Abstract
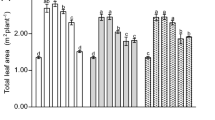
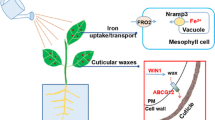
Nano-fertilization of agricultural systems is emerging as an innovative and unique strategy for agronomic fortification. In this study, a laboratory experiment was conducted to evaluate the physiological performance of soybean (Glycine max L.) exposed to either foliar or soil amendments of Fe2O3 nanoparticles (nFe2O3; 15, 30, and 60 mg/pot), fulvic acid-coated nFe2O3 (nFe2O3-FA; 60 mg nFe2O3/pot), and Fe-EDTA during an eight-week growing period. The experimental results demonstrated that none of the treatments produced toxicity stress or growth disorders. Amendments of nFe2O3 and nFe2O3-FA remarkably enhanced chlorophyll content, plant biomass, and root developmental indices. Fe-EDTA, a conventional fertilizer, did not provide satisfactory results compared with the other treatments. Regarding the supply of iron (Fe), foliar amendment provided 2–4 times higher shoot Fe concentration than soil application. Foliar amendments of nFe2O3-FA exclusively stimulated biological nitrogen fixation, which was primarily reflected in the formation of root nodules. This finding might be associated with the binary effect of the fulvic-Fe supply as well as enhanced potassium and zinc absorption in the plant than that of selective Fe penetration via negatively charged complexes. Further analysis of soil pH showed no evidence for facilitated Fe uptake via rhizosphere acidification. Conclusively, soybean responded better to the foliar amendment of nFe2O3-FA than nFe2O3 alone. This result suggests a novel perspective on the potential application of natural nanomaterial coating agents for nano-fertilization. From a practical perspective, it is necessary to consider the phosphorus (P) interaction and availability in the soil under nFe2O3 amendment, since the treatments substantially decreased P concentration in the soybean shoots, and thus a possible deficiency in plants under the critical pH value (below 6 and between 8–8.5) would be expected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidoust D, Isoda A (2013) Effect of γFe2O3 nanoparticles on photosynthetic characteristic of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.): foliar spray versus soil amendment. Acta Physiol Plant 35:3365–3375
Alidoust D, Isoda A (2014) Phytotoxicity assessment of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles on root elongation and growth of rice plant. Environ Earth Sci 71:5173–5182
Andresen E, Peiter E, Küpper H (2018) Trace metal metabolism in plants. J Exp Bot 69:909–954
Anjum SA, Wang LC, Farooq M, Xue LL, Ali S (2011) Fulvic acid application improves the maize performance under well-watered and drought conditions. J Agron Crop Sci 197:409–417
Bauhus J, Messier C (1999) Evaluation of fine rot length and diameter measurements obtained using RHIZO image analysis. Agron J 91:142–147
Bellaloui N, Reddy KN, Gillen AM, Abel CA (2010) Nitrogen metabolism and seed composition as influenced by foliar boron application in soybean. Plant Soil 336:143–155
Brady NC, Weil RR (1999) The Nature and Properties of Soils, 12th edn. Prentice Hall Inc., New Jersey
Campo RJ, Araujo RS, Hungria M (2009) Molybdenum-enriched soybean seeds enhance N accumulation, seed yield, and seed protein content in Brazil. Field Crops Res 110:219–224
Cesco S, Romheld V, Varanini Z, Pinton R (2000) Solubilization of iron by water-extractable humic substances. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:285–290
Chen J, Li Y, Wen S, Rosanoff A, Yang G, Sun X (2017) Magnesium fertilizer-induced increase of symbiotic microorganisms improves forage growth and quality. J Agric Food Chem 65:3253–3258
Cheng W, Xu J, Wang YJ, Wu F, Xu X, Li JJ (2015) Dispersion-precipitation synthesis of nanosized magnetic iron oxide for efficient removal of arsenite in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 445:93–101
Cheng W, Xu XY, Wu F, Li JJ (2016) Synthesis of cavity-containing iron oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal treatment of colloidal dispersion. Mater Lett 164:210–212
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (1996) The iron oxides. VCH Publ, Weinheim
