Abstract
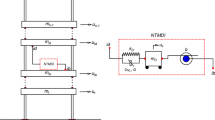
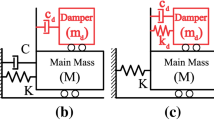
The current work describes the optimum design of a tuned mass damper inerter (TMDI) to control a benchmark 10-story base-excited linear shear building under seismic excitations. Mass and inertance ratios are preselected, and optimum free vibration parameters of the TMDI (i.e., natural frequency and damping ratios) are calculated for single degree-of-freedom (SDOF) and multi degree-of-freedom (MDOF) models with different configurations of single and double inerter TMDIs at different locations using the colliding bodies optimization technique. Four different inherent damping values are considered for each analysis. Minimizing the \(H_{\mathrm{\infty }}\) norm of the roof displacement transfer function is considered as the objective function for robust control of the building. Additionally, the optimum designed damper performance and its robustness is assessed in both the frequency and time domains. Results show that while being robust, the SDOF-based optimized TMDI approach should be used with caution and it is recommended to optimize and employ the TMDI using the MDOF model. Results indicate the superior performance of the proposed well-tuned damper with proper configuration in comparison to a same weight/mass classical TMD.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soong, T.T.: Active Structural Control Theory and Practice, 1st edn. Wiley, New York (1990)
Sun, J.Q., Jolly, M.R., Norris, M.A.: Passive, adaptive and active tuned vibration absorbers—a survey. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME 117, 234–242 (1995)
Tributsch, A., Adam, C.: Evaluation and analytical approximation of tuned mass damper performance in an earthquake environment. Smart Struct. Syst. 10(2), 155–179 (2012). https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2012.10.2.155
Gutierrez Soto, M., Adeli, H.: Tuned mass dampers. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 20(4), 419–431 (2013)
Den Hartog, J.P.: Mechanical Vibrations, 4th edn. Dover Publications, New York (1956)
Ruiz, R., Taflanidis, A.A., Giaralis, A., Lopez-Garcia, D.: Risk-informed optimization of the tuned mass-damper–inerter (TMDI) for the seismic protection of multi-storey building structures. Eng. Struct. 177, 836–850 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.08.074
Marian, L., Giaralis, A.: Optimal design of a novel tuned mass-damper–inerter (TMDI) passive vibration control configuration for stochastically support-excited structural systems. Probab. Eng. Mech. 38, 156–164 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.probengmech.2014.03.007
Elias, S., Matsagar, V.: Research developments in vibration control of structures using passive tuned mass dampers. Annu. Rev. Control 44, 129–156 (2017)
Bekdaş, G., Nigdeli, S.M., Yang, X.-S.: A novel bat algorithm based optimum tuning of mass dampers for improving the seismic safety of structures. Eng. Struct. 159, 89–98 (2018)
Bekdaş, G., Nigdeli, S.M.: Metaheuristic based optimization of tuned mass dampers under earthquake excitation by considering soil–structure interaction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 92, 443–461 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.10.019
Salvi, J., Rizzi, E.: Closed-form optimum tuning formulas for passive tuned mass dampers under benchmark excitations. Smart Struct. Syst. 17(2), 231–256 (2016)
Leung, A.Y.T., Zhang, H., Cheng, C.C., Lee, Y.Y.: Particle swarm optimization of TMD by non-stationary base excitation during earthquake. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 37(9), 1223–1246 (2008)
Matta, E.: Performance of tuned mass dampers against near-field earthquakes. Struct Eng. Mech. 39(5), 621–642 (2011). https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2011.39.5.621
Di Matteo, A., Furtmüller, T., Adam, C., Pirrotta, A.: Optimal design of tuned liquid column dampers for seismic response control of base-isolated structures. Acta Mech. 229(2), 437–454 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-1980-7
De Angelis, M., Perno, S., Reggio, A.: Dynamic response and optimal design of structures with large mass ratio TMD. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 41(1), 41–60 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.1117
Smith, M.C.: Synthesis of mechanical networks: the inerter. In: 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, pp. 1657–1662 (2002)
Siami, A., Karimi, H.R., Cigada, A., Zappa, E., Sabbioni, E.: Parameter optimization of an inerter-based isolator for passive vibration control of Michelangelo’s Rondanini Pietà. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 98, 667–683 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.05.030
Marian, L., Giaralis, A.: Optimal design of inerter devices combined with TMDs for vibration control of buildings exposed to stochastic seismic excitations. In: 11th International Conference on Structural Safety and Reliability, ICOSSAR 2013, New York, pp. 1025–1032 (2013)
