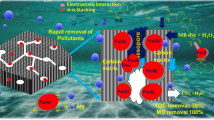
Abstract
In this work, the influences of carbon on structure, magnetic properties and Cr(VI) absorption efficiency of carbon-encapsulated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles (MFO/C NPs) are studied. SEM images indicate that the fabricated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles (MFO NPs) are enveloped by carbon layers, forming encapsulating structure. By the BET analysis, it is demonstrated that the average specific surface area of MFO/C samples is higher than that MFO sample. From FTIR and XPS spectra, the presence of carbon-coated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles is confirmed. It is found that the Cr(VI) absorption efficiency of the MFO/C NPs first increases to reach the maximum value at 5% C concentration, and then decreases with the further increment of C concentration. The maximum absorption efficiency and capacity of 90.1% and 73.26 mg/g are obtained, respectively. Finally, a removal mechanism for the removal of Cr(VI) is proposed. The obtained results demonstrate that the carbon-encapsulated MnFe2O4 NPs is a promising candidate as an advanced absorbent for the removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.J.M. Saeedi, Metal pollution assessment and multivariate analysis in sediment of Anzali international wetland. Environ. Earth Sci. 70, 1791 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2267-5
J. Hu, G. Chen, I.M.C. Lo, Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles. Water Res. 39, 4528–4536 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.05.051
K.P. Singh, A.K. Singh, S. Gupta, S. Sinha, Optimization of Cr (VI) reduction by zero-valent bimetallic nanoparticles using the response surface modeling approach. Desalination 270, 275–284 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.056
L. Alidokht, A.R. Khataee, A. Reyhanitabar, S. Oustan, Reductive removal of Cr (VI) by starch-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Desalination 270, 105–110 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.028
B. Eyvazi, A. Jamshidi-zanjani, A. Khodadadi, Synthesis of nano-magnetic MnFe2O4 to remove Cr (III) and Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: a comprehensive study. Environ. Pollut. 29, 113685 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113685
L. Shao, Z. Ren, G. Zhang, L. Chen, Facile synthesis, characterization of a MnFe2O4/activated carbon magnetic composite and its effectiveness in tetracycline removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 135, 16–24 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.03.035
T. Wang, J. Lin, Z. Chen, M. Megharaj, R. Naidu, Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 83, 413–419 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.07.006
K.P. Gadkaree, Carbon honeycomb structures for adsorption applications. Carbon 36, 981–989 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(97)00230-3
D. Clifford, P. Chu, A. Lau, Thermal regeneration of powdered activated carbon (pac) and pac-biological sludge mixtures. Water Res. 17, 1125–1138 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(83)90053-2
G. Zhang, H. Liu, A.T. Cooper, R. Wu, CuFe2O4/activated carbon composite: a novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of acid orange II and catalytic regeneration. Chemosphere 68, 1058–1066 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.01.081
N. Yang, S. Zhu, D. Zhang, S. Xu, Synthesis and properties of magnetic Fe3O4-activated carbon nanocomposite particles for dye removal. Mater. Lett. 62, 645–647 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.06.049
D. Fabris, V. Garg, K. Sapag, L.C.A. Oliveira, R.V.R.A. Rios, R.M. Lago, Activated carbon/iron oxide magnetic composites for the adsorption of contaminants in water. Carbon 40, 2177–2183 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00076-3
K. Lu, F. Yang, W. Lin, S. Zhou, T. Xi, C. Song, Y. Kong, Stabilized pony-sized-CuFe2O4/carbon nitride porous composites with boosting fenton-like oxidation activity. Chem. Sel. 3, 4207–4216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201800843
J. Du, W. Xu, J. Liu, Z. Zhao, Efficient degradation of Acid Orange 7 by persulfate activated with a novel developed carbon-based MnFe2O4 composite catalyst. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 95, 1135–1145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6298
C.A. Backes, R.G. Mclaren, A.W. Rate, R.S. Swift, Kinetics of cadmium and cobalt desorption from iron and manganese oxides. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 59, 778–785 (1988). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1995.03615995005900030021x
I. Nazionale, E. Division, Eddy-Current Losses in Mn–Zn Ferrites. IEEE T Magn. 50, 6300109 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2013.2279878
G. Wang, D. Zhao, F. Kou, Q. Ouyang, J. Chen, Z. Fang, Removal of norfloxacin by surface Fenton system (MnFe2O4/H2O2): Kinetics, mechanism and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 351, 747–755 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.033
S.V. Bhandare, R. Kumar, A.V. Anupama, H.K. Choudhary, V.M. Jali, B. Sahoo, Annealing temperature dependent structural and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles grown by sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 433, 29–34 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.02.040
W. Li, C. An, H. Guo, Y. Zhang, K. Chen, Z. Zhang, G. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, The encapsulation of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles into the carbon framework with superior rate capability for lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 12, 4445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr10002d
Z. Zhang, D. Zhou, S. Zou, X. Bao, X. He, One-pot synthesis of MnFe2O4/C by microwave sintering as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. J. Alloys Compd. 786, 565–569 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.015
M. Gorgizadeh, N. Behzadpour, F. Salehi, F. Daneshvar, R.D. Vais, N. Azarpira, M. Lotfi, N. Sattarahmady, A MnFe2O4/C nanocomposite as a novel theranostic agent in MRI, sonodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy of a melanoma cancer model. J. Alloys Compd. 816, 152597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152597
P. Kidkhunthod, S. Nilmoung, S. Mahakot, S. Rodporn, Journal of magnetism and magnetic materials a structural study and magnetic properties of electrospun carbon/manganese ferrite (C/MnFe2O4) composite nano fibers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 436–442 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.10.085
