Abstract
Purpose
The success of phytoremediation relies on beneficial plant-microbe interactions. However, the changes of soil microbiota, during the phytoremediation of ion-adsorption rare earth element (REE) mine tailings, are far from understood. The present study was conducted to reveal the co-occurrence patterns and key regulating factors of bacterial communities in ion-adsorption REE mine tailings with phytoremediation.
Materials and methods
A field experiment was conducted on an ion-adsorption REE mine tailing to test three phytoremediation strategies: (i) phytostabilization with grasses, (ii) phytostabilization with economic crops, and (iii) phytoextraction with REE hyperaccumulators. The bacterial community diversity, co-occurrence patterns, and the key regulating environmental factors in bulk and rhizospheric soils after 16 months of reclamation were studied by 16S Illumina high-throughput sequencing.
Results and discussion
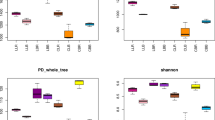
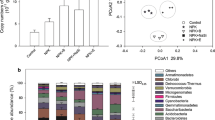
The soils of plots with REEs-hyperaccumulators had significantly higher α-diversity than those planted with non-accumulators. After phytoremediation, the diversity and relative abundances of bacteria assisting in nutrient acquisition pronouncedly increased in the bulk soil of the reclaimed plots. Some plant growth–promoting bacteria (PGPB), e.g., Rhodanobacter, Streptomyces, and Bacillus, were enriched in the rhizospheric soil samples. Meanwhile, soil nutrient (total carbon and total nitrogen) concentration and REE availability were the most significant factors shaping the bacterial communities. Furthermore, special bacterial consortia of Bacilli took up the positions of the keystone species.
Conclusions
The results revealed the co-occurrence patterns and key regulating factors of bacterial communities in ion-adsorption REE mine tailings, which will provide more crucial information for the optimization of the reclamation of REE tailings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai C, Liang GQ, Sun JW, Wang XB, He P, Zhou W, He XH (2015) Reduced dependence of rhizosphere microbiome on plant-derived carbon in 32-year long-term inorganic and organic fertilized soils. Soil Biol Biochem 80:70–78
Ajilogba CF, Babalola OO (2013) Integrated management strategies for tomato Fusarium wilt. Biocontrol Sci 18(3):117–127
Alonso E, Sherman AM, Wallington TJ, Everson MP, Field FR, Roth R, Kirchain RE (2012) Evaluating rare earth element availability: a case with revolutionary demand from clean technologies. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3406–3414
Alvarez-Lopez V, Prieto-Fernandez A, Becerra-Castro C, Monterroso C, Kidd PS (2016) Rhizobacterial communities associated with the flora of three serpentine outcrops of the Iberian Peninsula. Plant Soil 403(1–2):233–252
Banerjee S, Schlaeppi K, van der Heijden MGA (2018) Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(9):567–576
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi : an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media
Bi YL, Wang K, Wang J (2018) Effect of different inoculation treatments on AM fungal communities and the sustainability of soil remediation in Daliuta coal mining subsidence area in northwest China. Appl Soil Ecol 132:107–113
Bokulich NA, Kaehler BD, Rideout JR, Dillon M, Bolyen E, Knight R, Huttley GA, Caporaso JG (2018) Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6:17
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich N, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo JR, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang LJ, Kaehler BD, Bin Kang K, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, vander Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan YH, Wang MX, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang YL, Zhu QY, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37(8):852–857
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583
Chao YQ, Liu WS, Chen YM, Chen WH, Zhao LH, Ding QB, Wang SZ, Tang YT, Zhang T, Qiu RL (2016) Structure, variation, and co-occurrence of soil microbial communities in abandoned sites of a rare earth elements mine. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11481–11490
Chen YM, Ding QB, Chao YQ, Wei XG, Wang SZ, Qiu RL (2018a) Structural development and assembly patterns of the root-associated microbiomes during phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ 644:1591–1601
Chen YY, Liu WS, Ding KB, Tang YT, Qiu RL (2018b) Effects of organic amendments and biochar on ecological remediation of ionic rare earth mine tailing. Acta Scien Circum 38(12):4769–4778
