Abstract
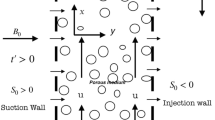
The purpose of this paper is to understand the capability and consistency of large eddy simulation (LES) in Eulerian–Lagrangian studies aimed at predicting inertial particle dispersion in turbulent wall-bounded flows, in the absence of ad hoc closure models in the Lagrangian equations of particle motion. The degree of improvement granted by LES models is object of debate, in terms of both accurate prediction of particle accumulation and local particle segregation; therefore, we assessed the accuracy in the prediction of the particle velocity statistics by comparison against direct numerical simulation (DNS) of a finer computational mesh, under both one-way and two-way coupling regimes. We performed DNS and LES at friction Reynolds number \(\hbox {Re}_{\tau }=180\) in smooth and rough channels, tracking particles with different inertia, with the aim to conduct a parametric study that examines the accuracy of particle statistics obtained from LES computations. The issue has been widely analysed in turbulent flow bounded by smooth walls, whereas the effect of rough boundaries on momentum coupled two-phase flows has been much less investigated until now. The action of the roughness of the wall is studied in terms of both turbulence modification and particle interaction with the wall surface due to particle rebounding off the solid boundary, without the introduction of a virtual rebound model. Results show that resolved LES adequately predicts particle-induced changes in both fluid and particle statistics in rough channels, at least for the range of parameters considered here.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaton, J.K., Fessler, J.R.: Preferential concentration of particles by turbulence. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 20(1), 169–209 (1994)
Kaftori, D., Hetsroni, G., Banerjee, S.: Particle behaviour in the turbulent boundary layer I. Motion, deposition and entrainment. Phys. Fluids 7(5), 1095–1106 (1995)
Rouson, D.W.I., Eaton, J.K.: On the preferential concentration of solid particles in turbulent channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 428, 149–169 (2001)
Marchioli, C., Soldati, A.: Mechanisms for particle transfer and segregation in a turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 468, 283–315 (2002)
Bec, J., Biferale, L., Cencini, M., Lanotte, A., Musacchio, S., Toschi, F.: Heavy particle concentration in turbulence at dissipative and inertial scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 085402 (2007)
Maxey, M.R., Riley, J.J.: Equation of motion for a small rigid sphere in a nonuniform flow. Phys. Fluids 26, 883–889 (1983)
Balachandar, S., Eaton, J.K.: Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 42, 111–133 (2001)
Pope, S.B.: Turbulent Flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Sagaut, P.: Large Eddy Simulation for Incompressible Flows. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Zang, Y., Street, R.L., Koseff, J.R.: A dynamic mixed subgride-scale model and its application to turbulent recirculating flows. Phys. Fluids 12, 3186–3196 (1993)
Armenio, V., Piomelli, U., Fiorotto, V.: Effect of the subgrid scales on particle motion. Phys. Fluids 11, 3030–3042 (1999)
Yamamoto, Y., Potthoff, M., Tanaka, T., Kajishima, T., Tsuji, Y.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent gas-particle flow in a vertical channel: effect of considering inter-particle collisions. J. Fluid Mech. 442, 303–334 (2001)
Pozorsky J., Apte S. V., Raman V.: Filtered particle tracking for dispersed two-phase turbulent flow. In: Proceedings of the Summer Program Summer Program, Center for Turbulence Research (2004)
Shotorban, B., Mashayek, F.: Modeling subgrid-scale effect on particles byfapproximate deconvolution. Phys. Fluids 17, 08701 (2005)
Fede, P., Simonin, O.: Numerical study of the subgrid fluid turbulence effects on the statistics of heavy colliding particles. Phys. Fluids 18, 045103 (2006)
Kuerten, J.G.M., Vreman, A.W.: Can turbophoresis be predicted by large-eddy simulation? Phys. Fluids 17, 011701 (2005)
Kuerten, J.G.M.: Subgrid modeling in particle-laden channel flow. Phys. Fluids 18, 025108 (2006)
Marchioli, C., Salvetti, M.V., Soldati, A.: Appraisal of energy recovering sub-grid scale models for large-eddy simulation of turbulent dispersed flows. Acta Mech. 201, 277–296 (2008)
