Abstract
Purpose
To investigate cerebral amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) changes during a single hemodialysis (HD) in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients who need maintenance HD.
Materials and Methods
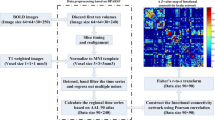
A total of 24 patients and 27 healthy subjects were included. The patients underwent neuropsychological tests and took twice resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) (before and after HD). Healthy group had one rs-fMRI. The zALFF based on rs-fMRI was calculated. Paired t and independent t test was applied to compare zALFF among groups. The associations between zALFF and duration of HD, ultrafiltration volume, and neuropsychological tests was calculated by partial correlation.
Results
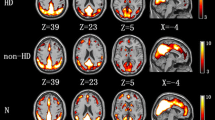
Compared to healthy group, patients before HD showed significant worse performances on digit symbol test (DST) and serial dotting test (SDT). Patients after HD performed DST better than before HD. The patients after HD showed higher zALFF in left putamen than before HD. Multiple regions of both HD groups showed significant lower zALFF than healthy group. The zALFF of left putamen of patients after HD was significant negative correlated with the ultrafiltration volume (R = −0.679). The zALFF in patients before HD exhibited significantly positive or negative correlations with DST and SDT in multiple regions. The zALFF of patients after HD significantly negative correlated with DST in right temporal, positive and negative correlated with ultrafiltration volume in right frontal, left putamen respectively.
Conclusion
ESRD patients showed changed spontaneous brain activity and cognitive impairments. After a single HD session, patients performed better in neuropsychological test, and spontaneous brain activity changed in left putamen. Ultrafiltration volume might be associated with activity of left putamen.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V, Neal B, Patrice HM, Okpechi I, Zhao MH, Lv J, Garg AX, Knight J, Rodgers A, Gallagher M, Kotwal S, Cass A, Perkovic V. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease. Lancet. 2013;385:1975–82.
Coresh J, Jafar TH. Disparities in worldwide treatment of kidney failure. Lancet. 2015;385:1926–8.
Wetmore JB, Collins AJ. Global challenges posed by the growth of end-stage renal disease. Ren Replace Ther. 2016;2:1–7.
Ong CY, Low SG, Vasanwala FF, Fook-Chong SM, Kaushik M, Low LL. Incidence and mortality rates of varicella among end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients in Singapore General Hospital, a 12-year review. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18:118.
Hermann DM, Kribben A, Bruck H. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease: clinical findings, risk factors and consequences for patient care. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014;121:627–32.
Madan P, Kalra OP, Agarwal S, Tandon OP. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:440–4.
Kurella M, Chertow GM, Luan J, Yaffe K. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:1863–9.
Chen HJ, Qi R, Kong X, Wen J, Liang X, Zhang Z, Li X, Lu GM, Zhang LJ. The impact of hemodialysis on cognitive dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal disease: a resting-state functional MRI study. Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30:1247–56.
Fazekas G, Fazekas F, Schmidt R, Kapeller P, Offenbacher H, Krejs GJ. Brain MRI findings and cognitive impairment in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis treatment. J Neurol Sci. 1995;134:83–8.
Bugnicourt JM, Godefroy O, Chillon JM, Choukroun G, Massy ZA. Cognitive disorders and dementia in CKD: the neglected kidney-brain axis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:353–63.
Sehgal AR, Grey SF, DeOreo PB, Whitehouse PJ. Prevalence, recognition, and implications of mental impairment among hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;30:41–9.
Murray AM, Tupper DE, Knopman DS, Gilbertson DT, Pederson SL, Li S, Smith GE, Hochhalter AK, Collins AJ, Kane RL. Cognitive impairment in hemodialysis patients is common. Neurology. 2006;67:216–23.
Hooper SR, Gerson AC, Butler RW, Gipson DS, Mendley SR, Lande MB, Shinnar S, Wentz A, Matheson M, Cox C, Furth SL, Warady BA. Neurocognitive functioning of children and adolescents with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6:1824–30.
Elias MF, Elias PK, Seliger SL, Narsipur SS, Dore GA, Robbins MA. Chronic kidney disease, creatinine and cognitive functioning. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:2446–52.
