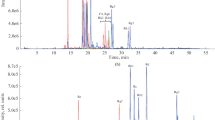
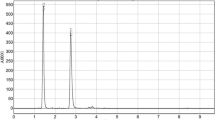
Abstract
Alpinia officinarum Hance is a medicine and food dual purposes plant. Its rhizomes have been widely used as food and medicine in Asia, Africa, and Europe for high dietary values and therapeutic benefits. Phytochemical studies showed that flavonoids and diarylheptanoids are two groups of characteristic and bioactive components in the rhizomes of A. officinarum. However, comprehensive quality assessment of the rhizomes of A. officinarum is usually ignored for the shortages of reference standards of bioactive constituents. In this work, a new strategy of using curcumin-d6 as single exogenous internal standard was developed to overcome both matrix effect and shortage of reference standards for determination of seven quality markers (galangin, kaempferol, kaempferide, rac-pinocembrin, pinobanksin, dihydroyashabushiketol, 1,7-diphenyl-4-en-3-heptanone) in the rhizome of A. officinarum based on UHPLC-MS/MS method. Chromatographic separation was carried out on a C18 reverse-phase column with gradient elution. Mass spectrometric detection was accomplished using multiple-reaction-monitoring mode. The method developed was fully validated in terms of LOD, LOQ, linearity, precision, accuracy, and stability, and the results obtained by the method new developed were also compared with those obtained by conventional external standard method. Finally, the new developed analytical strategy was successfully applied to determine seven Q-markers in fifteen batches of rhizomes of A. officinarum. The newly developed method was useful for quality assessment of the rhizomes of A. officinarum.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abubakar IB, Malami I, Yahaya Y, Sule SM (2018) A review on the ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Alpinia officinarum Hance. J Ethnopharmacol 224:45–62
Basri AM, Taha H, Ahmad N (2017) A review on the pharmacological activities and phytochemicals of Alpinia officinarum (galangal) extracts derived from bioassay-guided fractionation and isolation. Pharmacogn Rev 11:43–56
Chen P, Guo X, Liang H, Feng Y (2008) Analysis of the active constituents in Alpinia officinarum Hance. J Guangdong College Pharm 24:462–464
De Nicolò A, Cantù M, D'Avolio A (2017) Matrix effect management in liquid chromatography mass spectrometry: the internal standard normalized matrix effect. Bioanalysis 9:1093–1105
Honmore VS, Rojatkar SR, Nawale LU, Arkile MA, Khedkar VM, Natu AD, Sarkar D (2016) In vitro and ex vivo antitubercular activity of diarylheptanoids from the rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum Hance. Nat Prod Res 30:2825–2830
Hou JJ, Wu WY, da J, Yao S, Long HL, Yang Z, Cai LY, Yang M, Liu X, Jiang BH, Guo DA (2011) Ruggedness and robustness of conversion factors in method of simultaneous determination of multi-components with single reference standard. J Chromatogr A 1218:5618–5627
Hou JJ, Wu WY, Liang J, Yang Z, Long HL, Cai LY, Fang L, Wang DD, Yao S, Liu X, Jiang BH, Guo DA (2014) A single, multi-faceted, enhanced strategy to quantify the chromatographically diverse constituents in the roots of Euphorbia kansui. J Pharm Biomed Anal 88:321–330
Kunati SR, Yang S, William BM, Xu Y (2018) An LC–MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of curcumin, curcumin glucuronide and curcumin sulfate in a phase II clinical trial. J Pharm Biomed Anal 156:189–198
Lan X, Wang W, Li Q, Wang J (2016) The natural flavonoid pinocembrin: molecular targets and potential therapeutic applications. Mol Neurobiol 53:1794–1801
Lee HN, Shin SA, Choo GS, Kim HJ, Park YS, Kim BS, Kim SK, Cho SD, Nam JS, Choi CS, Che JH, Park BK, Jung JY (2018) Anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin and galangin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages and DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis animal models. Int J Mol Med 41:888–898
Li ZY, Sun DM, Zhang JJ (2010) Determination of galangin and kaempferol in Rhizoma Alpiniae Officinarum by HPLC. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm 25:1368
Lim TK (2016) Alpinia officinarum. In: Lim TK (ed) Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants, Modified stems, roots, vol 12. Bulbs. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 178–195