Cvjetko P, Milošić A, Domijan AM, Vinković-Vrček I, Tolić S, Peharec-Štefanić P, Letofsky-Papst I, Tkalec M, Balen B (2017) Toxicity of silver ions and differently coated silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:18–28
Ditta A, Arshad M, Ibrahim M (2015) Nanoparticles in sustainable agricultural crop production: applications and perspectives. In: Siddiqui M, Al-Whaibi M, Mohammad F (eds) Nanotechnology and plant sciences. Springer, Cham, pp 55–75
Fageria NK, Filho MPB, Moreira A, Guimaraes CM (2009) Foliar fertilization of crop plants. J Plant Nut 32:1044–1064
Fathi A, Zahedi M, Torabian S, Khoshgoftar A (2017) Response of wheat genotypes to foliar spray of ZnO and Fe2O3 nanoparticles under salt stress. J Plant Nutr 40:1376–1385
Fernández V, Ebert G (2005) Foliar iron fertilization: a critical review. J Plant Nutr 28:2113–2124
Gao F, Liu C, Qu C, Zheng L, Yang F, Su M, Hong F (2008) Was improvement of spinach growth by nano-TiO2 treatment related to the changes of Rubisco activase? Biometals 21:211–217
Goldberg S, Sposito G (1985) On the mechanism of phosphate adsorption by hydroxylated mineral surfaces: a review. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 16:801–821
Grignon C, Sentenac H (1991) pH and ionic conditions in the apoplast. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:103–128
Gui X, Deng Y, Rui Y, Gao B, Luo W, Chen S, Nhan LV, Li X, Liu S, Han Y, Liu L, Xing BS (2015) Response difference of transgenic and conventional rice (Oryza sativa) to nanoparticles (γFe2O3). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17716–17723
He SY, Feng YZ, Ren HX, Zhang Y, Gu N, Lin XG (2011) The impact of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles on the soil bacterial community. J Soils Sediments 11:1408–1417
Heckman JR (2007) Chlorine. In: Barker AV, Pilbeam DJ (eds) Handbook of plant nutrition. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, pp 279–291
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hsu HH, Ashmead HD (1984) Effect of urea and ammonium nitrate on the uptake of iron through leaves. J Plant Nutr 7:291–300
Hu J, Guo H, Li J, Gan Q, Wang Y, Xing B (2017a) Comparative impacts of iron oxide nanoparticles and ferric ions on the growth of Citrus maxima. Environ Pollut 221:199–208
Hu J, Guo H, Li J, Wang Y, Xiao L, Xing B (2017b) Interaction of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with Citrus maxima leaves and the corresponding physiological effects via foliar application. J Nanobiotechnol 15(1):51
Illés E, Tombácz E (2005) The effect of humic acid adsorption on pH-dependent surface charging and aggregation of magnetite nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 295:115–123
Jaberzadeh A, Moaveni P, Moghadam HRT, Zahedi H (2013) Influence of bulk and nanoparticles titanium foliar application on some agronomic traits, seed gluten and starch contents of wheat subjected to water deficit stress. Not Bot Horti Agrobo 41:201–207
Jiang HS, Qiu XN, Li GB, Li W, Yin LY (2014) Silver nanoparticles induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species and alteration of antioxidant systems in the aquatic plant Spirodela polyrhiza. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:1398–1405
Kämpf N, Scheinost AC, Schulze DG (2002) Oxide minerals. In: Sumner ME (ed) Handbook of soil science. CRC Press, London, pp 125–168
Kiss SA, Stefanovits-Bányai E, Takács-Hájos M (2004) Magnesium-content of rhizobium nodules in different plants: the importance of magnesium in nitrogen-fixation of nodules. J Am Coll Nutr 23:751–753
Lei C, Sun Y, Tsang DCW, Lin D (2018) Environmental transformations and ecological effects of iron-based nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 232:10–30
Lewinski N, Colvin V, Drezek R (2008) Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Small 4:26–49
Li J, Chang P, Huang J, Wang Y, Yuan H, Ren H (2013) Physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles towards watermelon. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 13:5561–5567