Chen LJ, Jiang YJ, Liang C, Luo Y, Xu QS, Han C, Zhao QG, Sun B (2019) Competitive interaction with keystone taxa induced negative priming under biochar amendments. Microbiome 7:18
Ciesielski H, Sterckeman T (1997) Determination of cation exchange capacity and exchangeable cations in soils by means of cobalt hexamine trichloride. Effects of experimental conditions. Agronomie (Paris) 17(1):1–7
Coleman-Derr D, Desgarennes D, Fonseca-Garcia C, Gross S, Clingenpeel S, Woyke T, North G, Visel A, Partida-Martinez LP, Tringe SG (2016) Plant compartment and biogeography affect microbiome composition in cultivated and native Agave species. New Phytol 209(2):798–811
Deng SQ, Ke T, Li LT, Cai SW, Zhou YY, Liu Y, Guo LM, Chen LZ, Zhang DY (2018) Impacts of environmental factors on the whole microbial communities in the rhizosphere of a metal-tolerant plant: Elsholtzia haichowensis Sun. Environ Pollut 237:1088–1097
Edwards J, Johnson C, Santos-Medellin C, Lurie E, Podishetty NK, Bhatnagar S, Eisen JA, Sundaresan V (2015) Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(8):E911–E920
Erdős P, Rényi A (1960) On the evolution of random graphs. Publ Math Inst Hung Acad Sci (5):17–61
Garaiyurrebaso O, Garbisu C, Blanco F, Lanzen A, Martin I, Epelde L, Becerril JM, Jechalke S, Smalla K, Grohmann E, Alkorta I (2017) Long-term effects of aided phytostabilisation on microbial communities of metal-contaminated mine soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93(3)
Garcia-Gonzalo P, del Real AEP, Lobo M, Perez-Sanz A (2017) Different genotypes of Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke grown on chromium-contaminated soils influence root organic acid composition and rhizosphere bacterial communities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(33):25713–25724
Giese EC, Jordao CS (2019) Biosorption of lanthanum and samarium by chemically modified free Bacillus subtilis cells. Appl Water Sci 9(8):8
Grandlic CJ, Mendez MO, Chorover J, Machado B, Maier RM (2008) Plant growth-promoting bacteria for phytostabilization of mine tailings. Environ Sci Technol 42(6):2079–2084
Grandlic CJ, Palmer MW, Maier RM (2009) Optimization of plant growth-promoting bacteria-assisted phytostabilization of mine tailings. Soil Biol Biochem 41(8):1734–1740
Griffiths BS, Philippot L (2013) Insights into the resistance and resilience of the soil microbial community. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37(2):112–129
Groom JD, Ford SM, Pesesky MW, Lidstrom ME (2019) A mutagenic screen identifies a TonB-dependent receptor required for the lanthanide metal switch in the type I methanotroph “Methylotuvimicrobium buryatense” 5GB1C. J Bacteriol 201(15):17
Hou DD, Wang K, Liu T, Wang HX, Lin Z, Qian J, Lu LL, Tian SK (2017) Unique rhizosphere micro-characteristics facilitate phytoextraction of multiple metals in soil by the hyperaccumulating plant Sedum alfredii. Environ Sci Technol 51(10):5675–5684
Hou DD, Wang RZ, Gao XY, Wang K, Lin Z, Ge J, Liu T, Wei S, Chen WK, Xie RH, Yang XE, Lu LL, Tian SK (2018) Cultivar-specific response of bacterial community to cadmium contamination in the rhizosphere of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 241:63–73
Houba VJG, Temminghoff EJM, Gaikhorst GA, van Vark W (2000) Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Commun Soil Sci Plan 31(9-10)
Jaillard B, Rapaport A, Harmand J, Brauman A, Nunan N (2014) Community assembly effects shape the biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships. Funct Ecol 28(6):1523–1533
Li JM, Jin ZX, Gu QP (2011) Effect of plant species on the function and structure of the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of lead-zinc mine tailings in Zhejiang, China. Can J Microbiol 57(7):569–577
Li Y, Jia ZJ, Sun QY, Zhan J, Yang Y, Wang D (2016) Ecological restoration alters microbial communities in mine tailings profiles. Sci Rep 6:11
Liu SH, Liu W, Yang MX, Zhou LY, Liang H (2016) The genetic diversity of soil bacteria affected by phytoremediation in a typical barren rare earth mined site of South China. Springerplus 5:12
Liu JL, Yao J, Wang F, Min N, Gu JH, Li ZF, Sunahara G, Duran R, Solevic-Knudsen T, Hudson-Edwards KA, Alakangas L (2019a) Bacterial diversity in typical abandoned multi-contaminated nonferrous metal(loid) tailings during natural attenuation. Environ Pollut 247:98–107
Liu WS, Guo MN, Liu C, Yuan M, Chen XT, Huot H, Zhao CM, Tang YT, Morel JL, Qiu RL (2019b) Water, sediment and agricultural soil contamination from an ion-adsorption rare earth mining area. Chemosphere 216:75–83
