Abstract
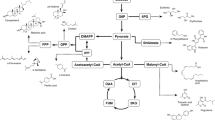
Yarrowia lipolytica is an oleaginous yeast that has been substantially engineered for production of oleochemicals and drop-in transportation fuels. The unique acetyl-CoA/malonyl-CoA supply mode along with the versatile carbon-utilization pathways makes this yeast a superior host to upgrade low-value carbons into high-value secondary metabolites and fatty acid-based chemicals. The expanded synthetic biology toolkits enabled us to explore a large portfolio of specialized metabolism beyond fatty acids and lipid-based chemicals. In this review, we will summarize the recent advances in genetic, omics, and computational tool development that enables us to streamline the genetic or genomic modification for Y. lipolytica. We will also summarize various metabolic engineering strategies to harness the endogenous acetyl-CoA/malonyl-CoA/HMG-CoA pathway for production of complex oleochemicals, polyols, terpenes, polyketides, and commodity chemicals. We envision that Y. lipolytica will be an excellent microbial chassis to expand nature’s biosynthetic capacity to produce plant secondary metabolites, industrially relevant oleochemicals, agrochemicals, commodity, and specialty chemicals and empower us to build a sustainable biorefinery platform that contributes to the prosperity of a bio-based economy in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cordova LT, Alper HS (2016) Central metabolic nodes for diverse biochemical production. Curr Opin Chem Biol 35:37–42
Levering J, Broddrick J, Zengler K (2015) Engineering of oleaginous organisms for lipid production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 36:32–39
Quarterman J et al (2017) A survey of yeast from the Yarrowia clade for lipid production in dilute acid pretreated lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(8):3319–3334
Groenewald M et al (2014) Yarrowia lipolytica: safety assessment of an oleaginous yeast with a great industrial potential. Crit Rev Microbiol 40(3):187–206
Kavscek M et al (2015) Optimization of lipid production with a genome-scale model of Yarrowia lipolytica. Bmc Syst Biol 9:72
Shi SB, Zhao HM (2017) Metabolic engineering of Oleaginous yeasts for production of fuels and chemicals. Front Microbiol 8:2185
Ledesma-Amaro R, Nicaud JM (2016) Metabolic engineering for expanding the substrate range of Yarrowia lipolytica. Trends Biotechnol 34(10):798–809
Michely S et al (2013) Comparative physiology of Oleaginous species from the Yarrowia Clade. PLoS One 8(5):e63356
Devillers H et al (2016) Draft genome sequence of Yarrowia tipotytica strain a-101 isolated from polluted soil in Poland. Microbiol Resour Announc 4(5):e01094-16
Devillers H, Neuveglise C (2019) Genome sequence of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica H222. Microbiol Resour Announc 8(4):e01547-18
Darvishi F et al (2018) Advances in synthetic biology of oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for producing non-native chemicals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(14):5925–5938
Dulermo R et al (2017) Using a vector pool containing variable-strength promoters to optimize protein production in Yarrowia lipolytica. Microbial Cell Factories 16:31
Wong L et al (2017) YaliBricks, a versatile genetic toolkit for streamlined and rapid pathway engineering in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng Commun 5(Supplement C):68–77
Wong L et al. (2019) Genetic tools for streamlined and accelerated pathway engineering in Yarrowia lipolytica, in microbial metabolic engineering: methods and protocols. In: Santos CNS, Ajikumar PK (Eds) Springer, New York, p. 155–177
Madzak C, Treton B, Blanchin-Roland S (2000) Strong hybrid promoters and integrative expression/secretion vectors for quasi-constitutive expression of heterologous proteins in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 2(2):207–216
Blazeck J, Alper HS (2013) Promoter engineering: recent advances in controlling transcription at the most fundamental level. Biotechnol J 8(1):46–58
Blazeck J et al (2013) Generalizing a hybrid synthetic promoter approach in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(7):3037–3052
Shabbir Hussain M et al (2016) Engineering promoter architecture in oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Acs Synth Biol 5(3):213–223
Larroude M et al (2018) Synthetic biology tools for engineering Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Adv 36(8):2150–2164
Hong SP et al (2012) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to express secretory invertase with strong FBA1IN promoter. Yeast 29(2):59–72
