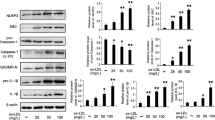
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is a progressive chronic inflammation in the arterial walls. It is believed that the deposition of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and its damage to endothelial cells play a vital role in atherosclerosis. Oxidized LDL (Ox-LDL) was confirmed to induce endothelial cell pyroptosis which plays an important role in intima inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis, but the underlying molecular mechanism needs to be explored. Here, we showed that ox-LDL upregulated the expression of mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL) protein at both the mRNA and protein levels in endothelial cells, associated with the augment of pro-caspase-1 cleavage, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) maturation, pro-IL-1β production, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. Overexpression of MLKL substantially aggravated ox-LDL-induced increasing levels of caspase-1, IL-1β, pro-IL-1β, and LDH. MLKL-induced caspase-1 activation and IL-1β maturation were abolished by NLR family, pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) specific inhibitor MCC950, or extracellular high potassium concentration. Our findings indicated that MLKL is essential for regulation of ox-LDL-induced pyroptosis and inflammation through the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, and suggested that MLKL could act as potential therapeutic targets to ameliorate atherosclerosis-related diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissberg, P.L., and M.R. Bennett. 1999. Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory disease. The New England Journal of Medicine 340: 1928–1929.
Suciu, C.F., M. Prete, P. Ruscitti, E. Favoino, R. Giacomelli, and F. Perosa. 2018. Oxidized low density lipoproteins: the bridge between atherosclerosis and autoimmunity. Possible implications in accelerated atherosclerosis and for immune intervention in autoimmune rheumatic disorders. Autoimmunity Reviews 17: 366–375.
Fernandez-Friera, L., V. Fuster, B. Lopez-Melgar, B. Oliva, J.M. Garcia-Ruiz, J. Mendiguren, et al. 2017. Normal LDL-cholesterol levels are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in the absence of risk factors. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 70: 2979–2991.
Tousoulis, D., E. Oikonomou, E.K. Economou, F. Crea, and J.C. Kaski. 2016. Inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerosis: current therapeutic approaches. European Heart Journal 37: 1723–1732.
Bergsbaken, T., S.L. Fink, and B.T. Cookson. 2009. Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nature Reviews. Microbiology 7: 99–109.
Gross, O., A.S. Yazdi, C.J. Thomas, M. Masin, L.X. Heinz, G. Guarda, et al. 2012. Inflammasome activators induce interleukin-1alpha secretion via distinct pathways with differential requirement for the protease function of caspase-1. Immunity 36: 388–400.
Miao, E.A., I.A. Leaf, P.M. Treuting, D.P. Mao, M. Dors, A. Sarkar, S.E. Warren, M.D. Wewers, and A. Aderem. 2010. Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis is an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria. Nature Immunology 11: 1136–1142.
Van Opdenbosch, N., and M. Lamkanfi. 2019. Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and disease. Immunity 50: 1352–1364.
Zhaolin, Z., L. Guohua, W. Shiyuan, and W. Zuo. 2019. Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Cell Proliferation 52: e12563.
Yin, Y., X. Li, X. Sha, H. Xi, Y.F. Li, Y. Shao, J. Mai, A. Virtue, J. Lopez-Pastrana, S. Meng, D.G. Tilley, M.A. Monroy, E.T. Choi, C.J. Thomas, X. Jiang, H. Wang, and X.F. Yang. 2015. Early hyperlipidemia promotes endothelial activation via a caspase-1-sirtuin 1 pathway. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 35: 804–816.
Xi, H., Y. Zhang, Y. Xu, W.Y. Yang, X. Jiang, X. Sha, X. Cheng, J. Wang, X. Qin, J. Yu, Y. Ji, X. Yang, and H. Wang. 2016. Caspase-1 inflammasome activation mediates homocysteine-induced pyrop-apoptosis in endothelial cells. Circulation Research 118: 1525–1539.
Zhang, Y., X. Li, A.L. Pitzer, Y. Chen, L. Wang, and P.L. Li. 2015. Coronary endothelial dysfunction induced by nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor protein with pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation during hypercholesterolemia: beyond inflammation. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 22: 1084–1096.
Sadeghi, H., A. Lockmann, A.C. Hund, U.K. Samavedam, E. Pipi, K. Vafia, et al. 2015. Caspase-1-independent IL-1 release mediates blister formation in autoantibody-induced tissue injury through modulation of endothelial adhesion molecules. Journal of Immunology 194: 3656–3663.