Bianco, F., Chibbaro, S., Marchioli, C., Salvetti, M.V., Soldati, A.: Intrinsic filtering errors of Lagrangian particle tracking in LES flow fields. Phys. Fluids 24, 045103 (2012)
Geurts, B.J., Kuerten, J.G.M.: Ideal stochastic forcing for the motion of particles in large-eddy simulation extracted from direct numerical simulation of turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 24, 081702 (2012)
Marchioli, C., Salvetti, M.V., Soldati, A.: Some issues concerning large-eddy simulation of inertial particle dispersion in turbulent bounded flows. Phys. Fluids 20, 040603 (2008)
Pozorski, J.: Models of turbulent flows and particle dynamics, In: Minier, J.P. ,Pozorski, J. (eds.) Particles in Wall-Bounded Turbulent Flows: Deposition, Resuspension and Agglomeration. CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences, vol. 571, Springer, Wien, pp. 97–120 (2017)
Khan, M.A.I., Luo, X.Y., Nicolleau, F.C.G.A., Tucker, P.G., LoIacono, G.: Effects of LES sub-grid flow structure on particle deposition in a plane channel with a ribbed wall. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 26, 995–1015 (2010)
Ray, B., Collins, L.R.: A subgrid model for clustering of high-inertia particles in large-eddy simulations of turbulence. J. Turbul. 15, 366–385 (2014)
Pozorski, J., Apte, S.V.: Filtered particle tracking in isotropic turbulence and stochastic modeling of subgrid-scale dispersion. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 35, 118–128 (2009)
Vinkovic, I., Aguirre, C., Simoens, S.: Large-eddy simulation and Lagrangian stochastic modeling of passive scalar dispersion in a turbulent boundary layer. J. Turbul 7, 1–14 (2006)
Kuerten, J.G.M.: Point-particle DNS and LES of particle-laden turbulent flow. A state-of-the-art review. Flow Turbul. Combust. 97, 689–713 (2016)
Marchioli, C.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent dispersed flows: a review of modelling approaches. Acta Mech. 228, 741–771 (2017)
Gualtieri, P., Casciola, C.M., Benzi, R., Piva, R.: Preservation of statistical properties in large-eddy simulation of shear turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 592, 471–494 (2007)
Le Ribault, C., Simoens, S., Vinkovic, I.: Hybrid large eddy simulation/Lagarangian stochastic model for turbulent passive and reactive scalar dispersion in a plane jet. Chem. Eng. Commun. 199, 435–460 (2012)
Kenjeres, S.: On recent progress in modelling and simulations of multi-scale transfer of mass, momentum and particles in bio-medical applications. Flow Turbul. Combust. 96, 837–860 (2016)
Balachandar, S.: A scaling analysis for point-particle approaches to turbulent multiphase flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 35, 801–810 (2009)
Mallouppas, G., vanWachem, B.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent particle-laden channel flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 54, 65–75 (2013)
Dritselis, C.D., Vlachos, N.S.: Large eddy simulation of gas-particle turbulent channel flow with momentum exchange between the phases. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 37, 706–721 (2011)
Marchioli, C., Armenio, V., Salvetti, M.V., Soldati, A.: Mechanisms for deposition and resuspension of heavy particles in turbulent flow over wavy interfaces. Phys. Fluids 18, 025102 (2006)
Vance, M.W., Squires, K.D., Simonin, O.: Properties of the particle velocity field in gas-solid turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 18, 063302 (2006)
Uijttewaal, W.S.J., Oliemans, R.V.A.: Particle dispersion and deposition in direct numerical and large eddy simulation of vertical pipe flows. Phys. Fluids 8, 2590–2604 (1996)
Wang, Q., Squires, K.: Large eddy simulation of particle-laden turbulent channel flows. Phys. Fluids 8, 1207–1223 (1996)
Volino, R.J., Schultz, M.P., Flack, K.A.: Turbulence structure in boundary layers over periodic two- and three-dimensional roughness. J. Fluid Mech. 676, 172–190 (2011)
Hong, J., Katz, J., Schultz, M.P.: Near-wall turbulence statistics and flow structures over three-dimensional roughness in a turbulent channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 667, 1–37 (2011)
De Marchis, M., Napoli, E.: Effects of irregular two-dimensional and three-dimensional surface roughness in turbulent channel flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 36, 7–17 (2012)