Li JL, Hu J, Ma C, Wang Y, Wu C, Huang J, Xing BS (2016) Uptake, translocation and physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles in corn (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 159:326–334
Lindsay WL, Vlek PLG, Chien SH (1989) Phosphate minerals. In: Dixon B, Weed SB (eds) Minerals in soil environment, 2nd edn. J SSSA, Madison, pp 1089–1130
Liu G, Gao J, Ai H, Chen X (2013) Applications and potential toxicity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Small 9:1533–1545
Lucena JJ, Gárate A, Villén M (2010) Stability in solution and reactivity with soils and soil components of iron and zinc complexes. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 173:900–906
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Marschner H, Treeby M, Römheld V (1989) Role of root-induced changes in the rhizosphere for iron acquisition in higher plants. Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenk 152:197–204
Mortvedt JJ (1991) Correcting iron deficiencies in annual and perennial plants: present technologies and future prospects. Plant Soil 130:273–279
Nardi S, Concheri G, Dell’Agnola G (1996) Biological activity of humic substances. In: Piccolo A (ed) Humic substances in terrestrial ecosystems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 361–406
Nardi S, Pizzeghello D, Muscolo A, Vianello A (2002) Physiological effects of humic substances on higher plants. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1527–1536
Nekrasova GF, Ushakova OS, Ermakov AE, Uimin MA (2011) Effects of copper (II) ions and copper oxide nanoparticles on Elodea densa Planch. Russ J Ecol 42:458463
Panpatte DG, Jhala YK, Shelat HN, Vyas RV (2016) Nanoparticles: the next generation technology for sustainable agriculture. In: Singh DP et al (eds) Microbial inoculants in sustainable agricultural productivity. Springer, Delhi, pp 289–300
Parfitt RL, Russell JD, Farmer VC (1976) Confirmation of the surface structures of goethite (-FeOOH) and phosphated goethite by infrared spectroscopy. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 72:1082–1087
Perez JM, Oloughin T, Simeone FJ, Weissleder R, Josephson L (2002) DNA-based magnetic nanoparticle assembly acts as a magnetic relaxation nanoswitch allowing screening of DNA-cleaving agents. J Am Che Soc 124:2856–2857
Prasad TNVKV, Sudhakar P, Sreenivasulu Y, Latha P, Munaswamy V, Raja Reddy K, Sreeprasad TS, Sajanlal PR, Pradeep T (2012) Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J Plant Nutr 35:906–927
Priya BNV, Mahavishnan K, Gurumurthy DS, Bindumadhava H, Upadhyay Ambika P, Sharma Navin K (2014) Fulvic acid (FA) for enhanced nutrient uptake and growth: insights from biochemical and genomic studies. J Crop Improv 28:740–757
Rafique R, Arshad M, Khokhar MF, Qazi IA, Hamza A, Virk N (2014) Growth response of wheat to titania nanoparticles application. NUST J Engin Sci 7:42–46
Raliya R, Nair R, Chavalmane S, Wang WN, Biswas P (2015) Mechanistic evaluation of translocation and physiological impact of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles on the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plant. Metallomics 7:1584–1594
Rastogi A, Zivcak M, Sytar O, Kalaji HM, He X, Mbarki S, Brestic M (2017) Impact of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on plant: a critical review. Front Chem 5:78
Rastogi A, Zivcak M, Tripathi DK, Yadav S, Kalaji HM, Brestic M (2019) Phytotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles in Triticum aestivum: improper regulation of photosystem I activity as the reason for oxidative damage in the chloroplast. Photosynthetica 57(1):209–216
Ren HX, Liu L, Liu C, He SY, Huang J, Li JL, Zhang Y, Huang XJ, Gu N (2011) Physiological investigation of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles towards Chinese mung bean. J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:677–684
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Farid M, Abbas F (2017) Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 322:2–16
Roriz M, Carvalho S, Vasconcelos MW (2014) High relative air humidity influences mineral accumulation and growth in iron deficient soybean plants. Front Plant Sci 5:726
