Abstract
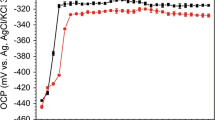
An electrochemical study of three API steels: X52, X65, and X80, exposed to seawater and sediment from seabed is presented. Two seabed samples were collected at 60 meters depth near a platform (seabed A) and at a distance of 500 m (seabed B) from the same platform of the Sonda of Campeche, México. In both samples, the seawater and sediment were separated in order to characterize their corrosiveness in an electrochemical cell of 100 mL. The physicochemical and electrochemical responses were determined in the water and sediment. Electrochemical impedance spectra and polarization curves for both water and sediment from the two seabed samples were carried out. A cathodic protection analysis for the three steel surfaces exposed to sediment was proposed based on cathodic polarization curves. Corrosion rates for the three studied low carbon steels could be attributed to their physicochemical properties and low temperatures from a specific seabed area. Thus, high susceptibility to corrosion was identified when three API steels were in contact with seabed B. A corrosive gas fixation and discharges of produced water into the seabed that are able to conduct the corrosion process were suggested. In order to study the activation energies of corrosion for the API steels exposed to sediment, a low temperature dependence was taken into account using the Arrhenius equation and Rct values from impedance data. Activation energy values were Ea = 23.06, 31.7, and 43.2 J mol–1 in X52, X80, and X65 steels, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
de Laune, R.D., Devai, I., Hou, A., and Jugsujinda, A., Soil Sediment Contam., 2008, vol. 17, pp. 98–106.
Pi, Y., Ye, Q., Jiang, H., Wang, P., et al., Geomicrobiol. J., 2009, vol. 26, pp. 227–237.
Flood, M., Frabutt, D., Floyd, D., Powers, A., et al., Environ. Technol., 2015, vol. 36, pp. 124–135.
Ye, G., Wang, S., Jiang, L., Xiao, X., et al., Geomicrobiol. J., 2009, vol. 26, pp. 370–381.
Wang, Y., Wharton, J.A., and Shenoi, R.A., Corros. Sci., 2014, vol. 86, pp. 42–60.
Tang, X., Xue, Z., Yang, Q., Li, T., et al., Drying Technol., 2017, vol. 35, pp. 1696–1710.
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Hu, Q., Huang, F., et al., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2015, vol. 62, pp. 103–108.
NRF-014-PEMEX,Inspection,Evaluation and Maintenance for Subsea Pipelines, 2013.
NRF-026-PEMEX, Protection with Anticorrosive Coatings for Buried and Submerged Pipelines, 2001.
NACE RP-0394: Application, Performance, and Quality Control of Plant-Applied Single Layer Fusion-Bonded Epoxy External Pipe Coating, Houston, TX: NACE Int., 2002.
Quej-Aké, L., Contreras, A., and Aburto, J. Materials Characterization, Pérez-Campos, R., Contreras-Cuevas, A., and Esparza-Muñoz, R., Eds., Glanz: Springer-Verlag, 2017.
Quej-Ake, L. and Contreras, A., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2018, vol. 65, pp. 97–106.
Ribeiro, A.P., Graciano, A.M., dos Santos, J.O., de Lima, P.A., et al., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2014, vol. 25, pp. 476–479.
Mills, G. and Fones, G., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2012, vol. 32, pp. 17–28.
Wang, D. and Abriak, N.E., Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol., 2015, vol. 33, pp. 419–428.
González-Lozano, M.C., Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C., Maeda-Martínez, A.M., Murugan, G., et al., J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng., 2010, vol. 45, pp. 121–127.
Örnek, D., Wood, T.K., Hsu, C.H., and Mansfeld, F., Corros. Sci., 2002, vol. 44, pp. 2291–2301.
Beech, I.B. and Campbell, S.A., Electrochim. Acta, 2008, vol. 54, pp. 14–21.
ASTM D1141-98, Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2013.
Sosa, E., Alamilla, J.L., Contreras, A., and Liu, H.B., Mexican Copyright no. 03-2015-120212493500-01, 2015.
Liu, H.B., Sosa, E., Alamilla, J.L., Contreras, A., and Quej-Ake, L.M., Mexican Copyright no. 03-2015-112512110000-01, 2015.
Quej-Ake, L.M., Marín Cruz, J., and Contreras, A., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2017, vol. 64, pp. 61–68.
ASTM E92, Standard Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2017.
ASTM E8/E8M, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2016.
Wang, J.Q., Atrens, A., Cousens, D.R., and Kinaev, N., J. Mater. Sci., 1999, vol. 34, pp. 1721–1728.
