Abstract
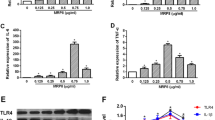
Sialic acid (N-acetylneuraminic acid, NANA) is found at all cell surfaces of vertebrates. Although it is widely accepted that sialic acid is an essential substrate for brain development via a significant role in nerve transfers, structure of glycosides, and synaptogenesis phenomena, there are some reports on the elevated levels of sialic acid and prevalence of neurodegeneration. Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are involved in neuroinflammation disorders and produced by many cell types, including activated T cells, macrophages, neurons, astrocytes, and microglial cells. It can be hypothesized that sialic acid may have a potentially critical role in regulation of a wide range of uncovered neurodegeneration factors as its downstream targets. In this study, for the first time, we aimed to analyze the possible effect of the sialic acid solution exposure in the human C118 cell line, which was derived from a human brain astrocytoma (glial cells), on the expression patterns of miR-218, NF-kB, MMP-9, and TIMP-1. For MMP-9, protein levels were studied too. Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of NANA was obtained by MTT assay. Glial cell line was treated with sialic acid (300, 500, and 1000 µg/ml) for 24 h to investigate the effects of this ligand on the expression of miR-218, NF-kB, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 genes. Protein levels were checked by Western blotting, and by using zymography, the gelatinolytic activity of MMP-9 secreted into conditioned media was assayed. At 300 µM, 500 µM, and 1000 µM sialic acid treatments, the expression of miR-218 was downregulated; subsequently, the NF-kB, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 genes as well as their protein expressions were upregulated. More interestingly, the enzyme activity of secreted MMP-9 was upregulated too (p-values ≤ 0.05). This study could demonstrate the significant effect of sialic acid on miR-218, NF-kB, MMP-9 , and TIMP-1 expressions in gene and protein levels and also the levels of enzyme activity of secreted MMP-9. Therefore, provided information indicates the novel idea of a possible linkage between sialic acid species and regulation of these neuroinflammation genes in Glial cell line.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer disease
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- IC50:
-
Half maximal inhibitory concentration
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteases
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- NCAMs:
-
Neural cell adhesion molecules
- NANA:
-
N-Acetylneuraminic acid
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- PD:
-
Parkinson disease
- polySia or PSA:
-
Polysialic acid
- TIMPs:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases
References
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam J, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 4:e05005. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Amin ND, Bai G, Klug JR et al (2015) Loss of motoneuron-specific microRNA-218 causes systemic neuromuscular failure. Science 80-(350):1525–1529. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad2509
Bergman P, James T, Kular L et al (2013) Next-generation sequencing identifies microRNAs that associate with pathogenic autoimmune neuroinflammation in rats. J Immunol 190:4066–4075. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200728
Bommarito A et al (2011) BRAFV600E mutation, TIMP-1 upregulation, and NF-κB activation: closing the loop on the papillary thyroid cancer trilogy. Endocr Relat Cancer 18:669–685. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-11-0076
Bossy-Wetzel E, Schwarzenbacher R, Lipton SA (2004) Molecular pathways to neurodegeneration. Nat Med 10:S2–S9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1067
Brkic M, Balusu S, Libert C, Vandenbroucke RE (2015) Friends or foes: matrix metalloproteinases and their multifaceted roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2015:620581. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/620581
Charles P, Hernandez MP, Stankoff B et al (2000) Negative regulation of central nervous system myelination by polysialylated-neural cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7585–7590. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.100076197
Charles P, Reynolds R, Seilhean D et al (2002) Re-expression of PSA-NCAM by demyelinated axons: an inhibitor of remyelination in multiple sclerosis? Brain 125:1972–1979. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awf216
Cheraghzadeh M, Azizidoost S, Nazeri Z et al (2018) The effect of sialic acid on viability and growth of mice astrocytes and human astroglia cells. J Isfahan Med Sch 36:264–269
Chou YC, Sheu JR, Chung CL, Chen CY, Lin FL, Hsu MJ, Kuo YH, Hsiao G (2010) Nuclear-targeted inhibition of NF-kappaB on MMP-9 production by N-2-(4-bromophenyl) ethyl caffeamide in human monocytic cells. Chem Biol Interact 30(184):403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.010
Dell'Agli M, Galli GV, Bosisio E, D'Ambrosio M (2009) Inhibition of NF-kB and metalloproteinase-9 expression and secretion by parthenolide derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:1858–1860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.02.080
Grigoriadis N, Grigoriadis S, Polyzoidou E, Milonas I, Karussis D (2006) Neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis: Evidence for autoimmune dysregulation, not simple autoimmune reaction. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108(3):241–244
Guan H, Wei G, Wu J et al (2013) Down-regulation of miR-218-2 and its host gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1334–1344. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-1053
Harraz MM, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2011) MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 42:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2011.01.005
Hoye ML, Regan MR, Jensen LA et al (2018) Motor neuron-derived microRNAs cause astrocyte dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 141:2561–2575. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy182
Jones SV, Kounatidis I (2017) Nuclear factor-kappa B and Alzheimer disease, unifying genetic and environmental risk factors from cell to humans. Front Immunol 8
Kaplan A, Spiller KJ, Towne C et al (2014) Neuronal matrix metalloproteinase-9 is a determinant of selective neurodegeneration. Neuron 81:333–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.009
Khatua B, Roy S, Mandal C (2013) Sialic acids siglec interaction: a unique strategy to circumvent innate immune response by pathogens. Indian J Med Res 138:648–662