Ding D, Li P, Ma XY, Dun WH, Yang SF, Ma SH, Liu HJ, Zhang M. The relationship between putamen-SMA functional connectivity and sensorimotor abnormality in ESRD patients. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018;12:1346–54.
Zhang R, Liu K, Yang L, Zhou T, Qian S, Li B, Peng Z, Li M, Sang S, Jiang Q, Sun G. Reduced white matter integrity and cognitive deficits in maintenance hemodialysis ESRD patients: a diffusion-tensor study. Eur Radiol. 2015;25:661–8.
Drew DA, Bhadelia R, Tighiouart H, Novak V, Scott TM, Lou KV, Shaffi K, Weiner DE, Sarnak MJ. Anatomic brain disease in hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;61:271–8.
Qiu Y, Lv X, Su H, Jiang G, Li C, Tian J. Structural and functional brain alterations in end stage renal disease patients on routine hemodialysis: a voxel-based morphometry and resting state functional connectivity study. PLoS One. 2014;9:e98346.
Prohovnik I, Post J, Uribarri J, Lee H, Sandu O, Langhoff E. Cerebrovascular effects of hemodialysis in chronic kidney disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:1861–9.
Jiang XL, Wen JQ, Zhang LJ, Zheng G, Li X, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Zheng LJ, Wu L, Chen HJ, Kong X, Luo S, Lu GM, Ji XM, Zhang ZJ. Cerebral blood flow changes in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients: an arterial-spin labeling MR imaging. Metab Brain Dis. 2016;31:929–36.
Ni L, Wen J, Zhang LJ, Zhu T, Qi R, Xu Q, Liang X, Zhong J, Zheng G, Lu GM. Aberrant default-mode functional connectivity in patients with end-stage renal disease: a resting-state functional MR imaging study. Radiology. 2014;271:543–52.
Zhang XD, Wen JQ, Xu Q, Qi R, Chen HJ, Kong X, Wei LD, Xu M, Zhang LJ, Lu GM. Altered long- and short-range functional connectivity in the patients with end-stage renal disease: a resting-state functional MRI study. Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30:1175–86.
Zheng G, Wen J, Zhang L, Zhong J, Liang X, Ke W, Kong X, Zhao T, He Y, Zuo X, Luo S, Zhang LJ, Lu GM. Altered brain functional connectivity in hemodialysis patients with end-stage renal disease: a resting-state functional MR imaging study. Metab Brain Dis. 2014;29:777–86.
Chen HJ, Wang YF, Qi R, Schoepf UJ, Varga-Szemes A, Ball BD, Zhang Z, Kong X, Wen J, Li X, Lu GM, Zhang LJ. Altered Amygdala Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Maintenance Hemodialysis End-Stage Renal Disease Patients with Depressive Mood. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:2223–33.
Liang X, Wen J, Ni L, Zhong J, Qi R, Zhang LJ, Lu GM. Altered pattern of spontaneous brain activity in the patients with end-stage renal disease: a resting-state functional MRI study with regional homogeneity analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71507.
Li C, Su HH, Qiu YW, Lv XF, Shen S, Zhan WF, Tian JZ, Jiang GH. Regional homogeneity changes in hemodialysis patients with end stage renal disease: in vivo resting-state functional MRI study. PLoS One. 2014;9:e87114.
Li P, Ding D, Ma XY, Zhang HW, Liu JX, Zhang M. Altered intrinsic brain activity and memory performance improvement in patients with end-stage renal disease during a single dialysis session. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018;12:1640–9.
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF. Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev. 2007;29:83–91.
Luo S, Qi RF, Wen JQ, Zhong JH, Kong X, Liang X, Xu Q, Zheng G, Zhang Z, Zhang LJ, Lu GM. Abnormal Intrinsic Brain Activity Patterns in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Resting-State Functional MR Imaging Study. Radiology. 2016;278:181–9.
Jia XZ, Wang J, Sun HY, Zhang H, Liao W, Wang Z, Yan CG, Song XW, Zang YF. RESTplus: an improved toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. Sci Bull. 2019;64:953–4.
Song XW, Dong ZY, Long XY, Li SF, Zuo XN, Zhu CZ, He Y, Yan CG, Zang YF. REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25031.
Cao J, Chen X, Chen J, Ai M, Gan Y, Wang W, Lv Z, Zhang S, Zhang S, Wang S, Kuang L, Fang W. Resting-state functional MRI of abnormal baseline brain activity in young depressed patients with and without suicidal behavior. J Affect Disord. 2016;205:252–63.