H. Pang, R.P. Sahu, Y. Duan, I.K. Puri, Diamond and Related Materials MnFe2O4 -coated carbon nanotubes with enhanced microwave absorption : Effect of CNT content and hydrothermal reaction time. Diam. Relat. Mater. 96, 31–43 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2019.04.027
Y. Yan, G. Guo, T. Li, D. Han, J. Zheng, J. Hu, D. Yang, A. Dong, Carbon-coated MnFe2O4 nanoparticle hollow microspheres as high-performance anode for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta. 246, 43–50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.06.020
Y. Liu, N. Zhang, C. Yu, L. Jiao, J. Chen, Y. Liu, N. Zhang, C. Yu, L. Jiao, J. Chen, Jun C, MnFe2O4@C nanofibers as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 16, 3321–3328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00942
L. Yang, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, X. Jiang, Z. Zhang, T. Zhang, L. Zhang, The investigation of synergistic and competitive interaction between dye Congo red and methyl blue on magnetic MnFe2O4. Chem. Eng. J. 246, 88–96 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.044
D. Yunchen, L. Wenwen, Q. Rong, W. Ying, H. Xijiang, M. Jun, X. Ping, Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 12997–13006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am502910d
J. Zheng, Z.Q. Liu, X.S. Zhao, M. Liu, X. Liu, W. Chu, One-step solvothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@C core-shell nanoparticles with tunable sizes. Nanotechnology. 23, 165601 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/23/16/165601
K. Cheng, Y.M. Zhou, Z.Y. Sun, H.B. Hu, H. Zhong, X.K. Kong, Q.W. Chen, Synthesis of carbon-coated, porous and water-dispersive Fe3O4 nanocapsules and their excellent performance for heavy metal removal applications. Dalton Trans. 41, 5854–5861 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT12312F
A. Goyal, S. Bansal, P. Samuel, S. Singhal, CoMn0.2Fe1.8O4 ferrite nanoparticles engineered by sol–gel technology: an expert and versatile catalyst for the reduction of nitroaromatic compounds. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2, 18848–18860 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA03900A
D.A. Links, K. Cheng, Y. Zhou, Z. Sun, H. Hu, H. Zhong, X. Kong, Q. Chen, Synthesis of carbon-coated, porous and water-dispersive Fe3O4 nanocapsules dand their excellent performance for heavy metal removal applications. Dalton Trans. 41, 5854–5861 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2dt12312f
P.T.L. Huong, L.T. Huy, H. Lan, L.H. Thang, T.T. An, N. Van Quy, P.A. Tuan, J. Alonso, M.H. Phan, A.T. Le, Magnetic iron oxide-carbon nanocomposites: Impacts of carbon coating on the As(V) adsorption and inductive heating responses. J. Alloys Compd. 739, 139–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.178
P.T.L. Huong, N. Tu, H. Lan, L.H. Thang, N.V. Quy, P.A. Tuan, N.X. Dinh, V.N. Phan, A.T. Le, Functional manganese ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites: effects of graphene oxide on the adsorption mechanisms of organic MB dye and inorganic As (V) ions from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 8, 12376–12389 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA00270C
L. Geng, F. Yan, C. Dong, C. An, Design and regulation of novel MnFe2O4@C nanowires as high performance electrode for supercapacitor. Nanomaterials 9, 777 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050777
S. Kumar, R.R. Nair, P.B. Pillai, S.N. Gupta, M.A.R. Iyengar, Graphene oxide—MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 17426–17436 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am504826q
O. Ajouyed, C. Hurel, M. Ammari, L. Ben, N. Marmier, Sorption of Cr(VI) onto natural iron and aluminum (oxy)hydroxides: effects of pH, ionic strength and initial concentration. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 616–622 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.096
Y. Zhao, W. Qi, G. Chen, M. Ji, Z. Zhang, Behavior of Cr(VI) removal from wastewater by adsorption onto HCl activated Akadama clay. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 50, 190–197 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.016
Y. Shi, R. Shan, L. Lu, H. Yuan, H. Jiang, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from glue residue. J. Clean. Prod. 254, 119935 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119935
N. Ngoc, P. Thi, B. Hanh, L. Thi, T. Ha, L. Ngoc, T. Vinh, Magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 33, 1214–1218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.12.013
M. Taghizadeh, S. Hassanpour, Selective adsorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions using a Cr(VI)-imprinted polymer supported by magnetic multiwall carbon nanotubes. Polymer (Guildf). 132(1–11), 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.10.045
Y.C. Sharma, V. Srivastava, Comparative studies of removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by magnetic nanoparticles. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 56, 819–825 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/je100428z
T. Altun, H. Ecevit, Cr(VI) removal using Fe2O3-chitosan-cherry kernel shell pyrolytic charcoal composite beads. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 25, 426–438 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2019.112
Y. Xiao, H. Liang, Z. Wang, MnFe2O4/chitosan nanocomposites as a recyclable adsorbent for the removal of hexavalent chromium. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 3910–3915 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.099
N. Li, F. Fu, J. Lu, Z. Ding, B. Tang, J. Pang, Facile preparation of magnetic mesoporous MnFe2O4@SiO2−CTAB composites for Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction. Environ. Pollut. 220, 1376–1385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.097
K.L. Bhowmik, A. Debnath, R.K. Nath, B. Saha, Synthesis of MnFe2O4 and Mn3O4 magnetic nano-composites with enhanced properties for adsorption of Cr(VI): artificial neural network modeling. Water Sci. Technol. 76, 3368–3378 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.501
Acknowledgement
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 103.02-2019.32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuyen, T.V., Chi, N.K., Tien, D.T. et al. Carbon-encapsulated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles: effects of carbon on structure, magnetic properties and Cr(VI) removal efficiency. Appl. Phys. A 126, 577 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03760-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03760-7