ASTM G51-95, Standard Test Method for Measuring pH of Soil for Use in Corrosion Testing, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2000.
ASTM G 200-09, Standard Test Method for Measurement of Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) of Soil, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2014.
ASTM D4959, Standard Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil by Directs Heating, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2007.
Boukamp, B.A., Equivalent Circuit: (equivcrt.pas). Users Manual, Enschede: Univ. of Twente, 1989, 2nd ed.
Quej-Ake, L.M., Cabrera-Sierra, R., Arce-Estrada, E.M., and Marín-Cruz, J., Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013, vol. 8, pp. 924–937
NOM-007-SECRE, Natural Gas Transportation, 2010.
ISO 15589-2, Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries-Cathodic Protection of Pipeline Transportation Systems, Part 2: Offshore Pipelines, Geneva: Int. Stand. Org., 2012.
ASTM G102-89, Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electro-Chemical Measurements, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM Int., 2004.
NRF-013-PEMEX, Design of Subsea Lines from Gulf of Mexico, 2009.
de Oliveira Júnior, S. and Van Hombeek, M., Energy Convers. Manage., 1997, vol. 38, pp. 1577–1584.
da Silva, J.A.M. and de Oliveira Jr., S., Energy, 2018, vol. 147, pp. 757–766.
Schifter, I., González-Macías, C., Salazar-Coria, L., Sánchez-Reyna, G., et al., Environ. Earth Sci., 2015, vol. 74, pp. 5813–5826.
Quej-Ake, L. and Contreras, A., Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., 2015, vol. 1766, pp. 415–426.
Quej-Ake, L., Mireles, M., Galván-Martinez, R., and Contreras, A., Materials Characterization, Pérez-Campos, R., Contreras-Cuevas, A., and Esparza-Muñoz, R., Eds. Glanz: Springer-Verlag, 2015, pp. 101–116.
Buljac, M., Bogner, D., Bralić, M., Periš, N., et al., Anal. Lett., 2014, vol. 47, pp. 1952–1964.
Rosliza, R., Senin, H.B., and Wan-Nik, W.B., Colloids Surf., A, 2008, vol. 312, pp. 185–189.
Vera, R., Verdugo, P., Orellana, M., and Muñoz, E., Corros. Sci., 2010, vol. 52, pp. 3803–3810.
Schifter, I., González-Macías, C., Salazar-Coria, L., Sánchez-Reyna, G., et al., Environ. Monit. Assess., 2015, vol. 187, pp. 699–723.
Bard, A.J. and Faulkner, L.R., Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, New York: Wiley, 1980.
NACE standard TM0497, Measurement Techniques Related to Criteria for Cathodic Protection on Underground or Submerged Metallic Piping Systems, Houston, TX: NACE Int., 2002.
Popova, A., Sokolova, E., Raicheva, S., and Christov, M., Corros. Sci., 2003, vol. 45, pp. 33–58.
Bentiss, F., Traisnel, M., Chaibi, N., Mernari, B., et al., Corros. Sci., 2002, vol. 44, pp. 2271–2289.
Rehim, S.S.A.E., Hassan, H.H., and Amin, M.A., Corros. Sci., vol. 46, pp. 5–25.
Karakus, M., Sahin, M., and Bilgic, S., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2005, vol. 92, pp. 565–571.
Negm, N.A., Al Sabagh, A.M., Migahed, M.A., Abdel Bary, H.M., et al., Corros. Sci., 2010, vol. 52, pp. 2122–2132.
Kairi, N.I. and Kassim, J., Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013, vol. 8, pp. 7138–7155.
Zdunek, A.D., Barlo, T.J., and Warfield, G., Mater. Perform., 1992, vol. 31, pp. 22–27.
Stansbury, E.E. and Buchanan, R.A., Fundamentals of Electrochemical Corrosion, Materials Park, OH: ASM Int., 2000.
Orazem, M.E. and Tribollet, B., Electrochem. Impedance Spectroscopy, New York: Wiley, 2008.
Macdonald, J.R., Impedance Spectroscopy, New York, Wiley, 1987.
Quej-Ake, L.M., Contreras, A., Liu, H.B., Alamilla, J.L., and Sosa, E., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2019, vol. 66, pp. 101–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Quej Ake, L.M., Liu, H.B., Alamilla, J. et al. Electrochemical Study of External Corrosion of Three API Steels Exposed to Seawater and Sediment from Seabed of the Gulf of México. Surf. Engin. Appl.Electrochem. 56, 365–380 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375520030126
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375520030126