Rui M, Ma C, Hao Y, Guo J, Rui Y, Tang X, Zhao Q, Fan X, Zhang Z, Hou T, Zhu S (2016) Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Front Plant Sci 7:815
Schönherr J, Huber R (1977) Plant cuticles are polyelectrolytes with isoelectric points around three. Plant Physiol 59:145–150
Schwertmann U, Taylor RM (1989) Iron oxides. In: Dixon JB, Weed SB (eds) Minerals in soil environment. SSSA Book Ser 1. SSSA, Madison, pp 379–438
Shankramma K, Yallappa S, Shivanna MB, Manjanna J (2015) Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles to enhance S. lycopersicum (tomato) plant growth and their biomineralization. Appl Nanosci 6:983–990
Tagoe SO, Horiuchi T, Matsui T (2008) Effects of carbonized and dried chicken manures on the growth, yield, and N content of soybean. Plant Soil 306:211–220
Tarafdar JC, Sharma S, Raliya R (2013) Nanotechnology: interdisciplinary science of applications. Afr J Biotechnol 12:219–226
Teske SS, Detweiler CS (2015) The biomechanisms of metal and metaloxide nanoparticles interactions with cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:1112–1134
Torrent J, Schwertmann U, Barron V (1992) Fast and slow phosphate sorption by goethite-rich natural minerals. Clays Clay Miner 40:14–21
Tunesi S, Poggi V, Gessa C (1999) Phosphate adsorption and precipitation in calcareous soils: the role of calcium ions in solution and carbonate minerals. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 53:219–227
Van Nhan L, Ma C, Rui Y, Cao W, Deng Y, Liu L, Xing B (2016) The effects of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on physiology and insecticide activity in non-transgenic and Bt-transgenic cotton. Front Plant Sci 6:1263
Van Schaik JWJ, Persson I, Kleja DB, Gustafsson JP (2008) EXAFS study on the reactions between iron and fulvic acid in acid aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Technol 42:2367–2373
Vance CP (2001) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation and phosphorus acquisition. Plant nutrition in a world of declining renewable resources. Plant Physiol 127:390–397
Wang P, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, Kopittke PM (2016) Nanotechnology: a new opportunity in plant sciences. Trends Plant Sci 21:699–712
Wang CY, Alidoust D, Isoda A, Li M (2017) Suppressive effects of thermal-treated oyster shells on cadmium and copper translocation in maize plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(23):19347–19356
Wang CY, Alidoust D, Yang XY, Isoda A (2018) Effects of bamboo biochar on soybean root nodulation in multi-elements contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150:62–69
Wei Y, Shohag MJI, Yang X, Yibin Z (2012) Effects of foliar iron application on iron concentration in polished rice grain and its bioavailability. J Agric Food Chem 60:11433–11439
Wu HH, Yin JJ, Wamer WG, Zeng MY, Lo YM (2014) Reactive oxygen species-related activities of nano-iron metal and nano-iron oxides. J Food Drug Anal 22:86–94
Xu G, Magen H, Tarchitzky J, Kafkaf U (2000) Advances in chloride nutrition of plants. Adv Agron 28:97–150
Yin L, Colman BP, McGill BM, Wright JP, Bernhardt ES (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on germination and early growth of eleven wetland plants. PLoS ONE 7:e47674
Zuo Y, Zhang FS (2011) Soil and crop management strategies to prevent iron deficiency in crops. Plant Soil 339:83–95
Acknowledgments
CW gratefully acknowledges the scientific support from the China Ministry of Science and Technology. We would also like to thank our valued reviewers for their insightful comments, which contributed greatly to the manuscript overall quality and completeness.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program, Ministry of Science and Technology, China, Grant No. 2017 YFD0300101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by O. Ferrarese-Filho.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Alidoust, D. & Wang, C. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on the mineral composition and growth of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. Acta Physiol Plant 42, 128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03104-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03104-1