Wang, L., Y. Chen, X. Li, Y. Zhang, E. Gulbins, and Y. Zhang. 2016. Enhancement of endothelial permeability by free fatty acid through lysosomal cathepsin B-mediated Nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Oncotarget 7: 73229–73241.
Back, M., A.J. Yurdagul, I. Tabas, K. Oorni, and P.T. Kovanen. 2019. Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nature Reviews. Cardiology 16: 389–406.
Quarato, G., C.S. Guy, C.R. Grace, F. Llambi, A. Nourse, D.A. Rodriguez, R. Wakefield, S. Frase, T. Moldoveanu, and D.R. Green. 2016. Sequential engagement of distinct MLKL phosphatidylinositol-binding sites executes necroptosis. Molecular Cell 61: 589–601.
Dhuriya, Y.K., and D. Sharma. 2018. Necroptosis: a regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. Journal of Neuroinflammation 15: 199.
Xia, B., S. Fang, X. Chen, H. Hu, P. Chen, H. Wang, and Z. Gao. 2016. MLKL forms cation channels. Cell Research 26: 517–528.
Murphy, J.M., P.E. Czabotar, J.M. Hildebrand, I.S. Lucet, J.G. Zhang, S. Alvarez-Diaz, R. Lewis, N. Lalaoui, D. Metcalf, A.I. Webb, S.N. Young, L.N. Varghese, G.M. Tannahill, E.C. Hatchell, I.J. Majewski, T. Okamoto, R.C.J. Dobson, D.J. Hilton, J.J. Babon, N.A. Nicola, A. Strasser, J. Silke, and W.S. Alexander. 2013. The pseudokinase MLKL mediates necroptosis via a molecular switch mechanism. Immunity 39: 443–453.
Van Hoecke, L., S. Van Lint, K. Roose, A. Van Parys, P. Vandenabeele, J. Grooten, et al. 2018. Treatment with mRNA coding for the necroptosis mediator MLKL induces antitumor immunity directed against neo-epitopes. Nature Communications 9: 3417.
Zhang, S., M.B. Tang, H.Y. Luo, C.H. Shi, and Y.M. Xu. 2017. Necroptosis in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential therapeutic target. Cell Death & Disease 8: e2905.
Guo, F.X., Q. Wu, P. Li, L. Zheng, S. Ye, X.Y. Dai, C.M. Kang, J.B. Lu, B.M. Xu, Y.J. Xu, L. Xiao, Z.F. Lu, H.L. Bai, Y.W. Hu, and Q. Wang. 2019. The role of the LncRNA-FA2H-2-MLKL pathway in atherosclerosis by regulation of autophagy flux and inflammation through mTOR-dependent signaling. Cell Death and Differentiation 26: 1670–1687.
Najafov, A., A.K. Mookhtiar, H.S. Luu, A. Ordureau, H. Pan, P.P. Amin, et al. 2019. TAM kinases promote necroptosis by regulating oligomerization of MLKL. Molecular Cell 75: 457–468.e4.
Yuan, J., P. Amin, and D. Ofengeim. 2019. Necroptosis and RIPK1-mediated neuroinflammation in CNS diseases. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 20: 19–33.
Zhao, Q., X. Yu, M. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Han, X. Zhang, X.M. Li, X.X. Wu, J. Qin, J. Fang, and H. Zhang. 2019. MLKL attenuates colon inflammation and colitis-tumorigenesis via suppression of inflammatory responses. Cancer Letters 459: 100–111.
Liu, W., B. Chen, Y. Wang, C. Meng, H. Huang, X.R. Huang, J. Qin, S.R. Mulay, H.J. Anders, A. Qiu, B. Yang, G.J. Freeman, H.J. Lu, H.Y. Lin, Z.H. Zheng, H.Y. Lan, Y. Huang, and Y. Xia. 2018. RGMb protects against acute kidney injury by inhibiting tubular cell necroptosis via an MLKL-dependent mechanism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 115: E1475–E1484.
Paramel, V.G., L. Folkersen, R.J. Strawbridge, B. Halvorsen, A. Yndestad, T. Ranheim, et al. 2016. NLRP3 inflammasome expression and activation in human atherosclerosis. Journal of the American Heart Association 5.
Rayner, K.J. 2017. Cell death in the vessel wall: the good, the bad, the ugly. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 37: e75–e81.
Zhou, W., C. Chen, Z. Chen, L. Liu, J. Jiang, Z. Wu, et al. 2018. NLRP3: a novel mediator in cardiovascular disease. Journal of Immunology Research 2018: 5702103.