Tai M, Stephanopoulos G (2013) Engineering the push and pull of lipid biosynthesis in oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for biofuel production. Metab Eng 15:1–9
Trassaert M et al (2017) New inducible promoter for gene expression and synthetic biology in Yarrowia lipolytica. Microbial Cell Factories 16:141
Pignede G et al (2000) Characterization of an extracellular lipase encoded by LIP2 in Yarrowia lipolytica. J Bacteriol 182(10):2802–2810
Curran KA et al (2015) Short synthetic terminators for improved heterologous gene expression in yeast. Acs Synth Biol 4(7):824–832
Blazeck J et al (2011) Tuning gene expression in Yarrowia lipolytica by a hybrid promoter approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(22):7905–7914
Le Dall MT, Nicaud JM, Gaillardin C (1994) Multiple-copy integration in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Curr Genet 26(1):38–44
Kretzschmar A et al (2013) Increased homologous integration frequency in Yarrowia lipolytica strains defective in non-homologous end-joining. Curr Genet 59(1–2):63–72
Wagner JM, Williams EV, Alper HS (2018) Developing a piggyBac transposon system and compatible selection markers for insertional mutagenesis and genome engineering in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol J 13(5):e1800022
Hamilton M et al (2020) Identification of a Yarrowia lipolytica acetamidase and its use as a yeast genetic marker. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):22
Shaw AJ et al (2016) Metabolic engineering of microbial competitive advantage for industrial fermentation processes. Science 353(6299):583–586
De Pourcq K et al (2012) Engineering the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for the production of therapeutic proteins homogeneously glycosylated with Man(8)GlcNAc(2) and Man(5)GlcNAc(2). Microb Cell Fact 11:53
Lv YK et al (2019) Combining 26s rDNA and the Cre-IoxP system for iterative gene integration and efficient marker curation in Yarrowia lipolytica. Acs Synth Biol 8(3):568–576
Madzak C (2015) Yarrowia lipolytica: recent achievements in heterologous protein expression and pathway engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(11):4559–4577
Fickers P et al (2003) New disruption cassettes for rapid gene disruption and marker rescue in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Microbiol Methods 55(3):727–737
Schwartz CM et al (2016) Synthetic RNA polymerase III promoters facilitate high-efficiency crispr-cas9-mediated genome editing in Yarrowia lipolytica. Acs Synth Biol 5(4):356–359
Liu LQ et al (2014) Increasing expression level and copy number of a Yarrowia lipolytica plasmid through regulated centromere function. FEMS Yeast Res 14(7):1124–1127
Holkenbrink C et al (2018) EasyCloneYALI: CRISPR/Cas9-based synthetic toolbox for engineering of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol J 13(9):e1700543
Bulani SI et al (2012) Development of a novel rDNA based plasmid for enhanced cell surface display on Yarrowia lipolytica. Amb Express 2(1):27
Bordes F et al (2007) A new recombinant protein expression system for high-throughput screening in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Microbiol Methods 70(3):493–502
Juretzek T et al (2001) Vectors for gene expression and amplification in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 18(2):97–113
Nicaud JM et al (2002) Protein expression and secretion in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Yeast Res 2(3):371–379
Guo ZP et al (2020) An artificial chromosome ylAC enables efficient assembly of multiple genes in Yarrowia lipolytica for biomanufacturing. Commun Biol 3(1):199
Gao SL et al (2014) One-step integration of multiple genes into the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotech Lett 36(12):2523–2528
Xu P et al (2012) ePathBrick: a synthetic biology platform for engineering metabolic pathways in E-coli. ACS Synth Biol 1(7):256–266
Leplat C, Nicaud JM, Rossignol T (2015) High-throughput transformation method for Yarrowia lipolytica mutant library screening. Fems Yeast Res 15(6):fov052
Gibson DG et al (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6(5):343–345
Rodriguez GM et al (2016) Engineering xylose utilization in Yarrowia lipolytica by understanding its cryptic xylose pathway. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:149
Engler C, Kandzia R, Marillonnet S (2008) A one pot, one step, precision cloning method with high throughput capability. PLoS ONE 3(11):e3647
Celinska E et al (2017) Golden gate assembly system dedicated to complex pathway manipulation in Yarrowia lipolytica. Microb Biotechnol 10(2):450–455
Larroude M et al (2019) A modular golden gate toolkit for Yarrowia lipolytica synthetic biology. Microb Biotechnol 12(6):1249–1259
