Abstract
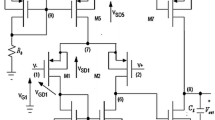
In this paper, a new population-based evolutionary technique namely symbiotic organisms search (SOS) optimisation algorithm is proposed to optimize the design variables of transistors used in analog circuit. Here length and width of the transistors are considered to be the design variables, the optimisation of which minimizes the input-referred noise, total MOSFET area, and power consumption. This algorithm is quite useful in solving optimization problems but it suffers from higher computational time. Thus in order to minimize the computational time along with SOS algorithm, gm/ID design methodology is used. The proposed method not only guarantees appropriate bias conditions but also estimates the reduced search spaces for the design variables of the MOSFETs. To analyse the performance of SOS algorithm along with gm/ID design methodology, a low noise differential folded-cascode operational transconductance amplifier has been designed and verified using Cadence Spectre circuit simulator in UMC 0.18 µm CMOS process and MATLAB. From the optimisation results, it is observed that the gm/ID method combined with SOS algorithm converges earlier than SOS alone. The total computational time of simulation obtained using the proposed method is 8.59 s while errors found are less than 8%. Hence, this method not only reduces computational time but also improves the accuracy of the circuit design.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guerra-Gmez, I., McConaghy, T., & Tlelo-Cuautle, E. (2013). Operating-point driven formulation for analog computer-aided design. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process, 74, 345–353.
Vural, R., Yildirim, T., Kadioglu, T., & Basargan, A. (2012). Performance evaluation of evolutionary algorithms for optimal filter design. IEEE Trans Evol Comput, 16(1), 135–147.
Kundu, S., & Mandal, P. (2014). ISGP: iterative sequential geometric programming for precise and robust analog circuit sizing. Integr VLSI J, 47, 510–531.
Grimbleby, J. B., et al. (2000). Automatic analogue circuit synthesis using genetic algorithms. IEE Proc Circuits Devices Systems, 6, 319–323.
Guerra-Gomez, I., & Tlelo-Cuautle, E. (2013). Sizing analog integrated circuits by current-branches-bias assignments with heuristics. Elektronikair Elektrotechnika, 74, 81–86.
Panda, M., Patnaik, S. K., Mal, A. K., & Ghosh, S. (2019). Fast and optimised design of a differential VCO using symbolic echnique and multi objective algorithms. IET Circuits Devices Systems, 13(8), 1187–1195.
Shams, M., Rashedi, E., & Hakimi, A. (2015). Clustered-gravitational search algorithm and its application in parameter optimization of a low noise amplifier. Appl Math Comput, 258, 436–453.
Ghosh, S., De, B. P., Kar, R., & Mal, A. K. (2019). Symbiotic organisms search algorithm for optimal design of CMOS two-stage op-amp with nulling resistor and robust bias circuit. IET Circuits Devices Systems, 13(5), 679–688.
Dammak, H. D., et al. (2008). Design of folded cascode OTA in different regions of operationthrough gm/ID methodology. World Acad Sci Eng Technol, 45, 28–33.
Jespers, P. (2010). The gm/ID methodology, a sizing tool for low-voltage analog CMOS circuits. Boston: Springer.
Sabry, M. N., Omran, H., & Dessouky, M. (2018). Systematic design and optimization of operational transconductance amplifier using gm/ID design methodology. Microelectron J, 75, 87–96.
Silveira, D. F., & Jespers, P. G. A. (1996). A gm/ID based methodology for the design of CMOS analog circuits and its application to the synthesis of a silicon-on-insulator micropower OTA. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 31(9), 1314–1319.
Ou, J. (2011). gm/ID based noise analysis for CMOS analog. In Proceedings of the IEEE MWCAS (pp. 26–29).
Flandre, D., et al. (1997). Improved synthesis of gain-boosted regulated-cascode CMOS stages using symbolic analysis and gm/ID methodology. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 32, 1006–1012.
