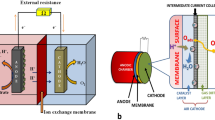
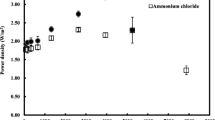
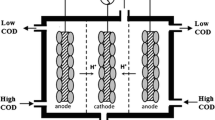
Abstract
We report a novel strategy of integrating microbial fuel cell (MFC) with microbial immobilization technology (MIT) in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) to test the performance of nitrate removal for the first time. Results showed that MFC could enhance nitrate removal in the novel integrated system, especially for wastewater with low carbon-to-nitrogen ratios, and the nitrate removal efficiency reached 91.35% in the lab-scale integrated system, including 12.25% nitrate consumption by MFC in one typical cycle. The anode of MFC recovered energy in the form of electricity, floating cathode of MFC prevented the loss of immobilized denitrifying bacteria particles and degraded a portion of nitrate, and the maximum voltage production of MFC was 0.246 V. The novel integrated system in this paper showed excellent nitrate removal performance and it will be a highly potential novel setup for efficient nitrate removal of wastewater treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCarty, P. L. (2018) What is the best biological process for nitrogen removal: when and why? Environ. Sci. Technol. 52: 3835–3841.
Shannon, M. A., P. W. Bohn, M. Elimelech, J. G. Georgiadis, B. J. Marinas, and A. M. Mayes (2008) Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature. 452: 301–310.
Ji, B., K. Yang, L. Zhu, Y. Jiang, H. Wang, J. Zhou, and H. Zhang (2015) Aerobic denitrification: A review of important advances of the last 30 years. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 20: 643–651.
Wang, D., G. Wang, F. Yang, C. Liu, L. Kong, and Y. Liu (2018) Treatment of municipal sewage with low carbon-to-nitrogen ratio via simultaneous partial nitrification, anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and denitrification (SNAD) in a non-woven rotating biological contactor. Chemosphere. 208: 854–861.
Liu, J., Y. Yuan, B. Li, Q. Zhang, L. Wu, X. Li, and Y. Peng (2017) Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater in an anaerobic-aerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor with sludge fermentation products as carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 244: 1158–1165.
Liu, F., Y. Tian, Y. Ding, and Z. Li (2016) The use of fermentation liquid of wastewater primary sedimentation sludge as supplemental carbon source for denitrification based on enhanced anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 219: 6–13.
Jia, L., R. Wang, L. Feng, X. Zhou, J. Lv, and H. Wu (2018) Intensified nitrogen removal in intermittently-aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands with agricultural biomass: Effect of influent C/N ratios. Chem. Eng. J. 345: 22–30.
Sekoai, P. T., A. A. Awosusi, K. O. Yoro, M. Singo, O. Oloye, A. O. Ayeni, M. Bodunrin, and M. O. Daramola (2018) Microbial cell immobilization in biohydrogen production: a short overview. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 38: 157–171.
Jo, S., S. Park, Y. Oh, J. Hong, H. J. Kim, K. J. Kim, K. K. Oh, and S. H. Lee (2019) Development of cellulose hydrogel microspheres for lipase immobilization. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 24: 145–154.
Sekaran, G., S. Karthikeyan, C. Nagalakshmi, and A. B. Mandal (2013) Integrated Bacillus sp. immobilized cell reactor and Synechocystis sp. algal reactor for the treatment of tannery wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 20: 281–291.
Kim, H. J., J. N. Jin, E. Kan, K. J. Kim, and S. H. Lee (2017) Bacterial cellulose-chitosan composite hydrogel beads for enzyme immobilization. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 22: 89–94.
Dong, H., W. Wang, Z. Song, H. Dong, J. Wang, S. Sun, Z. Zhang, M. Ke, Z. Zhang, W. M. Wu, G. Zhang, and J. Ma (2017) A high-efficiency denitrification bioreactor for the treatment of acrylonitrile wastewater using waterborne polyurethane immobilized activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 239: 472–481.
Song, S. H., S. S. Choi, K. Park, and Y. J. Yoo (2005) Novel hybrid immobilization of microorganisms and its applications to biological denitrification. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 37: 567–573.
Ranjan, B., S. Pillai, K. Permaul, and S. Singh (2019) Simultaneous removal of heavy metals and cyanate in a wastewater sample using immobilized cyanate hydratase on magnetic-multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 363: 73–80.
Katam, K. and D. Bhattacharyya (2019) Simultaneous treatment of domestic wastewater and bio-lipid synthesis using immobilized and suspended cultures of microalgae and activated sludge. J. Ind. Eng Chem. 69: 295–303.
Sarioglu, O. F., O. Yasa, A. Celebioglu, T. Uyar, and T. Tekinay (2013) Efficient ammonium removal from aquatic environments by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus STB1 immobilized on an electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibrous web. Green Chem. 15: 2566–2572.