Jinek M et al (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337(6096):816–821
Gao SL et al (2016) Multiplex gene editing of the Yarrowia lipolytica genome using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(8):1085–1093
Schwartz C et al (2019) Validating genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 function improves screening in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 55:102–110
Yang Z, Edwards H, Xu P (2020) CRISPR-Cas12a/Cpf1-assisted precise, efficient and multiplexed genome-editing in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng Commun 10:e00112
Schwartz C et al (2017) CRISPRi repression of nonhomologous end-joining for enhanced genome engineering via homologous recombination in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(12):2896–2906
Zhang JL et al (2018) Gene repression via multiplex gRNA strategy in Y. lipolytica. Microbial Cell Factories 17:62
Schwartz C et al (2018) Multiplexed CRISPR activation of cryptic sugar metabolism enables Yarrowia lipolytica growth on cellobiose. Biotechnol J 13(9):e1700584
Lazar Z, Liu N, Stephanopoulos G (2018) Holistic approaches in lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Trends Biotechnol 36(11):1157–1170
Xu P et al (2011) Genome-scale metabolic network modeling results in minimal interventions that cooperatively force carbon flux towards malonyl-CoA. Metab Eng 13(5):578–587
Loira N et al (2012) A genome-scale metabolic model of the lipid-accumulating yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. BMC Syst Biol 6:35
Pan P, Hua Q (2012) Reconstruction and in silico analysis of metabolic network for an oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica. PLoS ONE 7(12):e51535
Kerkhoven EJ et al (2016) Regulation of amino-acid metabolism controls flux to lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica. Npj Syst Biol Appl 2:16005
Mishra P et al (2018) Genome-scale model-driven strain design for dicarboxylic acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica. Bmc Syst Biol 12(Suppl 2):12
Kim M et al (2019) In silico identification of metabolic engineering strategies for improved lipid production in Yarrowia lipolytica by genome-scale metabolic modeling. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:187
Robles-Rodriguez CE et al (2017) Dynamic metabolic modeling of lipid accumulation and citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Comput Chem Eng 100:139–152
Wang GY et al (2018) Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals multiple functions for Mhy1p in lipid biosynthesis in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1863(1):81–90
Trebulle P et al (2017) Inference and interrogation of a coregulatory network in the context of lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica. Npj Syst Biol Appl 3:21
Xu P et al (2016) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica as a platform for synthesis of drop-in transportation fuels and oleochemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(39):10848–10853
Xu P et al (2013) Modular optimization of multi-gene pathways for fatty acids production in E. coli. Nat Commun 4:1409
Ledesma-Amaro R et al (2016) Combining metabolic engineering and process optimization to improve production and secretion of fatty acids. Metab Eng 38:38–46
Spagnuolo M, Yaguchi A, Blenner M (2019) Oleaginous yeast for biofuel and oleochemical production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 57:73–81
Bruder S et al (2019) Drop-in biofuel production using fatty acid photodecarboxylase from Chlorella variabilis in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Biofuels 12(1):202
Rutter CD, Rao CV (2016) Production of 1-decanol by metabolically engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 38:139–147
Wang GK et al (2016) Exploring fatty alcohol-producing capability of Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:107
Zhang JL et al (2019) High production of fatty alcohols in Yarrowia lipolytica by coordination with glycolysis. Sci China-Chem 62(8):1007–1016
Duda K et al (2018) Comparison of performance and emissions of a CRDI diesel engine fuelled with biodiesel of different origin. Fuel 212:202–222
Xu P, Qiao K, Stephanopoulos G (2017) Engineering oxidative stress defense pathways to build a robust lipid production platform in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(7):1521–1530
Friedlander J et al (2016) Engineering of a high lipid producing Yarrowia lipolytica strain. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:77
Xu JY et al (2017) Application of metabolic controls for the maximization of lipid production in semicontinuous fermentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(27):E5308–E5316