Milici, B., De Marchis, M., Sardina, G., Napoli, E.: Effects of roughness on particle dynamics in turbulent channel flows: a DNS analysis. J. Fluid Mech. 739, 465–478 (2014)
Konan, N.A., Kannengieiser, O., Simonin, O.: Stochastic modeling of the multiple rebound effects for particle-rough wall collisions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 35(10), 933–945 (2009)
Sommerfeld, M., Kussin, J.: Wall roughness effects on pneumatic conveying of spherical particles in a narrow horizontal channel. Powder Technol. 142(2–3), 180–192 (2004)
Chang, Y., Scotti, A.: Entrainment and suspension of sediments into a turbulent flow over ripples. J. Turbul. 4(1), 1–19 (2003)
De Angelis, V., Lombardi, P., Banerjee, S.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent flow over a wavy wall. Phys. Fluids 9, 2429–2442 (1997)
Marchioli, C., Armenio, V., Soldati, A.: Simple and accurate scheme for fluid velocity interpolation for Eulerian–Lagrangian computation of dispersed flows in 3D curvilinear grids. Comput. Fluids 36(7), 1187–1198 (2007)
Vreman, A.W.: Turbulence attenuation in particle-laden flow in smooth and rough channels. J. Fluid Mech. 773, 103–136 (2015)
Sommerfeld, M., Huber, N.: Experimental analysis and modelling of particle-wall collisions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 25(6–7), 1457–1489 (1999)
Squires, K., Simonin, O.: LES-DPS of the effect of wall roughness on dispersed-phase transport in particle-laden turbulent channel flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 27(4), 619–626 (2006)
Elghobashi, S., Truesdell, G.C.: On the two-way interaction between homogeneous turbulence and dispersed solid particles. I: Turbulence modification. Phys. Fluids A 5(7), 1790–1801 (1993)
Horwitz, J.A.K., Mani, A.: Accurate calculation of Stokes drag for point-particle tracking on two-way coupled flows. J. Comput. Phys. 318, 85–109 (2016)
Battista, F., Gualtieri, P., Mollicone, J.P., Casciola, C.M.: Application of the Exact Regularixed Point Particle method (ERPP) to particle laden turbulent shear flows in the two-way coupling regime. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 101, 113–124 (2018)
Lilly, D.K.: A proposed modification of the germano subgrid-scale closure method. Phys. Fluids A 4, 633–635 (1992)
Elghobashi, S., Truesdell, G.C.: Direct simulation of particle dispersion in a decaying isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 242, 655–700 (1992)
Soltani, M., Ahmadi, G.: Direct numerical simulation of particle entrainment in turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 7, 647–657 (1995)
Arcen, B., Taniere, A., Oesterlé, B.: On the influence of near-wall forces in particle-laden channel flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 32, 1326–1339 (2006)
De Marchis, M., Milici, B., Napoli, E.: Solid sediment transport in turbulent channel flow over irregular rough boundaries. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 65, 114–126 (2017)
Armenio, V., Fiorotto, V.: The importance of the forces acting on particles in turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 13(8), 2437 (2001)
Schiller, H., Naumann, A.: Uber die grundlegenden Berechnungen bei der Schwerkraftaufbereitung. Z. Ver. Deut. Ing. 77, 318–320 (1935)
Crowe, C.T., Sharma, M.P., Stock, D.E.: The particle-source-in cell (PSI-CELL) model for gas-droplet flows. J. Fluids Eng. 99, 325–332 (1977)
Dritselis, C.D., Vlachos, N.S.: Numerical investigation of momentum exchange between particles and coherent structures in low Re turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 23, 025103 (2011)
Vreman, A.W.: Particle-resolved direct numerical simulation of homogeneous isotropic turbulence modified by small fixed spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 796, 40–85 (2016)
Eaton, J.K.: Two-way coupled turbulence simulations of gas-particle flows using point-particle tracking. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 35, 792–800 (2009)
Gualtieri, P., Picano, F., Sardina, G., Casciola, C.M.: Exact regularized point particle method for multi-phase flows in the two-way coupling regime. J. Fluid Mech. 773, 520–561 (2015)
Breuer, M., Alletto, M.F.: Efficient simulation of particle-laden turbulent flows with high mass loadings using LES. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 35, 2–12 (2012)
