Abstract
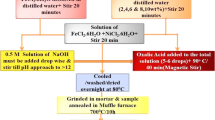
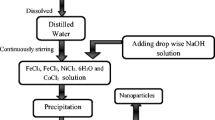
The aim of this research work was to study the structural and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. The as-prepared sample was synthesized by a co-precipitation route and annealed at different temperatures. The annealed samples were investigated using different techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), and Mössbauer spectrometry (MS). The XRD results indicate the formation of three phases which have been identified as magnetite (Fe3O4), maghemite (γ-Fe2O3), and hematite (a-Fe2O3). The crystallite size was very similar for both magnetite and maghemite, and it was higher for hematite. The TEM observations showed that the particle shapes were affected by the annealing temperature (Tan). In addition, the SEM analysis revealed a wide distribution of the particle size. The magnetic measurements enabled the determination of a blocking temperature for both Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 as 210 and 240 K, respectively. The Morin transition temperature was determined in the case of α-Fe2O3 from the magnetization and the MS measurements. The synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles can be good candidates for hyperthermia applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Can, M.M., Coskun, M., Fırat, T.: A comparative study of nanosized iron oxide particles; magnetite (Fe3O4), maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) and hematite (a-Fe2O3) using ferromagnetic resonance. J. Alloys Compd. 542, 241–247 (2012)
Sun, Y., Ma, M., Zhang, Y., Gu, N.: Synthesis of nanometer-size maghemite particles from magnetite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 245, 15–19 (2004)
Oh, J.K., Park, J.M.: Iron oxide-based superparamagnetic polymeric nanomaterials: design, preparation, and biomedical application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 36, 168–189 (2011)
Gupta, A.K., Gupta, M.: Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 26, 3995–4021 (2005)
Guo, S., Li, D., Zhang, L., Li, J., Wang, E.: Monodisperse mesoporous superparamagnetic single-crystal magnetite nanoparticles for drug delivery. Biomaterials. 30, 1881–1889 (2009)
Liu, X., Tao, Y., Mao, H., Kong, Y., Shen, J., Deng, L., Yang, L.: Construction of magnetic-targeted and NIR irradiation-controlled drug delivery platform with Fe3O4@au@SiO2 nanospheres. Ceram. Int. 43, 5061–5067 (2017)
Haw, C.Y., Mohamed, F., Chia, C.H., Radiman, S., Zakaria, S., Huang, N.M., Lim, H.N.: Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Ceram. Int. 36, 1417–1422 (2010)
Zhang, L., Wu, H.B., Lou, X.W., Iron-oxide-based advanced anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Adv. Energy Mater. 4 (2014) 1–11
Wu, C., Yin, P., Zhu, X., Yang, C.O., Xie, Y.: Synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanorods: diameter-size and shape effects on their applications in magnetism, lithium ion battery, and gas sensors. J. Phys. Chem. B. 110, 17806–17812 (2006)
Yanyan, X., Shuang, Y., Guoying, Z., Yaqiu, S., Dongzhao, G., Yuxiu, S.: Uniform hematite α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: morphology, size-controlled hydrothermal synthesis and formation mechanism. Mater. Lett. 65, 1911–1914 (2011)
Fleet, M.E.: The structure of magnetite: symmetry of cubic spinels. J. Solid State Chem. 62, 75–82 (1986)
Shokrollahi, H.: A review of the magnetic properties, synthesis methods and applications of maghemite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 74–81 (2017)
Rollmann, G., Rohrbach, A., Entel, P., Hafner, J.: First-principles calculation of the structure and magnetic phases of hematite. Phys. Rev. B. 69, 1–12 (2004)
Amin, N., Arajs, S.: Morin temperature of annealed submicronic α-Fe2O3 particles. Phys. Rev. B. 35, 4810–4811 (1987)
Sato, J., Kobayashi, M., Kato, H., Miyazaki, T., Kakihana, M.: Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite particles with uncommon crystal facets. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2, 258–262 (2014)
Chen, Z., Du, Y., Li, Z., Yang, K., Lv, X.: Controllable synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 particles with different morphology by one-step hydrothermal route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 121–125 (2017)
Zhu, L.P., Xiao, H.M., Zhang, W.D., Yang, G., Fu, S.Y.: One-pot template-free synthesis of monodisperse and single-crystal magnetite hollow spheres by a simple solvothermal route. Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 957–963 (2008)
Wang, W.W., Zhu, Y.J., Ruan, M.L.: Microwave-assisted synthesis and magnetic property of magnetite and hematite nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 9(2007), 419–426
Xu, J., Yang, H., Fu, W., Du, K., Sui, Y., Chen, J., Zeng, Y., Li, M., Zou, G.: Preparation and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 309, 307–311 (2007)