Lin LY, Peng CC, Yeh XY, Huang BY, Wang HE, Chen KC, Peng RY (2015) Antihyperlipidemic bioactivity of Alpinia officinarum (Hance) Farw Zingiberaceae can be attributed to the coexistance of curcumin, polyphenolics, dietary fibers and phytosterols. Food Funct 6:1600–1610
Lin L, Liu X, Zhao M (2018) Screening of xanthine oxidase inhibitor from selected edible plants and hypouricemic effect of Rhizoma Alpiniae Officinarum extract on hyperuricemic rats. J Funct Foods 50:26–36
Liu Z, Sang S, Hartman TG, Ho CT, Rosen RT (2005) Determination of diarylheptanoids from Alpinia officinarum (lesser galangal) by HPLC with photodiode array and Electrochemical Detection. Phytochem Anal 16:252–256
Liu D, Liu YW, Guan FQ, Liang JY (2014a) New cytotoxic diarylheptanoids from the rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum Hance. Fitoterapia 96:76–80
Liu Y, Wang X, Liu Y, Di X (2014b) Simultaneous determination of four flavonoids in Alpinia officinarum hance by RP-HPLC. J Shenyang Pharm Univ 31:13–16
National Commission of Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2015) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s republic of China, vol. I. China Medical Science Press, Beijing, pp 287–288
National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (2002) Notice of the Chinese Ministry of Health on Further Regulating the Management of Raw Materials of Healthy Foods, Wei Fa Jian Fa No. 51, 2002. < http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s3593/200810/a298f342c464475b923bcdc3c9d0575a.shtml> Accessed 14.02.2020
Ning Z, Liu Z, Song Z, Zhao S, Dong Y, Zeng H, Shu Y, Lu C, Liu Y, Lu A (2016) A single marker choice strategy in simultaneous characterization and quantification of multiple components by rapid resolution liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (RRLC-QqQ-MS). J Pharm Biomed Anal 124:174–188
Peng G, Zhou G, Qin H (2014) Simultaneous determination of six compounds in Alpinia officinarum by HPLC. Chin J Pharm Anal 34:966–970
Theodoridis GA, Gika HG, Want EJ, Wilson ID (2012) Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry based global metabolite profiling: a review. Anal Chim Acta 711:7–16
Wang W, Ma X, Guo X, Zhao M, Tu P, Jiang Y (2015) A series of strategies for solving the shortage of reference standards for multi-components determination of traditional Chinese medicine, Mahoniae caulis as a case. J Chromatogr A 1412:100–111
Zhang JQ, Wang Y, Li HL, Wen Q, Yin H, Zeng NK, Lai WY, Wei N, Cheng SQ, Kang SL, Chen F, Li YB (2015) Simultaneous quantification of seventeen bioactive components in rhizome and aerial parts of Alpinia officinarum Hance using LC-MS/MS. Anal Methods 7:4919–4926
Zhang G, Zhao L, Zhu J, Feng Y, Wu X (2018) Anti-inflammatory activities and glycerophospholipids metabolism in KLA-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by diarylheptanoids from the rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum. Biomed Chromatogr 32:e4094
Zhao X, Chen X, Geng L, Bi K (2009) HPLC simultaneous determination of 3 flavonoids in Alpinia officinarum Hance. Chin J Pharm Anal 29:2036–2039
Zhu C, Li X, Zhang B, Lin Z (2017) Quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker—a rational method for the internal quality of Chinese herbal medicine. Integr Med Res 6:1–11
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31400302), the China Scholarship Council (No. 201708420116), and Qingmiao Project of Hubei university of Chinese Medicine (No. 2015ZXX015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dan Liu and Yan Xu contributed equally to the study conception and design. Dan Liu and Gang Xu developed methodology and performed data acquisition. Xiaoqing Ma collected the materials. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dan Liu and Yan Xu make critical corrections. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 30.4 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Xu, G., Ma, X. et al. A New Strategy of Overcoming both Matrix Effect and Shortage of Reference Standards for Determination of Multi-components in the Rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum Hance Using UHPLC-MS/MS with Single Exogenous Internal Standard. Food Anal. Methods 13, 1867–1878 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01802-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01802-7