Alletto, M., Breuer, M.: One-way, two-way and four-way coupled LES predictions of a particle-laden turbulent flow at high mass loading downstream of a confined bluff body. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 45, 70–90 (2012)
Yuu, S., Ueno, T., Umekage, T.: Numerical simulation of the high Reynolds number slit nozzle gas-particle jet using subgrid-scale coupling large eddy simulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 56, 4293–4307 (2002)
Squires, K., Eaton, J.K.: Particle response and turbulence modification in isotropic turbulence. Phys. Fluids A 2(7), 1191–1203 (1990)
Crowe, C.T., Troutt, T.R., Chung, J.N.: Numerical models for two-phase turbulent flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 28, 11–43 (1996)
Maxey, M.R., Patel, B.K., Wang, L.P.: Simulations of dispersed turbulent multiphase flow. Fluid Dyn. Res. 20, 143–148 (1997)
Boivin, M., Simonin, O., Squires, K.D.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulence modulation by particles in isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 375, 235–263 (1998)
Li, Y., Mc Laughlin, J.B., Kontomaris, K., Portela, L.: Numerical simulation of particle-laden turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 13(10), 2957–2967 (2001)
Dritselis, C.D., Vlachos, N.S.: Numerical study of educed coherent structures in the near-wall region of a particle-laden channel flow. Phys. Fluids 20, 055103 (2008)
Nasr, H., Ahmadi, G., McLaughlin, J.B.: A DNS study of effects of particle-particle collisions and two-way coupling on particle deposition and phasic fluctuations. J. Fluid Mech. 640, 507–536 (2009)
De Marchis, M., Milici, B., Sardina, G., Napoli, E.: Interaction between turbulent structures and particles in roughened channel. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 78, 117–131 (2016)
Napoli, E., De Marchis, M., Gianguzzi, C., Milici, B., Monteleone, A.: A coupled finite volume-smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 310, 674–693 (2016)
De Marchis, M., Milici, B., Napoli, E.: Numerical observations of turbulence structure modification in channel flow over 2D and 3D rough walls. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 56, 108–123 (2015)
De Marchis, M.: Large eddy simulations of roughened channel flows: estimation of the energy losses using the slope of the roughness. Comput. Fluids 140, 148–157 (2016)
Monteleone, A., De Marchis, M., Milici, B., Napoli, E.: A multi-domain approach for smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations of highly complex flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 340, 956–977 (2018)
De Marchis, M., Milici, B., Napoli, E.: Large eddy simulations on the effects of the irregular roughness shape on turbulent channel flows. Int. J. Heat. Fluid Flow 80, 108494 (2019)
Milici, B., De Marchis, M.: Statistics of inertial particle deviation from fluid particle trajectories in horizontal rough wall turbulent channel flow. Int. J. Heat. Fluid Flow 60, 1–11 (2016)
Boivin, M., Simonin, O., Squires, K.D.: On the prediction of gas-solid flows with two-way coupling using large eddy simulation. Int. J. Heat. Fluid Flow 60, 1–11 (2016)
Piomelli, U., Balaras, E.: Wall-layer models for large-eddy-simulations. Phys. Fluids. 12, 2080–2090 (2000)
Jelly, T.O., Busse, A.: A Reynolds and dispersive shear stress contributions above highly skewed roughness. J. Fluid Mech. 852, 710–724 (2018)
Schmid, M.F., Lawrence, G.A., Parlange, M.B., Giometto, M.G.: Volume averaging for urban canopies. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 173, 349–372 (2019)
Milici, B.: Modification of particle laden near-wall turbulence in a vertical channel bounded by rough walls. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 103, 151–168 (2018)
Molin, D., Marchioli, C., Soldati, A.: Turbulence modulation and microbubble dynamics in vertical channel flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 42, 80–95 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milici, B., De Marchis, M. & Napoli, E. Large eddy simulation of inertial particles dispersion in a turbulent gas-particle channel flow bounded by rough walls. Acta Mech 231, 3925–3946 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02740-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02740-5