Deshpande, K., Mukasyan, A., Varma, A.: Direct synthesis of iron oxide nanopowders by the combustion approach: reaction mechanism and properties. Chem. Mater. 16, 4896–4904 (2004)
de Carvalho, J.F., de Medeiros, S.N., Morales, M.A., Dantas, A.L., Carriço, A.S.: Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles by high energy ball milling. Appl. Surf. Sci. 275, 84–87 (2013)
Yazdani, F., Seddigh, M.: Magnetite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method: the effects of various iron anions on specifications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 184, 318–323 (2016)
Shen, L., Qiao, Y., Guon, Y., Meng, S., Yang, G., Wu, M., Zhao, J.: Facile co-precipitation synthesis of shape-controlled magnetite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40, 1519–1524 (2014)
Petcharoen, K., Sirivat, A.: Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 177, 421–427 (2012)
Morato, A., Rives, V.: Comments on the application of the Scherrer equation in “Copper aluminum mixed oxide (CuAlMO) catalyst: a green approach for the one-pot synthesis of imines under solvent-free conditions”. Appl. Catal. B. 202, 418–419 (2017)
Hankare, P.P., Vader, V.T., Patil, N.M., Jadhav, S.D., Sankpal, U.B., Kadam, M.R., Chouguleb, B.K., Gajbhiye, N.S.: Synthesis, characterization and studies on magnetic and electrical properties of Mg ferrite with Cr substitution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 233–238 (2009)
Uvarov, V., Popov, I.: Metrological characterization of X-ray diffraction methods at different acquisition geometries for determination of crystallite size in nano-scale materials. Mater. Charact. 85, 111–123 (2013)
McCusker, L.B., VonDreele, R.B., Cox, D.E., Louër, D., Scardi, P.: Rietveld refinement guidelines. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 32, 36–50 (1999)
Jafaria, A., Shayesteha, S.F., Saloutib, M., Boustani, K.: Effect of annealing temperature on magnetic phase transition in Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 379, 305–312 (2015)
Alves, A.F., Mendo, S.G., Ferreira, L.P., Mendonça, M.H., Ferreira, P., Godinho, M., Cruz, M.M., Carvalho, M.D.: Gelatine-assisted synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Nanopart. Res. 18–27 (2016)
Legodi, M.A., de Waal, D.: The preparation of magnetite, goethite, hematite and maghemite of pigment quality from mill scale iron waste. Dyes Pigments. 74, 161–168 (2007)
Upadhyay, S., Parekh, K., Pandey, B.: Influence of crystallite size on the magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 678, 478–485 (2016)
Tadic, M., Citakovic, N., Panjan, M., Stanojevic, B., Markovic, D., Jovanovic, D., Spasojevic, V.: Synthesis, morphology and microstructure of pomegranate-like hematite (a-Fe2O3) superstructure with high coercivity. J. Alloys Compd. 543, 118–124 (2012)
Tadic, M., Trpkov, D., Kopanja, L., Vojnovic, S., Panjan, M.: Hydrothermal synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticle forms: synthesis conditions, structure, particle shape analysis, cytotoxicity and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 792, 599–609 (2019)
Tadic, M., Kopanja, L., Panjan, M., Nikodinovic-Runic, J.: Synthesis of core–shell hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoplates: quantitative analysis of the particle structure and shape, high coercivity and low cytotoxicity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 403, 628–634 (2017)
Jacob, J., AbdulKhadar, M.: VSM and Mössbauer study of nanostructured hematite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 614–621 (2010)
Aslibeiki, B., Ehsani, M.H., Nasirzadeh, F., Mohammadi, M.A.: The effect of interparticle interactions on spin glass and hyperthermia properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express. 4, 075051 (2017)
Ericsson, T., Krisnhamurthy, A., Srivastava, B.K.: Morin-transition in Ti-substituted hematite: a Mössbauer study. J. Phys. Scripta. 33, 88–90 (1986)
Özdemir, Ö., Dunlop, D.J.: Morin transition in hematite: size dependence and thermal hysteresis. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, 1–12 (2008)
Yoshida, Y., Langouche, G.: Mössbauer spectroscopy, tutorial book, pp. 110–115. Springer, Fukuroi (2013)
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by funds from FEDER (Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade COMPETE) and from FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia under Project No. UID/FIS/04564/2016. Access to TAIL-UC facility funded under QREN-Mais Centro Project No. ICT_2009_02_012_1890 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ounacer, M., Essoumhi, A., Sajieddine, M. et al. Structural and Magnetic Studies of Annealed Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 3249–3261 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05586-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05586-z