Song SH, Kim IJ, Kim SJ, Kwak IS, Kim YK. Cerebral glucose metabolism abnormalities in patients with major depressive symptoms in pre-dialytic chronic kidney disease: statistical parametric mapping analysis of F-18-FDG PET, a preliminary study. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2008;62:554–61.
Kielstein H, Suntharalingam M, Perthel R, Song R, Schneider SM, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Jäger K, Bode-Böger SM, Kielstein JT. Role of the endogenous nitric oxide inhibitor asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depression and behavioural changes: clinical and preclinical data in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30:1699–705.
Murray AM. Cognitive impairment in the aging dialysis and chronic kidney disease populations: an occult burden. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2008;15:123–32.
Toyoda K, Fujii K, Fujimi S, Kumai Y, Tsuchimochi H, Ibayashi S, Iida M. Stroke in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a 22-year single-center study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45:1058–66.
Yang H, Long XY, Yang Y, Yan H, Zhu CZ, Zhou XP, Zang YF, Gong QY. Amplitude of low frequency fluctuation within visual areas revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Neuroimage. 2007;36:144–52.
Winkelman JW, Gagnon A, Clair AG. Sensory symptoms in restless legs syndrome: the enigma of pain. Sleep Med. 2013;14:934–42.
Gorges M, Rosskopf J, Müller HP, Lindemann K, Hornyak M, Kassubek J. Patterns of increased intrinsic functional connectivity in patients with restless legs syndrome are associated with attentional control of sensory inputs. Neurosci Lett. 2016;617:264–9.
van Beilen M, Leenders KL. Putamen FDOPA uptake and its relationship tot cognitive functioning in PD. J Neurol Sci. 2006;248:68–71.
Ren P, Lo RY, Chapman BP, Mapstone M, Porsteinsson A, Lin F; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Longitudinal Alteration of Intrinsic Brain Activity in the Striatum in Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;54:69–78.
Dahlin E, Neely AS, Larsson A, Bäckman L, Nyberg L. Transfer of learning after updating training mediated by the striatum. Science. 2008;320:1510–2.
Han Y, Wang J, Zhao Z, Min B, Lu J, Li K, He Y, Jia J. Frequency-dependent changes in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a resting-state fMRI study. Neuroimage. 2011;55:287–95.
Bai F, Liao W, Watson DR, Shi Y, Wang Y, Yue C, Teng Y, Wu D, Yuan Y, Jia J, Zhang Z. Abnormal whole-brain functional connection in amnestic mild cognitive impairment patients. Behav Brain Res. 2011;216:666–72.
Cheng BC, Chen PC, Chen PC, Lu CH, Huang YC, Chou KH, Li SH, Lin AN, Lin WC. Decreased cerebral blood flow and improved cognitive function in patients with end-stage renal disease after peritoneal dialysis: An arterial spin-labelling study. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:1415–24.
Findlay MD, Dawson J, Dickie DA, Forbes KP, McGlynn D, Quinn T, Mark PB. Investigating the Relationship between Cerebral Blood Flow and Cognitive Function in Hemodialysis Patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:147–58.
Polinder-Bos HA, García DV, Kuipers J, Elting JWJ, Aries MJH, Krijnen WP, Groen H, Willemsen ATM, van Laar PJ, Strijkert F, Luurtsema G, Slart RHJA, Westerhuis R, Gansevoort RT, Gaillard CAJM, Franssen CFM. Hemodialysis Induces an Acute Decline in Cerebral Blood Flow in Elderly Patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:1317–25. Erratum in: J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:2256.
Acknowledgements
Our team thank all patients and healthy volunteers for their participation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
C. Peng, H. Yang, Q. Ran, L. Zhang, C. Liu, Y. Fang, Y. Liu, Y. Cao, R. Liang, H. Ren, Q. Hu, X. Mei, Y. Jiang and T. Luo declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, C., Yang, H., Ran, Q. et al. Immediate Abnormal Intrinsic Brain Activity Patterns in Patients with End-stage Renal Disease During a Single Dialysis Session. Clin Neuroradiol 31, 373–381 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-020-00915-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-020-00915-0