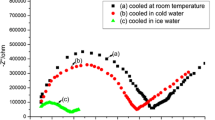
Abstract
The effects of different lithium salt contents on the crystallinity and conductivity of solid polymer electrolytes PEO-LiClO4 were analyzed by DSC thermal analysis method and AC impedance method. Furthermore, the variation of bonding current and time during the bonding process between metal aluminum and PEO-LiClO4 with different LiClO4 content was studied under different bonding voltages. The results show that with the addition of lithium salt and increasing its content, it can effectively hinder the crystallization of PEO and improve its room temperature conductivity. The more the lithium salt content, the higher the bonding voltage, the larger the peak current generated during the bonding process, the thicker the intermediate transition layer, and the higher the bonding strength.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen Shizhu, Research on MEMS. China Mech. Eng. 14(2), 160–163 (2003)
Z. Zhenyue, Excellent local enterprises in China’s MEMS sensor potential market and subdivision field in 2019. China Electron News. (2019)
N. Ren, Y. Song, C. Tao et al., Effect of the soft and hard segment composition on the properties of waterborne polyurethane-based solid polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 14, 1–13 (2017)
X.Y. Yu, M. Xiao, S.J. Wang et al., Fabrication and characterization of PEO/PPC polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion battery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 115(5), 2718–2722 (2010)
D. Xiong, J. Cheng, H. Li, W. Deng, K. Ye, Anodic bonding of glass–ceramics to stainless steel coated with intermediate SiO2 layer. Microelectron. Eng. 87(9), 1741–1746 (2010)
P. Mrozek, Glass-to-glass anodic bonding using TiNx interlayers for fully transparent device applications. Sens Actuators A 174, 139–143 (2012)
A. Manthiram, X. Yu, S. Wang, Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes. Nat Rev Mater 2(3), 16103 (2017)
L. Wang, W. Yang, J. Wang, D.G. Evans, New nanocomposite polymer electrolyte comprising nanosized ZnAl2O4 with a mesopore network and PEO-LiClO4. Solid State Ion. 180(4–5), 392–397 (2009)
E.M. Masoud, A.-A. El-Bellihi, W.A. Bayoumy, M.A. Mousa, Effect of LiAlO2 nanoparticle filler concentration on the electrical properties of PEO–LiClO4 composite. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(3), 1148–1154 (2013)
Z. Xue, D. He, X. Xie, Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(38), 19218–19253 (2015)
R. Zhen, Q.W. Chi, X.Y. Wang et al., Preparation and characterization of poly(ethylene-oxide)/kaolinite composite electrolyte. Acta Polym. Sin. 8, 1312–1319 (2017)
M. Ghelich, N.T. Qazvini, S.H. Jafari et al., Conformational, thermal, and ionic conductivity behavior of PEO in PEO/PMMA miscible blend: investigating the effect of lithium salt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 129(4), 1868–1874 (2013)
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 5187052685 ), and the Shanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 201801D121085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Liu, CR., Meng, YY. et al. Microstructure and Connection Mechanism of the Bonding Interface Between Lithium Ion Polymer Electrolyte and Aluminum Under Strong Electrostatic Field. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 4732–4738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01647-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01647-x