Abstract
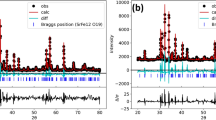
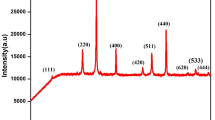
Ni0.7 – xZn0.3MxFe2O4 (M = Mn2+, Co2+, and Cu2+; x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, and 0.7) spinel-type ferrite were fabricated through citrate technique. The X-ray diffraction analysis disclosed the creation of the cubic phase spinel structure in all prepared samples, except for the high concentration of Mn (x = 0.7). As the concentration of dopant ions increased, the structural parameters, such as lattice constant, particle size, X‑ray density, bulk density, and percentage porosity showed interesting changes. The experimental lattice parameter was found in the range from 0.839 to 0.843 nm for the three investigated series. The average particle size ranged from 52 to 107 nm. The density decreased with the addition of Mn and Co, while it improved considerably with the increment of Cu content. Besides, the percentage porosity for Ni–Zn–Cu ferrite was lower than those for the Ni–Zn–Mn and Ni–Zn–Co ferrite series. Several magnetic properties were studied at room temperature. Magnetization curves were measured in the range of magnetizing field up to 6000 A m–1. The magnetization was studied at a constant magnetic field (4500 A m–1) and it was found to rise with Mn2+ ions content up to x = 0.3 followed by a subsequent decline at x = 0.5. Furthermore, a monotonic decrease in the magnetization was observed by the incorporation of Co into Ni–Zn ferrite, while an increase was noticed for Cu-substituted samples. Among the three investigated series, the Ni–Zn–Cu ferrite series exhibited the highest magnetization, making it appropriate for high-density recording media. The initial permeability (μi) was studied as a function of temperature for all samples. The Curie temperature TC was estimated from the μi(T) plot and was determined to decrease with the upsurge in the content of substitute ions (Mn2+, Co2+, and Cu2+).













Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Hashim, S. Alimuddin, S. E. Kumar, S. Ali, B. H. Koo, H. Chung, and R. Kumar, J. Alloys. Compd. 511, 107 (2012).
A. M. M. Farea, S. Kumar, K. M. Batoo, A. Yousef, C. G. Lee, and S. Alimuddin, J. Alloys Compd. 469, 451 (2009).
K. M. Batoo, S. Kumar, and C. G. Lee, J. Alloys Compd. 480, 596 (2009).
D. Ravinder and K. Latha, Mater. Lett. 41, 247 (1999).
J. Smit and H. P. J. Wijn, Ferrites (Philips Technical Library, Eindhoven, 1959), p. 73.
M. Sertkol, Y. Koseoglu, A. Baykal, H. Kavas, A. Bozkurt, and M. S. Toprak, J. Alloys Compd. 486, 325 (2009).
S. E. Shirsath, B. G. Toksha, R. H. Kadam, S. M. Patange, D. R. Mane, G. S. Jangam, and A. Ghasemi, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 1669 (2010).
B. P. Rao and K. H. Rao, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 6049 (1997).
A. M. Wahba, N. A. Ali, and M. M. Eltabey, Mater. Chem. Phys. 146, 224 (2014).
S. A. Mazen and N. I. Abu-Elsaad, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 265 (2010).
S. A. Mazen, A. H. Wafik, and S. F. Mansour, J. Mater. Sci. 31, 2661 (1996).
K. Pubby, S. S. Meena, S. M. Yusuf, and S. B. Narang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 430 (2018).
S. A. Mazen, M. H. Abdalla, R. L. Nakhla, H. M. Zaki, and F. Metawe, J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 34, 35 (1993).
T. R. Tatarchuk, N. D. Paliychuk, M. Bououdina, B. Al-Najar, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, and A. Shyichuk, J. Alloys Compd. 731, 1256 (2018).
B. D. Cullity, in Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1959), Vol. 99.
S. Torkian, A. Ghasemi, and R. S. Razavi, Ceram. Int. 43, 6987 (2017).
A. Rais, K. Taibi, A. Addou, A. Zanoun, and Y. Al-Douri, Ceram. Int. 40, 14413 (2014).
K. J. Standley, in Oxide Magnetic Materials (Clarendon, Oxford, 1972).
S. Sagadevan, I. Das, and J. Podder, R. T. Mater. Sci. Appl. 189, 145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44890-9_14
A. C. F. M. Costa, E. Tortella, M. R. Morelli, and R. H. G. A. Kiminami, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256, 174 (2003).
M. C. Dimri, A. Verma, S. C. Kashyap, D. C. Dube, O. P. Thakur, and C. Prakash, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 133, 42 (2006).
E. Rezlescu, L. Sachelarie, P. D. Popa, and N. Rezlescu, IEEE Trans. Magn. 36, 3962 (2000).
M. Li, X. Liu, T. Xu, Y. Nie, H. Li, and C. Zhang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 439, 228 (2017).
S. Ghosh, P. Ayyub, N. Kumar, S. A. Khan, and D. Banerjee, Phys. Res. 77, 510 (2003).
S. A. Mazen and N. I. Abu-Elsaad, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3366 (2012).
A. P. G. Rodrigues, D. K. S. Gomes, J. H. Araujo, D. M. A. Melo, N. A. S. Oliveira, and R. M. Braga, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 748 (2015).
A. V. Humbe, A. C. Nawle, A. B. Shinde, and K. M. Jadhav, J. Alloys Compd. 691, 343 (2017).
A. M. Shaikh, S. C. Watawe, S. S. Bellad, S. A. Jadhav, and B. K. Chougule, Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, 46 (2000).
A. Globus, in Proceedings of Cardiff Conference, USA,1975.
R. Islam, M. A. Hakim, M. O. Rahman, H. N. Das, and M. A. Mamun, J. Alloys Compd. 559, 174 (2013).
S. C. Watawe, B. D. Sarwade, S. S. Bellad, B. D. Sutar, and B. K. Chaugule, Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, 173 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors confirm that they have conflicts of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazen, S., Abu-Elsaad, N.I. & Nawara, A.S. The Influence of Various Divalent Metal Ions (Mn2+, Co2+, and Cu2+) Substitution on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of Nickel–Zinc Spinel Ferrite. Phys. Solid State 62, 1183–1194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378342007015X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378342007015X