Qiao KJ et al (2017) Lipid production in Yarrowia lipolytica is maximized by engineering cytosolic redox metabolism. Nat Biotechnol 35(2):173–177
Liu H et al (2019) Understanding lipogenesis by dynamically profiling transcriptional activity of lipogenic promoters in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(7):3167–3179
Xie DM, Jackson EN, Zhu Q (2015) Sustainable source of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid from metabolically engineered Yarrowia lipolytica: from fundamental research to commercial production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(4):1599–1610
Xie DM et al (2017) Omega-3 production by fermentation of Yarrowia lipolytica: from fed-batch to continuous. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(4):798–812
Gemperlein K et al (2019) Polyunsaturated fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica employing designed myxobacterial PUFA synthases. Nat Commun 10:4055
Sun ML et al (2017) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for efficient gamma-linolenic acid production. Biochem Eng J 117:172–180
Liu HH et al (2017) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for arachidonic acid production through rapid assembly of metabolic pathway. Biochem Eng J 119:52–58
Liu HH et al (2019) Improved production of arachidonic acid by combined pathway engineering and synthetic enzyme fusion in Yarrowia lipolytica. J Agric Food Chem 67(35):9851–9857
Imatoukene N et al (2017) A metabolic engineering strategy for producing conjugated linoleic acids using the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(11):4605–4616
Fu GY et al (2016) Cloning and characterization of a pyruvate carboxylase gene from penicillium rubens and overexpression of the gene in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for enhanced citric acid production. Mar Biotechnol 18(1):1–14
Tan MJ et al (2016) Enhanced citric acid production by a yeast Yarrowia lipolytica over-expressing a pyruvate carboxylase gene. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39(8):1289–1296
Kamzolova SV, Morgunov IG (2017) Metabolic peculiarities of the citric acid overproduction from glucose in yeasts Yarrowia lipolytica. Biores Technol 243:433–440
Zeng WZ et al (2015) A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing alpha-ketoglutaric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica by random mutagenesis. Process Biochem 50(10):1516–1522
Zeng WZ et al (2016) Comparative genomics analysis of a series of Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06 mutants with varied capacity for alpha-ketoglutarate production. J Biotechnol 239:76–82
Zeng WZ et al (2017) Biosynthesis of keto acids by fed-batch culture of Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06. Biores Technol 243:1037–1043
Gao CJ et al (2016) Robust succinic acid production from crude glycerol using engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:179
Yang XF et al (2017) Restoring of Glucose Metabolism of engineered Yarrowia lipolytica for succinic acid production via a simple and efficient adaptive evolution strategy. J Agric Food Chem 65(20):4133–4139
Li C et al (2018) Hydrolysis of fruit and vegetable waste for efficient succinic acid production with engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. J Clean Prod 179:151–159
Li C et al (2019) Bio-refinery of waste streams for green and efficient succinic acid production by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica without pH control. Chem Eng J 371:804–812
Carlya F et al (2017) Enhancing erythritol productivity in Yarrowia lipolytica using metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 42:19–24
Qiu X et al (2020) Combining genetically-encoded biosensors with high throughput strain screening to maximize erythritol production in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 60:66–76
Marsafari M et al (2020) Genetically-encoded biosensors for analyzing and controlling cellular process in yeast. Curr Opin Biotechnol 64:175–182
Lv Y et al (2020) Coupling metabolic addiction with negative autoregulation to improve strain stability and pathway yield. Metab Eng 61:79–88
Li ZJ et al (2017) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for poly-3-hydroxybutyrate production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(4–5):605–612
Markham KA et al (2018) Rewiring Yarrowia lipolytica toward triacetic acid lactone for materials generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(9):2096–2101
Liu H et al (2019) Engineering acetyl-CoA metabolic shortcut for eco-friendly production of polyketides triacetic acid lactone in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 56:60–68