Lin, J., X. Shou, X. Mao, J. Dong, N. Mohabeer, K.K. Kushwaha, et al. 2013. Oxidized low density lipoprotein induced caspase-1 mediated pyroptotic cell death in macrophages: implication in lesion instability? PLoS One 8: e62148.
Usui, F., K. Shirasuna, H. Kimura, K. Tatsumi, A. Kawashima, T. Karasawa, S. Hida, J. Sagara, S’. Taniguchi, and M. Takahashi. 2012. Critical role of caspase-1 in vascular inflammation and development of atherosclerosis in Western diet-fed apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 425: 162–168.
Shi, X., W.L. Xie, W.W. Kong, D. Chen, and P. Qu. 2015. Expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome in carotid atherosclerosis. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 24: 2455–2466.
Zhang, L., L. Lu, X. Zhong, Y. Yue, Y. Hong, Y. Li, and Y. Li. 2019. Metformin reduced NLRP3 inflammasome activity in Ox-LDL stimulated macrophages through adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase and protein phosphatase 2A. European Journal of Pharmacology 852: 99–106.
Schneider, K.S., C.J. Gross, R.F. Dreier, B.S. Saller, R. Mishra, O. Gorka, et al. 2017. The inflammasome drives GSDMD-independent secondary pyroptosis and IL-1 release in the absence of caspase-1 protease activity. Cell Reports 21: 3846–3859.
Gage, J., M. Hasu, M. Thabet, and S.C. Whitman. 2012. Caspase-1 deficiency decreases atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology 28: 222–229.
Hendrikx, T., M.L. Jeurissen, P.J. van Gorp, M.J. Gijbels, S.M. Walenbergh, T. Houben, et al. 2015. Bone marrow-specific caspase-1/11 deficiency inhibits atherosclerosis development in Ldlr(−/−) mice. The FEBS Journal 282: 2327–2338.
Zheng, F., Z. Gong, S. Xing, and Q. Xing. 2014. Overexpression of caspase-1 in aorta of patients with coronary atherosclerosis. Heart, Lung & Circulation 23: 1070–1074.
Gong, Y.N., C. Guy, J.C. Crawford, and D.R. Green. 2017. Biological events and molecular signaling following MLKL activation during necroptosis. Cell Cycle 16: 1748–1760.
Karunakaran, D., M. Geoffrion, L. Wei, W. Gan, L. Richards, P. Shangari, E.M. DeKemp, R.A. Beanlands, L. Perisic, L. Maegdefessel, U. Hedin, S. Sad, L. Guo, F.D. Kolodgie, R. Virmani, T. Ruddy, and K.J. Rayner. 2016. Targeting macrophage necroptosis for therapeutic and diagnostic interventions in atherosclerosis. Science Advances 2: e1600224.
Szobi, A., E. Goncalvesova, Z.V. Varga, P. Leszek, M. Kusmierczyk, M. Hulman, et al. 2017. Analysis of necroptotic proteins in failing human hearts. Journal of Translational Medicine 15: 86.
Gutierrez, K.D., M.A. Davis, B.P. Daniels, T.M. Olsen, P. Ralli-Jain, S.W. Tait, et al. 2017. MLKL activation triggers NLRP3-mediated processing and release of IL-1beta independently of gasdermin-D. Journal of Immunology 198: 2156–2164.
Conos, S.A., K.W. Chen, D. De Nardo, H. Hara, L. Whitehead, G. Nunez, et al. 2017. Active MLKL triggers the NLRP3 inflammasome in a cell-intrinsic manner. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114: E961–E969.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (grant numbers 81871701 and 81772244), the Natural Science Fund of Guangdong (grant numbers 2020B1515020013, 2017A030313532 and 2017A030313535), and the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (grant number 201704020213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Qian Wu and Xin He designed the study, performed most part of the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript. Li-Mei Wu, Ru-Yi Zhang, and Li-Min Li performed part of the experimental procedures. Chang-Meng Wu, Yuan-Bin Lu, Bing Hu, Chao Shi, Zhi-Feng Lu, and Biao Yang contributed to data acquisition. Lei Zheng, Yan-Wei Hu, and Qian Wang provided financial support and guided the completion of the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., He, X., Wu, LM. et al. MLKL Aggravates Ox-LDL-Induced Cell Pyroptosis via Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Inflammation 43, 2222–2231 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01289-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01289-8