Marian, L., Giaralis, A.: The tuned mass-damper–inerter for harmonic vibrations suppression, attached mass reduction, and energy harvesting. Smart Struct. Syst. 19(6), 665–678 (2017). https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2017.19.6.665
Lazar, I.F., Neild, S.A., Wagg, D.J.: Using an inerter-based device for structural vibration suppression. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 43(8), 1129–1147 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.2390
Ikago, K., Saito, K., Inoue, N.: Seismic control of single-degree-of-freedom structure using tuned viscous mass damper. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 41(3), 453–474 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.1138
De Domenico, D., Ricciardi, G.: Improving the dynamic performance of base-isolated structures via tuned mass damper and inerter devices: a comparative study. Struct. Control Health Monit. 25(10), e2234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2234
De Domenico, D., Deastra, P., Ricciardi, G., Sims, N.D., Wagg, D.J.: Novel fluid inerter based tuned mass dampers for optimised structural control of base-isolated buildings. J. Frankl. Inst. 356, 7626–7649 (2018)
Di Matteo, A., Masnata, C., Pirrotta, A.: Simplified analytical solution for the optimal design of tuned mass damper inerter for base isolated structures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 134, 106337 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106337
Masnata, C., Matteo, A.D., Adam, C., Pirrotta, A.J.M.R.C.: Smart structures through nontraditional design of tuned mass damper inerter for higher control of base isolated systems. Mech. Res. Commun. 105, 103513 (2020)
Masri, S.F., Caffrey, J.P., Li, H.: Transient response of MDOF systems with inerters to nonstationary stochastic excitation. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037551
Giaralis, A., Taflanidis, A.A.: Optimal tuned mass-damper–inerter (TMDI) design for seismically excited MDOF structures with model uncertainties based on reliability criteria. Struct. Control Health Monit. 25(2), e2082 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2082
Ziegler, F.: Mechanics of Solids and Fluids, Corrected reprint of the 2 edn. Springer, New York (1998)
Debnath, N., Deb, S.K., Dutta, A.: Frequency band-wise passive control of linear time invariant structural systems with \(H_{\infty }\) optimization. J. Sound Vib. 332(23), 6044–6062 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2013.06.018
Asami, T., Nishihara, O., Baz, A.M.: Analytical solutions to \(H_{\infty }\) and \(H_2\) optimization of dynamic vibration absorbers attached to damped linear systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 124(2), 284–295 (2002)
Sadek, F., Mohraz, B., Taylor, A.W., Chung, R.M.: A method of estimating the parameters of tuned mass dampers for seismic applications. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 26(6), 617–635 (1998)
Kaveh, A., Mahdavi, V.R.: Colliding bodies optimization: a novel meta-heuristic method. Comput. Struct. 139, 18–27 (2014)
Fahimi Farzam, M., Kaveh, A.: Optimum design of tuned mass dampers using colliding bodies optimization in frequency domain. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-019-00296-6
Kaveh, A.: Applications of Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms in Civil Engineering. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, Cham (2017)
Kaveh, A.: Advances in Metaheuristic Algorithms for Optimal Design of Structures, 2nd edn. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, Cham (2017)
Hadi, M.N.S., Arfiadi, Y.: Optimum design of absorber for MDOF structures. J. Struct. Eng. (ASCE) 124(11), 1272–1279 (1998)
Bekdaş, G., Nigdeli, S.M.: Estimating optimum parameters of tuned mass dampers using harmony search. Eng. Struct. 33(9), 2716–2723 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.05.024
Nigdeli, S.M., Bekdaş, G.: Optimum tuned mass damper design in frequency domain for structures. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 21(3), 912–922 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0829-2
Khatibinia, M., Gholami, H., Kamgar, R.: Optimal design of tuned mass dampers subjected to continuous stationary critical excitation. Intl. J. Dyn. Control 6(3), 1094–1104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-017-0386-7
Spencer Jr, B.F., Christenson, R.E., Dyke, S.J.: Next generation benchmark control problem for seismically excited buildings. In: Proceedings of the Second World Conference on Structural Control 1998, pp. 1135–1360. Kyoto
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaveh, A., Fahimi Farzam, M., Hojat Jalali, H. et al. Robust optimum design of a tuned mass damper inerter. Acta Mech 231, 3871–3896 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02720-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02720-9