Lv Y et al (2019) Optimizing oleaginous yeast cell factories for flavonoids and hydroxylated flavonoids biosynthesis. ACS Synth Biol 8(11):2514–2523
Chandran SS, Kealey JT, Reeves CD (2011) Microbial production of isoprenoids. Process Biochem 46(9):1703–1710
Ma YR et al (2019) Advances in the metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for the production of terpenoids. Bioresour Technol 281:449–456
Ignea C et al (2014) Engineering monoterpene production in yeast using a synthetic dominant negative geranyl diphosphate synthase. Acs Synth Biol 3(5):298–306
Cao X et al (2017) Enhancing linalool production by engineering oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biores Technol 245:1641–1644
Cao X et al (2016) Metabolic engineering of oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for limonene overproduction. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:214
Yang X et al (2016) Heterologous production of alpha-farnesene in metabolically engineered strains of Yarrowia lipolytica. Biores Technol 216:1040–1048
Jia D et al (2019) Yarrowia lipolytica construction for heterologous synthesis of -santalene and fermentation optimization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(8):3511–3520
Guo XY et al (2018) Heterologous biosynthesis of (+)-nootkatone in unconventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochem Eng J 137:125–131
Marsafari M, Xu P (2020) Debottlenecking mevalonate pathway for antimalarial drug precursor amorphadiene biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng Commun 10:e00121
Pateraki I, Heskes AM, Hamberger B (2015) Cytochromes P450 for terpene functionalisation and metabolic engineering. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 148:107–39
Sun J et al (2019) Glycerol improves heterologous biosynthesis of betulinic acid in engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Chem Eng Sci 196:82–90
Jin CC et al (2019) Boosting the biosynthesis of betulinic acid and related triterpenoids in Yarrowia lipolytica via multimodular metabolic engineering. Microbial Cell Factories 18:77
Li DS et al (2019) Production of triterpene ginsenoside compound K in the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Agric Food Chem 67(9):2581–2588
Mata-Gomez LC et al (2014) Biotechnological production of carotenoids by yeasts: an overview. Microb Cell Fact 13:12
Schwartz C et al (2017) Host and pathway engineering for enhanced lycopene biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica. Front Microbiol 8:2233
Gao SL et al (2017) Iterative integration of multiple-copy pathway genes in Yarrowia lipolytica for heterologous beta-carotene production. Metab Eng 41:192–201
Larroude M et al (2018) A synthetic biology approach to transform Yarrowia lipolytica into a competitive biotechnological producer of beta-carotene. Biotechnol Bioeng 115(2):464–472
Kildegaard KR et al (2017) Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for production of astaxanthin. Synth Syst Biotechnol 2(4):287–294
Du HX et al (2016) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for campesterol overproduction. PLoS One 11(1):e0146773
Zhang Y et al (2017) Improved campesterol production in engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strains. Biotech Lett 39(7):1033–1039
Zhang R et al (2019) Pregnenolone overproduction in Yarrowia lipolytica by integrative components pairing of the cytochrome P450scc system. Acs Synth Biol 8(12):2666–2678
Wagner JM et al (2018) A comparative analysis of single cell and droplet-based FACS for improving production phenotypes: riboflavin overproduction in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 47:346–356
Gu Y et al (2020) Refactoring ehrlich pathway for high-yield 2-phenylethanol production in Yarrowia lipolytica. ACS Synth Biol 9(3):623–633
Gu Y et al. (2020) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica as a chassis for de novo synthesis of aromatic-derived natural products and chemicals. bioRxiv: p. 2020.04.04.025288
Spagnuolo M et al. (2018) Alternative substrate metabolism in Yarrowia lipolytica. Front Microbiol 9
den Haan R et al (2015) Progress and challenges in the engineering of non-cellulolytic microorganisms for consolidated bioprocessing. Curr Opin Biotechnol 33:32–8
Lane S et al (2015) Development and physiological characterization of cellobiose-consuming Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Bioeng 112(5):1012–1022
Lazar Z et al (2014) Hexokinase-a limiting factor in lipid production from fructose in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 26:89–99
