Abstract
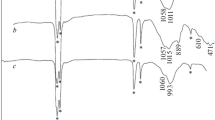
The study describes direct precipitation, original template, and additional thermal reduction methods for the synthesis of materials based on cobalt oxides and their composites, promising as magnetic sorbents for the selective extraction and preconcentration of uranium(VI) from aqueous media. The thermal decomposition of intermediates and the phase formation of final materials were studied by differential thermal analysis and powder X-ray diffraction. The surface morphology and structure of the obtained sorbent samples were investigated. The sorption activity and capacity of the materials were estimated in relation to the extraction of uranyl ions from aqueous solutions over a broad pH range (2–10), in particular, in the presence of carbonate ions (0.001, 0.01, 0.1, and 1 mg/L). It was found that quantitative sorption of uranium(VI) is dictated, to a higher extent, by the composition of the sorbent solid phase containing metallic cobalt. A set of magnetic measurements were carried out and magnetic characteristics of sorption materials were determined. The saturation magnetization for reduced sorbents can reach 133–237 emu/g, which is an additional benefit for their separation from solutions after treatment by magnetic separation techniques.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. B. Singh, G. Nagpal, S. Agrawal, et al., Environ. Technol. Innov. 11, 87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.006
R. D. Ambashta and M. Sillanpää, J. Hazard. Mater. 180, 38 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.105
P. D. Bhalara, D. Punetha, and K. Balasubramanian, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 1621 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.06.007
T. Missana, M. Garcia-Gutierrez, and C. Maffiotte, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 260, 291 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(02)00246-1
X. Shuibo, Z. Chun, Z. Xinghuo, et al., J. Environ. Radioact. 100, 162 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.09.008
C. Jing, Y. L. Li, and S. Landsberger, J. Environ. Radioact. 164, 65 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.06.027
P. Zong, S. Wang, Y. Zhao, et al., Chem. Eng. J. 220, 45 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.038
N. A. Palchik, L. I. Razvorotneva, T. N. Moroz, et al., Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 64, 308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602361903015X
O. Riba, T. B. Scott, K. Vala Ragnarsdottir, et al., Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 72, 4047 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.041
E. K. Papynov, A. S. Portnyagin, A. I. Cherednichenko, et al., Dokl. Phys. Chem. 468, 67 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S001250161605002X
E. K. Papynov, I. A. Tkachenko, V. Y. Maiorov, et al., Radiochemistry 61, 28 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1066362219010053
H. Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, Z. Ayazi, and S. Hosseinzadeh, Microchem. J. 153, 104268 (2020).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104268
J. Zolgharnein, K. Dalvand, M. Rastgordani, et al., J. Alloys Compd. 725, 1006 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.07.228
J. Bin Chung and J. S. Chung, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60, 1515 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.11.002
F. Nekouei, S. Nekouei, I. Tyagi, et al., J. Mol. Liq. 201, 124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.09.027
Y. S. Haiduk, A. A. Savitsky, A. A. Khort, et al., Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 64, 717 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602361906007X
H. H. Wang, X. R. Li, G. Q. Fei, et al., Express Polym. Lett. 4, 670 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2010.82
E. K. Papynov, V. Y. Mayorov, M. S. Palamarchuk, et al., J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 68, 374 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3039-0
A. I. Busev, V. G. Tiptsova, and V. M. Ivanov, Manual on Analytical Chemistry of Rare Earths (Khimiya, Moscow, 1978) [in Russian].
R. J. Wu, J. G. Wu, T. K. Tsai, et al., Sensors Actuat. 120, 104 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2006.01.053
D. Zhao, X. Wang, S. Yang, et al., J. Environ. Radioact. 103, 20 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2011.08.010
R. A. Crane, M. Dickinson, I. C. Popescu, et al., Water Res. 45, 2931 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.012
T. B. Scott, G. C. Allen, P. J. Heard, et al., Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 461, 1247 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2004.1441
R. A. Crane and T. B. Scott, J. Hazard. Mater. 211–212, 112 (2012 )https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.073
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The study was carried out using research equipment of Shimadzu with the support of Genzo Shimadzu scholarship and equipment of the Center for Collective Use “Far Eastern Center of Structural Studies” (Institute of Chemistry, Far East Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences) and the interdisciplinary Center for Collective Use in the Field of Nanotechnologies and New Functional Materials (Far Eastern Federal University, Vladivostok, Russia).
Funding
Experimental work on the reduction synthesis and study of the physicochemical characteristics of magnetic sorbents was performed within State Assignment of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation 4.8063.2017/BCh. The evaluation of the sorption properties was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-33-00066 mol_a).
The experimental work on the precipitation synthesis and measurement and analysis of the magnetic properties of the developed materials was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 19-72-20071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by Z. Svitanko
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papynov, E.K., Dran’kov, A.N., Tkachenko, I.A. et al. Synthesis and Sorption Characteristics of Magnetic Materials Based on Cobalt Oxides and Their Reduced Forms. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 65, 820–828 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023620060157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023620060157