Kim SY, Kim DH, Han SJ et al (2007) Repression of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression by ginsenoside Rh2 in human astroglioma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 74:1642–1651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2007.08.015
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2632
Leibowitz SM, Yan Y (2016) NF-κB pathways in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and the therapeutic implications. Front Mol Neurosci 9
Ma X, Zhou J, Zhong Y et al (2014) Expression, regulation and function of microRNAs in multiple sclerosis. Int J Med Sci 11:810–818. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.8647
Maes O, Chertkow H, Wang E, Schipper H (2009) MicroRNA: implications for Alzheimer disease and other human CNS disorders. Curr Genomics 10:154–168. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920209788185252
Marie-Françoise (2000) Molecular mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases. Brain 124(7):1467–1468. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.7.1467
Miranda KC et al (2006) A pattern-based method for the identification of microRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell 126:1203–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.031
Mrak RE, Griffin WST (2005) Glia and their cytokines in progression of neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging 26:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.05.010
Muir EM, Adcock KH, Morgenstern DA et al (2002) Matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors are produced by overlapping populations of activated astrocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 100:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00132-8
Noorbakhsh F, Ellestad KK, Maingat F et al (2011) Impaired neurosteroid synthesis in multiple sclerosis. Brain 134:2703–2721. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr200
Nunez-Iglesias J, Liu CC, Morgan TE et al (2010) Joint genome-wide profiling of miRNA and mRNA expression in Alzheimer’s disease cortex reveals altered miRNA regulation. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008898
Olsen M, Zuber C, Roth J et al (1995) The ability to re-express polysialylated NCAM in soleus muscle after denervation is reduced in aged rats compared to young adult rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 13:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/0736-5748(95)00003-Y
Ouali Alami N, Schurr C, Heuvel FO, Tang L, Li Q, Tasdogan A, Kimbara A, Nettekoven M, Ottaviani G, Raposo C, Röver S, Rogers‐Evans M, Rothenhäusler B, Ullmer C, Fingerle J, Grether U, Knuesel I, Boeckers TM, Ludolph A, Wirth T, Roselli F, Baumann (2018) NF‐κB activation in astrocytes drives a stage‐specific beneficial neuroimmunological response in ALS. The EMBO Journal 37(16)
Pillai S, Netravali IA, Cariappa A, Mattoo H (2012) Siglecs and immune regulation. Annu Rev Immunol 30:357–392. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075018
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M, Giegerich R (2004) Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA 10:1507–1517. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.5248604
Rhee JW, Lee KW, Kim D, Lee Y, Jeon OH, Kwon HJ, Kim DS (2007) NF-kappaB-dependent regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression by lipopolysaccharide in a macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:88–94. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2007.40.1.088
Sbardella D, Fasciglione GF, Gioia M et al (2012) Human matrix metalloproteinases: an ubiquitarian class of enzymes involved in several pathological processes. Mol Aspects Med 33:119–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.015
Schauer R (2009) Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:507–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2009.06.003
Schnaar RL, Gerardy-Schahn R, Hildebrandt H (2014) Sialic acids in the brain: gangliosides and polysialic acid in nervous system development, stability, disease, and regeneration. Physiol Rev 94:461–518. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00033.2013
Shih R-H, Wang C-Y, Yang C-M (2015) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077
Song L, Huang Q, Chen K et al (2010) miR-218 inhibits the invasive ability of glioma cells by direct downregulation of IKK-β. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.10.003
Sun J (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases are essential for the inflammatory response in cancer cells. J Signal Transduct 2010:1–7
Varki A (2008) Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol Med 14:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2008.06.002
Walker FR, Beynon SB, Jones KA et al (2014) Dynamic structural remodelling of microglia in health and disease: a review of the models, the signals and the mechanisms. Brain Behav Immunol 37:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.010
Wang C, Ji B, Cheng B et al (2014) Neuroprotection of microRNA in neurological disorders (Review). Biomed Rep 2:611–619. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2014.297
Wielgat P, Braszko JJ (2012a) Significance of the cell adhesion molecules and sialic acid in neurodegeneration. Adv Med Sci 57:23–30. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10039-012-0011-0
Wielgat P, Braszko JJ (2012b) The participation of sialic acids in microglia–neuron interactions. Cell Immunol 273:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.12.002
Wilczynska KM, Gopalan SM, Bugno M, Kasza A, Konik BS, Bryan L, Wright S, Griswold-Prenner I, Kordula T (2006) A novel mechanism of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 activation by interleukin-1 in primary human astrocytes. J Biol Chem 281(46):34955–34964. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M604616200
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by Master's thesis grant (code: 96/3/02/16670) from Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. The authors would like to thank all the participants for taking part in this study and specially Dr. Maryam Cheraghzadeh, Ms. Tahereh Seifi, and Mr. Saleh Zahraei for supporting this project. The authors wish to appreciate Department of Clinical Biochemistry of Jundishapur University of Medical Science. Also they would like to appreciate Dr. Leila Heidarvand for comments and suggestions on manuscript improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabani Sadr, N.K., Shafiei, M., Galehdari, H. et al. The Effect of Sialic Acid on the Expression of miR-218, NF-kB, MMP-9, and TIMP-1. Biochem Genet 58, 883–900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09981-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09981-y