med 39:1208–1215
Guo H, Li KX, Wang W, Wang CG, Shen YC (2017) Effects of copper on hemocyte apoptosis, ROS production, and gene expression in White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Biol Trace Elem Res 179:318–326
Habig WH, Jakoby WB (1981) Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferase. Method Enzymol 77:398–405
Jia DA, Zhou DM, Wang YJ, Zhu HW, Chen JL (2008) Adsorption and cosorption of Cu(II) and tetracycline on two soils with different characteristics. Geoderma 146:224–230
Kahana C (2007) Ubiquitin dependent and independent protein degradation in the regulation of cellular polyamines. Amino Acids 33:225–230
Kaushal S, Ahsan AU, Sharma VL, Chopra M (2019) Epigallocatechin gallate attenuates arsenic induced genotoxicity via regulation of oxidative stress in balb/C mice. Mol Biol Rep 46:5355–5369
Knecht E, Aguado C, Cárcel J, Esteban I, Esteve JM, Ghislat G, Moruno JF, Vidal JM, Sáez R (2009) Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian cells: recent developments. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2427–2443
Kong WD, Zhu YG, Fu BJ, Marschner P, He JZ (2006) The veterinary antibiotic oxytetracycline and Cu influence functional diversity of the soil microbial community. Environ Pollut 143:129–137
Lertpaitoonpan W, Moorman TB, Ong SK (2015) Effect of swine manure on sulfamethazine degradation in aerobic and anaerobic soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:81
Li YW, Wu XL, Mo CH, Tai YP, Huang XP, Xiang L (2011) Investigation of sulfonamide, tetracycline, and quinolone antibiotics in vegetable farmland soil in the Pearl River Delta area, southern China. J Agr Food Chem 59:7268–7276
Lin CL, Chen HJ, Hou WC (2002) Activity staining of glutathione peroxidase after electrophoresis on native and sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 23:513–516
Liu BL, Fei F, Li XT, Wang XY, Huang B (2019) Effects of stocking density on stress response, innate immune parameters, and welfare of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquacult Int 27:1599–1612
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
OECD (2004) Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetidal Eisenia Andrei). Guideline for testing chemicals. No.222. OECD, Paris
Polge C, Jaquinod M, Holzer F, Bourguignon J, Walling L, Brouquisse R (2009) Evidence for the existence in Arabidopsis thaliana of the proteasome proteolytic pathway, activation in response to cadmium. J Biol Chem 284:35412–35424
Roberts RJ, Agius C, Saliba C, Bossier P, Sung YY (2010) Heat shock proteins (chaperones) in fish and shellfish and their potential role in relation to fish health: a review. J Fish Dis 33:789–801
Sagi M, Fluhr R (2001) Superoxide production by plant homologues of the gp91phox NADPH oxidase. Modulation of activity by calcium and by tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Physiol 126:1281–1290
Smalle J, Vierstra RD (2004) The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:555–590
Stadtman ER, Levine RL (2003) Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 25:207–218
Sun LL, Wang JN, Li XP, Cao CW (2019) Effects of phenol on glutathione S-transferase expression and enzyme activity in Chironomus kiiensis larvae. Ecotoxicology 28:754–762
Tompkins LM, Wallace AD (2007) Mechanisms of cytochrome P450 induction. J Biochem Mol Toxic 21:176–181
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164:645–655
Wang CR, Tian Y, Wang XR, Geng JJ, Jiang JL, Yu HX, Wang C (2010) Lead-contaminated soil induced oxidative stress, defense response and its indicative biomarkers in roots of Vicia faba seedlings. Ecotoxicology 19:1130–1139
Wang CR, Luo X, Tian Y, Xie Y, Wang SC, Li YY, Tian LM, Wang XR (2012) Biphasic effects of lanthanum on Vicia faba L. seedlings under cadmium stress, implicating finite antioxidation and potential ecological risk. Chemosphere 86:530–537
Wang CR, Rong H, Liu HT, Wang XF, Gao YX, Deng RH, Liu RY, Liu Y, Zhang D (2018) Detoxification mechanisms, defense responses, and toxicity threshold in the earthworm Eisenia foetida exposed to ciprofloxacin-polluted soils. Sci Total Environ 612:442–449
Xu YG, Yu WT, Ma Q, Zhou H, Jiang CM (2017) Toxicity of sulfadiazine and copper and their interaction to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe 142:250–256
Zhang Y, Cai X, Lang X, Qiao X, Li X, Chen J (2012) Insights into aquatic toxicities of the antibiotics oxytetracycline and ciprofloxacin in the presence of metal: complexation versus mixture. Environ Pollut 166:48–56
Zhao FK, Yang L, Chen LD, Li SJ, Sun L (2018) Co-contamination of antibiotics and metals in peri-urban agricultural soils and source identification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34063–34075
Zhao RX, Feng J, Liu J, Fu WJ, Li XY, Li B (2019) Deciphering of microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge reactors under high selective pressure of different antibiotics. Water Res 151:388–402
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse of China (No. PCRRF19036), the fund from the Major Science and Technology Project of Anhui Province (No. 18030701189) and the Foundation of Scientific Research Project of Huainan Normal University, China (No. 2019XJZD02). We would also like to express our thanks to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, H., Wang, C., Liu, H. et al. Biochemical Toxicity and Potential Detoxification Mechanisms in Earthworms Eisenia fetida Exposed to Sulfamethazine and Copper. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 105, 255–260 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02927-5