Tlelo-Cuautle, E., & Sanabria Borbon, A. (2016). Optimising operational amplifiers by evolutionary algorithms and gm/Id method. Int J Electron, 103, 1–20.
Ma, W., Wang, M., & Zhu, X. (2014). Improved particle swarm optimization based approach for bi-level programming problem-an application on supply chain model. Int J Mach Learn Cybernet, 5(2), 281–292.
Mourad, F., Cooren, Y., Sallem, A., et al. (2010). Analog circuit design optimization through the particle swarm optimization technique. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process, 63, 71–82.
Eberhart, R., Shi, C. Y. (1998). Comparison between genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. In Evolutionary programming VII (pp. 611–616). Springer, Berlin.
Panda, M., Patnaik, S. K., & Mal, A. K. (2018). Performance enhancement of a VCO using symbolic modelling and optimisation. IET Circuits Devices Systems, 12(2), 196–202.
Yu, J., Mao, Z. (2007). Automated design method for parameters optimization of CMOS analog circuits based on adaptive genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 7th international conference on ASIC (pp. 1217–1220).
Gupta, H., & Ghosh, B. (2010). Analog circuits design using ant colony optimization. International Journal of Electronics, Computer and Communications Technologies, 2, 9–21.
Prayogo, D. (2015). An innovative parameter-free symbiotic organisms search (SOS) for solving construction-engineering problems. PhD thesis, Department of Construction Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology.
Abdullahi, M., & Ngadi, M. A. (2016). Symbiotic organism search optimization based task scheduling in cloud computing environment. Futur Gener Comput Syst, 56, 640–650.
Zhang, G., Xia, X., Xu, J., Nie, K., & Gao, Z. (2016). Particle swarm optimization design of low- power multistage amplifier using gm/ID methodology. J Circuits Systems Comput, 2016, 1650104–01–1650104-31.
Konishi, T., Inazu, K., Lee, J. G., Natsui, M., Masui, S., & Murmann, B. (2011). Design optimization of high-speed and low-power operational transconductance amplifier using gm/ID lookup table methodology. IEICE Trans Electron, E94-C(3), 334–345.
Jespers, P. G. A., & Murmann, B. (2015). Calculation of MOSFET distortion using the transconductance to current ratio (gm/ID). IEEE ISCAS, 2015, 529–532.
Fiorelli, R., Peralías, E., & Silveira, F. (2012). An all-inversion-regiongm/IDbased design methodology for radiofrequency blocks in CMOS nanometer technologies. In G. Cornetta, D. Santos, & J. Vazquez (Eds.), Wireless radio-frequency standards and system design: advanced techniques. Harrisburg: IGI Global.
Ou, J., & Ferreira, P. M. (2015). A unified explanation of gm/ID based noise analysis. J Circuit Syst Comput, 24, 1550010-1–1550010-13.
Cheng, M. Y., & Prayogo, D. (2014). Symbiotic organisms search: A new metaheuristic optimization algorithm. Comput Struct, 139, 98–112.
Aulady, M. (2014). A hybrid symbiotic organism’s search-quantum neural network for predicting high performance concrete compressive strength. Master Thesis, Department of Construction Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology.
Vincent, F. Y., Redi, A. P., Yang, C. L., Ruskartina, E., & Santosa, B. (2017). Symbiotic organisms search and two solution representations for solving the capacitated vehicle routing problem”. Appl Soft Comput, 52, 657–672.
Stefanovic, D., & Kayal, M. (2010). Structured analog CMOS design (pp. 141–156). Dordrecht: Springer.
Ou, J., & Ferreira, P. M. (2014). A gm/ID based noise optimization for CMOS folded-cascode operational amplifier. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Exp Briefs, 61, 783–787.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, M., Patnaik, S.K., Mal, A.K. et al. An evolutionary-based design methodology for performance enhancement of a folded-cascode OTA using symbiotic organisms search algorithm and gm/ID technique. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 105, 215–227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01668-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01668-z