Liu WS, Wu LL, Zheng MY, Chao YQ, Zhao CM, Zhong X, Ding KB, Huot H, Zhang MY, Tang YT, Li C, Qiu RL (2019c) Controls on rare-earth element transport in a river impacted by ion-adsorption rare-earth mining. Sci Total Environ 660:697–704
Liu WS, Zheng HX, Guo MN, Liu C, Huot H, Morel JL, van der Ent A, Tang YT, Qiu RL (2019d) Co-deposition of silicon with rare earth elements (REEs) and aluminium in the fern Dicranopteris linearis from China. Plant Soil 437(1–2):427–437
Lopez S, Piutti S, Vallance J, Morel JL, Echevarria G, Benizri E (2017) Nickel drives bacterial community diversity in the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Alyssum murale. Soil Biol Biochem 114:121–130
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8228–8235
Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Kelley ST, Knight R (2007) Quantitative and qualitative beta diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(5):1576–1585
Luo SL, Chen L, Chen JL, Xiao X, Xu TY, Wan Y, Rao C, Liu CB, Liu YT, Lai C, Zeng GM (2011) Analysis and characterization of cultivable heavy metal-resistant bacterial endophytes isolated from Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. and their potential use for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 85(7):1130–1138
Ma B, Wang HZ, Dsouza M, Lou J, He Y, Dai ZM, Brookes PC, Xu JM, Gilbert JA (2016) Geographic patterns of co-occurrence network topological features for soil microbiota at continental scale in eastern China. ISME J 10(8):1891–1901
Martinez RE, Pourret O, Takahashi Y (2014) Modeling of rare earth element sorption to the Gram positive Bacillus subtilis bacteria surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 413:106–111
Morriën E, Hannula SE, Snoek LB, Helmsing NR, Zweers H, de Hollander M, Soto RL, Bouffaud M-L, Buée M, Dimmers W, Duyts H, Geisen S, Girlanda M, Griffiths RI, Jørgensen H-B, Jensen J, Plassart P, Redecker D, Schmelz RM, Schmidt O, Thomson BC, Tisserant E, Uroz S, Winding A, Bailey MJ, Bonkowski M, Faber JH, Martin F, Lemanceau P, de Boer W, van Veen JA, van der Putten WH (2017) Soil networks become more connected and take up more carbon as nature restoration progresses. Nat Commun 8(1)
Newman MEJ (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(23):8577–8582
Ofek M, Voronov-Goldman M, Hadar Y, Minz D (2014) Host signature effect on plant root-associated microbiomes revealed through analyses of resident vs. active communities. Environ Microbiol 16(7):2157–2167
Oteino N, Lally RD, Kiwanuka S, Lloyd A, Ryan D, Germaine KJ, Dowling DN (2015) Plant growth promotion induced by phosphate solubilizing endophytic Pseudomonas isolates. Front Microbiol 6:9
Peiffer JA, Spor A, Koren O, Jin Z, Tringe SG, Dangl JL, Buckler ES, Ley RE (2013) Diversity and heritability of the maize rhizosphere microbiome under field conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(16):6548–6553
Puri A, Padda KP, Chanway CP (2015) Can a diazotrophic endophyte originally isolated from lodgepole pine colonize an agricultural crop (corn) and promote its growth? Soil Biol Biochem 89:210–216
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D590–D596
Rastogi G, Barua S, Sani RK, Peyton BM (2011) Investigation of microbial populations in the extremely metal-contaminated Coeur d’Alene River sediments. Microbial Ecol 62(1):1–13
Reinhold-Hurek B, Bunger W, Burbano CS, Sabale M, Hurek T (2015) Roots shaping their microbiome: global hotspots for microbial activity. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53(1):403–424
Shi S, Nuccio EE, Shi ZJ, He Z, Zhou J, Firestone MK (2016) The interconnected rhizosphere: high network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol Lett 19(8):926–936
Shi P, Zhang Y, Hu Z, Ma K, Wang H, Chai T (2017) The response of soil bacterial communities to mining subsidence in the west China aeolian sand area. Appl Soil Ecol 121:1–10
Solano R, de la Iglesia MTP, Probanza A, Garcia JAL, Megias M, Manero FJG (2006) Screening for PGPR to improve growth of Cistus ladanifer seedlings for reforestation of degraded Mediterranean ecosystems. Plant Soil 287(1–2):59–68
Sun WM, Xiao EZ, Krumins V, Haggblom MM, Dong YR, Pu ZL, Li BQ, Wang Q, Xiao TF, Li FB (2018a) Rhizosphere microbial response to multiple metal(loid)s in different contaminated arable soils indicates crop-specific metal-microbe interactions. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(24):13
