Abstract
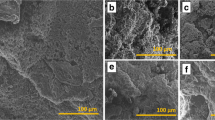
Here, we demonstrate multifunctional activity of a polydimethyl siloxane (PDMS) nanocomposite sponge for microbial mitigation and oil contaminant removal from water. Different concentrations of silver (Ag) nanoparticles have been studied for their anti-microbial activity along with activated Carbon (AC). Further, AC and Ag nanoparticles were incorporated inside the PDMS sponge using a unique non-aqueous in-situ reduction synthesis method to generate a nanocomposite sponge thus, rendering a hierarchical (i.e. micropores decorated with nanoparticles) texture on the sponge. The as-grown sponges were tested for their physico-chemical characteristics along with features including anti-microbial activity as well as absorption of floating-oil contaminants from water.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi S-J, Kwon T-H, Im H, Moon DI, Baek DJ, Seol ML, Duarte JP, Choi YK (2011) A Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sponge for the selective absorption of oil from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4552–4556. https://doi.org/10.1021/am201352w
Lu Y, Yuan W (2017) Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic and reinforced ethyl cellulose sponges for oil/water separation: synergistic strategies of cross-linking, carbon nanotube composite, and Nanosilica modification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:29167–29176. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09160
Lei Z, Zhang G, Deng Y, Wang C (2017) Thermoresponsive melamine sponges with switchable wettability by Interface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:8967–8974. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b14565
Mi H-YY, Jing X, Huang H-XX, Turng L-SS (2017) Controlling Superwettability by microstructure and surface energy manipulation on three-dimensional substrates for versatile gravity-driven oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:37529–37535. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10901
Dong X, Chen J, Ma Y, Wang J, Chan-Park MB, Liu X, Wang L, Huang W, Chen P (2012) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic hybrid foam of graphene and carbon nanotube for selective removal of oils or organic solvents from the surface of water. Chem Commun 48:10660–10662. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc35844a
Kim DH, Jung MC, Cho S-H, Kim SH, Kim HY, Lee HJ, Oh KH, Moon MW (2015) UV-responsive nano-sponge for oil absorption and desorption. Sci Rep 5:12908. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12908
Zhang A, Chen M, Du C et al (2013) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) oil absorbent with a three-dimensionally interconnected porous structure and Swellable skeleton. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10201–10206. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4029203
Tran DNH, Kabiri S, Sim TR, Losic D (2015) Selective adsorption of oil–water mixtures using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)–graphene sponges. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 1:298–305. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00035A
Liu Y, Ma J, Wu T, Wang X, Huang G, Liu Y, Qiu H, Li Y, Wang W, Gao J (2013) Cost-effective reduced Graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient and reusable oil-absorbent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10018–10026. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4024252
Gupta RK, Dunderdale GJ, England MW, Hozumi A (2017) Oil/water separation techniques: a review of recent progresses and future directions. J Mater Chem A 5:16025–16058. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA02070H
Wang M, Ma Y, Sun Y, Hong SY, Lee SK, Yoon B, Chen L, Ci L, Nam JD, Chen X, Suhr J (2017) Hierarchical porous chitosan sponges as robust and recyclable adsorbents for anionic dye adsorption. Sci Rep 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18302-0
He Y, Li J, Luo K, Li L, Chen J, Li J (2016) Engineering reduced Graphene oxide aerogel produced by effective γ-ray radiation-induced self-assembly and its application for continuous oil–water separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:3775–3781. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00073
Yun J, Khan FA, Baik S (2017) Janus Graphene oxide sponges for high-purity fast separation of both water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16694–16703. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03322
Guo J, Wang J, Gao Y, Wang J, Chang W, Liao S, Qian ZM, Liu YX (2017) PH-responsive sponges fabricated by Ag-S ligands possess smart double-transformed Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic-Superhydrophilic wettability for oil-water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:10772–10782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02734
Peng H, Wang H, Wu J, Meng G, Wang Y, Shi Y, Liu Z, Guo X (2016) Preparation of Superhydrophobic magnetic cellulose sponge for removing oil from water. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:832–838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03862
Liu F, Ma M, Zang D, Gao Z, Wang C (2014) Fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic cotton for application in the field of water/oil separation. Carbohydr Polym 103:480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.022
Zhang L, Xu L, Sun Y, Yang N (2016) Robust and durable Superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge for oil/water separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:11260–11268. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02897
Cherukupally P, Acosta EJ, Hinestroza JP, Bilton AM, Park CB (2017) Acid–Base polymeric foams for the adsorption of micro-oil droplets from industrial effluents. Environ Sci Technol 51:8552–8560. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01255
Khosravi M, Azizian S (2015) Synthesis of a novel highly Oleophilic and highly hydrophobic sponge for rapid oil spill cleanup. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:25326–25333. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b07504