Rakicka M et al (2016) Efficient utilization of inulin and glycerol as fermentation substrates in erythritol and citric acid production using Yarrowia lipolytica expressing inulinase. Chem Pap 70(11):1452–1459
Hapeta P et al (2017) Transforming sugars into fat—lipid biosynthesis using different sugars in Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 34(7):293–304
Ledesma-Amaro R, Dulermo T, Nicaud JM (2015) Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to produce biodiesel from raw starch. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:148
Lazar Z et al (2015) Awakening the endogenous Leloir pathway for efficient galactose utilization by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:185
Ledesma-Amaro R et al (2016) Metabolic engineeringof Yarrowia lipolytica to produce chemicals and fuels from xylose. Metab Eng 38:115–124
Wu YF et al (2019) Enhanced protopanaxadiol production from xylose by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Microbial Cell Factories 18:83
Beopoulos A, Chardot T, Nicaud JM (2009) Yarrowia lipolytica: a model and a tool to understand the mechanisms implicated in lipid accumulation. Biochimie 91(6):692–6
Fickers P et al (2005) Identification and characterisation of LIP7 and LIP8 genes encoding two extracellular triacylglycerol lipases in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Fungal Genet Biol 42(3):264–74
Yu M et al (2007) High-level expression of extracellular lipase Lip2 from Yarrowia lipolytica in Pichia pastoris and its purification and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 53(2):255–63
Kohlwein SD, Paltauf F (1984) Uptake of fatty acids by the yeasts, Saccharomyces uvarum and Saccharomycopsis lipolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta 792(3):310–7
Kamzolova SV et al (2005) Lipase secretion and citric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast grown on animal and vegetable fat. Food Technol Biotechnol 43(2):113–122
Liu XY et al (2017) A cost-effective process for the coproduction of erythritol and lipase with Yarrowia lipolytica M53 from waste cooking oil. Food Bioprod Process 103:86–94
Pang YR et al (2019) Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica to produce limonene from waste cooking oil. Biotechnol Biofuels 12(1):241
Magdouli S et al (2017) Valorization of raw glycerol and crustacean waste into value added products by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biores Technol 243:57–68
Sarris D et al (2017) Production of added-value metabolites by Yarrowia lipolytica growing in olive mill wastewater-based media under aseptic and non-aseptic conditions. Eng Life Sci 17(6):695–709
Fickers P et al (2005) Hydrophobic substrate utilisation by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, and its potential applications. FEMS Yeast Res 5(6–7):527–43
Workman M, Holt P, Thykaer J (2013) Comparing cellular performance of Yarrowia lipolytica during growth on glucose and glycerol in submerged cultivations. Amb Express 3:58
Gajdos P, Nicaud JM, Certik M (2017) Glycerol conversion into a single cell oil by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Eng Life Sci 17(3):325–332
Mironczuk AM et al (2016) A novel strain of Yarrowia lipolytica as a platform for value-added product synthesis from glycerol. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:180
Rzechonek DA et al (2019) Aseptic production of citric and isocitric acid from crude glycerol by genetically modified Yarrowia lipolytica. Biores Technol 271:340–344
Liu N, Qiao KJ, Stephanopoulos G (2016) C-13 Metabolic flux analysis of acetate conversion to lipids by Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 38:86–97
Lv Y et al (2019) Coupling feedback genetic circuits with growth phenotype for dynamic population control and intelligent bioproduction. Metab Eng 54:109–116
Wan X, Marsafari M, Xu P (2019) Engineering metabolite-responsive transcriptional factors to sense small molecules in eukaryotes: current state and perspectives. Microb Cell Fact 18(1):61
Xu P (2018) Production of chemicals using dynamic control of metabolic fluxes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 53:12–19
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Grant number OPP1188443) and the Cellular and Biochem Engineering Program of the National Science Foundation under Grant no.1805139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Gu, Y., Marsafari, M. et al. Synthetic biology, systems biology, and metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica toward a sustainable biorefinery platform. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47, 845–862 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-020-02290-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-020-02290-8