Sun XY, Zhou YL, Tan YJ, Wu ZX, Lu P, Zhang GH, Yu FX (2018b) Restoration with pioneer plants changes soil properties and remodels the diversity and structure of bacterial communities in rhizosphere and bulk soil of copper mine tailings in Jiangxi Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(22):22106–22119
Walters WA, Jin Z, Youngblut N, Wallace JG, Sutter J, Zhang W, Gonzalez-Pena A, Peiffer J, Koren O, Shi QJ, Knight R, del Rio TG, Tringe SG, Buckler ES, Dangl JL, Ley RE (2018) Large-scale replicated field study of maize rhizosphere identifies heritable microbes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(28):7368–7373
Wang CY, Wu BD, Jiang K, Wei M, Wang S (2019) Effects of different concentrations and types of Cu and Pb on soil N-fixing bacterial communities in the wheat rhizosphere. Appl Soil Ecol 144:51–59
Wei ZW, Hao ZK, Li XH, Guan ZB, Cai YJ, Liao XR (2019) The effects of phytoremediation on soil bacterial communities in an abandoned mine site of rare earth elements. Sci Total Environ 670:950–960
Wu ZX, Yu FX, Sun XY, Wu SL, Li XH, Liu TY, Li YQ (2018) Long term effects of Lespedeza bicolor revegetation on soil bacterial communities in Dexing copper mine tailings in Jiangxi Province, China. Appl Soil Ecol 125:192–201
Yan ZS, Hao Z, Wu HF, Jiang HL, Yang MZ, Wang CH (2019) Co-occurrence patterns of the microbial community in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated riverine sediments. J Hazard Mater 367:99–108
Yang SX, Liao B, Yang ZH, Chai LY, Li JT (2016) Revegetation of extremely acid mine soils based on aided phytostabilization: a case study from southern China. Sci Total Environ 562:427–434
Yang JH, Zhang XW, Xie YW, Song C, Sun JY, Zhang Y, Giesy JP, Yu HX (2017) Ecogenomics of zooplankton community reveals ecological threshold of ammonia nitrogen. Environ Sci Technol 51(5):3057–3064
Yang WH, Li P, Rensing C, Ni WZ, Xing SH (2019) Biomass, activity and structure of rhizosphere soil microbial community under different metallophytes in a mining site. Plant Soil 434(1–2):245–262
Ye RW, Thomas SM (2001) Microbial nitrogen cycles: physiology, genomics and applications. Curr Opin Microbiol 4(3):307–312
Yuan M, Guo MN, Liu WS, Liu C, van der Ent A, Morel JL, Huot H, Zhao WY, Wei XG, Qiu RL, Tang YT (2017) The accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements in hydroponically grown Phytolacca americana L. Plant Soil 421(1–2):67–82
Zeng P, Guo ZH, Xiao XY, Peng C (2019) Dynamic response of enzymatic activity and microbial community structure in metal(loid)-contaminated soil with tree-herb intercropping. Geoderma 345:5–16
Zhalnina K, Louie KB, Hao Z, Mansoori N, da Rocha UN, Shi SJ, Cho HJ, Karaoz U, Loque D, Bowen BP, Firestone MK, Northen TR, Brodie EL (2018) Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat Microbiol 3(4):470–480
Zhang HH, Feng J, Chen SN, Zhao ZF, Li BQ, Wang Y, Jia JY, Li SL, Wang Y, Yan MM, Lu KY, Hao HY (2019) Geographical patterns of nirS gene abundance and nirS-type denitrifying bacterial community associated with activated sludge from different wastewater treatment plants. Microbial Ecol 77(2):304–316
Zhao X, Huang J, Lu J, Sun Y (2019) Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotox Environ Safe 170:218–226
Zhong WH, Gu T, Wang W, Zhang B, Lin XG, Huang QR, Shen WS (2010) The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 326(1–2):511–522
Zhou LY, Li ZL, Liu W, Liu SH, Zhang LM, Zhong LY, Luo XM, Liang H (2015) Restoration of rare earth mine areas: organic amendments and phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(21):17151–17160
Zloch M, Thiem D, Gadzala-Kopciuch R, Hrynkiewicz K (2016) Synthesis of siderophores by plant-associated metallotolerant bacteria under exposure to Cd2+. Chemosphere 156:312–325
Zornoza R, Acosta JA, Martinez-Martinez S, Faz A, Baath E (2015) Main factors controlling microbial community structure and function after reclamation of a tailing pond with aided phytostabilization. Geoderma 245:1–10
Funding
This study was funded by the Key R&D Program of Jiangxi Province (20192ACB70016), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 4177134), the Sino-French Cai Yuanpei Project (No. 38896SC), and the 111 Project (No. B18060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yongtao Li
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2938 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhong, X., Huot, H. et al. Reclamation with organic amendments and plants remodels the diversity and structure of bacterial community in ion-adsorption rare earth element mine tailings. J Soils Sediments 20, 3669–3680 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02704-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02704-1