Stolz A, Le Floch S, Reinert L et al (2016) Melamine-derived carbon sponges for oil-water separation. Carbon N Y 107:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.05.059
Wang Z, Jin P, Wang M, Wu G, Dong C, Wu A (2016) Biomass-derived porous carbonaceous aerogel as sorbent for oil-spill remediation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:32862–32868. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11648
Lukhele L., Krause R, Mamba B, Momba M (2010) Synthesis of silver impregnated carbon nanotubes and cyclodextrin polyurethanes for the disinfection of water Water SA 36:. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v36i4.58416
Jo Y-K, Kim BH, Jung G (2009) Antifungal activity of silver ions and nanoparticles on Phytopathogenic Fungi. Plant Dis 93:1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-93-10-1037
Losasso C, Belluco S, Cibin V, Zavagnin P, Mičetić I, Gallocchio F, Zanella M, Bregoli L, Biancotto G, Ricci A (2014) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: sensitivity of different Salmonella serovars. Front Microbiol 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00227
Kim SH, Lee HS, Ryu DS et al (2011) Antibacterial activity of silver-nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Korean J Microbiol Biotechnol 39:77–85
Busscher HJ, Dijkstra RJB, Engels E, Langworthy DE, Collias DI, Bjorkquist DW, Mitchell MD, van der Mei HC (2006) Removal of two waterborne pathogenic bacterial strains by activated carbon particles prior to and after charge modification. Environ Sci Technol 40:6799–6804. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061282r
Burlingame GA, Suffet IH, Pipes WO (1986) Predominant bacterial genera in granular activated carbon water treatment systems. Can J Microbiol 32:226–230. https://doi.org/10.1139/m86-045
Rivera-Garza M, Olguín MT, García-Sosa I et al (2000) Silver supported on natural Mexican zeolite as an antibacterial material. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 39:431–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(00)00217-1
Matsumura Y, Yoshikata K, Kunisaki S-I, Tsuchido T (2003) Mode of bactericidal action of silver zeolite and its comparison with that of silver nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4278–4281. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.7.4278-4281.2003
Jain P, Pradeep T (2005) Potential of silver nanoparticle-coated polyurethane foam as an antibacterial water filter. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:59–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20368
Nguyen DD, Tai N-H, Lee S-B, Kuo W-S (2012) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ Sci 5:7908. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee21848h
Goyal A, Kumar A, Patra PK, Mahendra S, Tabatabaei S, Alvarez PJJ, John G, Ajayan PM (2009) In situ synthesis of metal nanoparticle embedded free standing multifunctional PDMS films. Macromol Rapid Commun 30:1116–1122. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200900174
Zhang Q, Xu J-J, Liu Y, Chen H-Y (2008) In-situ synthesis of poly(dimethylsiloxane)–gold nanoparticles composite films and its application in microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 8:352–357. https://doi.org/10.1039/B716295M
Kuila BK, Garai A, Nandi AK (2007) Synthesis, optical, and electrical characterization of organically soluble silver nanoparticles and their poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanocomposites: enhanced luminescence property in the Nanocomposite thin films. Chem Mater 19:5443–5452. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm7020214
Sharma J, Chaki NK, Mandale AB, et al (2004) Controlled interlinking of au and Ag nanoclusters using 4-aminothiophenol as molecular interconnects. 272:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2003.09.016
Green M, O’Brien P (2000) A simple one phase preparation of organically capped gold nanocrystals. Chem Commun 183–184. https://doi.org/10.1039/a907532a
Ramajo L, Parra R, Reboredo M, Castro M (2009) Preparation of amine coated silver nanoparticles using triethylenetetramine. J Chem Sci 121:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-009-0009-8
Kumar KS, Vázquez G, Rodríguez A (2012) Microwave assisted synthesis and characterizations of decorated activated carbon. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:5484–5494
Qiao Z-A, Wang Y, Gao Y, Li H, Dai T, Liu Y, Huo Q (2010) Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem Commun 46:8812. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc02724c
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012
Yoon K-Y, Hoon Byeon J, Park J-H, Hwang J (2007) Susceptibility constants of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to silver and copper nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 373:572–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.11.007
Cho K-H, Park J-E, Osaka T, Park S-G (2005) The study of antimicrobial activity and preservative effects of nanosilver ingredient. Electrochim Acta 51:956–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.04.071
Byeon JH, Yoon KY, Park JH, Hwang J (2007) Characteristics of electroless copper-deposited activated carbon fibers for antibacterial action and adsorption–desorption of volatile organic compounds. Carbon N Y 45:2313–2316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.06.026
Bakshi S, Pandey K, Bose S, Gunjan, Paul D, Nayak R (2019) Permanent superhydrophilic surface modification in microporous polydimethylsiloxane sponge for multi-functional applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 552:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.06 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, K., Bindra, H.S., Paul, D. et al. Smart multi-tasking PDMS Nanocomposite sponges for microbial and oil contamination removal from water. J Polym Res 27, 189 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02109-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02109-1