Zhang, Y. and I. Angelidaki (2012) Bioelectrode-based approach for enhancing nitrate and nitrite removal and electricity generation from eutrophic lakes. Water Res. 46: 6445–6453.
Cetin, E., E. Karakas, E. Dulekgurgen, S. Ovez, M. Kolukirik, and G. Yilmaz (2018) Effects of high-concentration influent suspended solids on aerobic granulation in pilot-scale sequencing batch reactors treating real domestic wastewater. Water Res. 131: 74–89.
Zhang, T., M. F. Shao, and L. Ye (2012) 454 Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. ISME J. 6: 1137–1147.
Seviour, R. J., T. Mino, and M. Onuki (2003) The microbiology of biological phosphorus removal in activated sludge systems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27: 99–127.
Saunders, A. M., M. Albertsen, J. Vollertsen, and P. H. Nielsen (2016) The activated sludge ecosystem contains a core community of abundant organisms. ISME J. 10: 11–20.
Flemming, H. C. and S. Wuertz (2019) Bacteria and archaea on earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 17: 247–260.
Goglio, A., M. Tucci, B. Rizzi, A. Colombo, P. Cristiani, and A. Schievano (2019) Microbial recycling cells (MRCs): A new platform of microbial electrochemical technologies based on biocompatible materials, aimed at cycling carbon and nutrients in agro-food systems. Sci. Total Environ. 649: 1349–1361.
Shu, D., Y. He, H. Yue, and Q. Wang (2015) Microbial structures and community functions of anaerobic sludge in six full-scale wastewater treatment plants as revealed by 454 high-throughput pyrosequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 186: 163–172.
Yang, Q., H. Zhao, N. Zhao, J. Ni, and X. Gu (2016) Enhanced phosphorus flux from overlying water to sediment in a bioelectrochemical system. Bioresour. Technol. 216: 182–187.
Santoro, C., C. Arbizzani, B. Erable, and I. Ieropoulos (2017) Microbial fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. A review. J. Power Sources. 356: 225–244.
Wang, H. and Z. J. Ren (2013) A comprehensive review of microbial electrochemical systems as a platform technology. Biotechnol. Adv. 31: 1796–1807.
Uria, N., I. Ferrera, and J. Mas (2017) Electrochemical performance and microbial community profiles in microbial fuel cells in relation to electron transfer mechanisms. BMC Microbiol. 17: 208.
Clauwaert, P., K. Rabaey, P. Aelterman, L. De Schamphelaire, T. H. Pham, P. Boeckx, N. Boon, and W. Verstraete (2007) Biological denitrification in microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41: 3354–3360.
Virdis, B., K. Rabaey, R. A. Rozendal, Z. Yuan, and J. Keller (2010) Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and carbon removal in microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 44: 2970–2980.
Huang, H., S. Cheng, F. Li, Z. Mao, Z. Lin, and K. Cen (2019) Enhancement of the denitrification activity by exoelectrogens in single-chamber air cathode microbial fuel cells. Chemosphere. 225: 548–556.
Srinivasan, V., J. Weinrich, and C. Butler (2016) Nitrite accumulation in a denitrifying biocathode microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2: 344–352.
Wang, X., Y. Tian, H. Liu, X. Zhao, and Q. Wu (2019) Effects of influent COD/TN ratio on nitrogen removal in integrated constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell systems. Bioresour. Technol. 271: 492–495.
Du, Z., H. Li, and T. Gu (2007) A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: A promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnol. Adv. 25: 464–482.
Hang, Q., H. Wang, Z. Chu, B. Ye, C. Li, and Z. Hou (2016) Application of plant carbon source for denitrification by constructed wetland and bioreactor: review of recent development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23: 8260–8274.
Liu, X. W., Y. P. Wang, Y. X. Huang, X. F. Sun, G. P. Sheng, R. I. Zeng, F. Li, F. Dong, S. G. Wang, Z. H. Tong, and H. Q. Yu (2011) Integration of a microbial fuel cell with activated sludge process for energy-saving wastewater treatment: taking a sequencing batch reactor as an example. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 108: 1260–1267.
Xiao, B., M. Luo, X. Wang, Z. Li, H. Chen, I. Liu, and X. Guo (2017) Electricity production and sludge reduction by integrating microbial fuel cells in anoxic-oxic process. Waste Manag. 69: 346–352.
Liu, W., H. Jia, I. Wang, H. Zhang, C. Xin, and Y. Zhang (2018) Microbial fuel cell and membrane bioreactor coupling system: recent trends. Environ. Sci. Pollution Res. 25: 23631–23644.
Hou, L., I. Li, Z. Zheng, Q. Sun, Y. Liu, and K. Zhang (2019) Cultivating river sediments into efficient denitrifying sludge for treating municipal wastewater. R Soc. Open Sci. 6: 190304.
Rice, E. W., R. B. Baird, A. D. Eaton, and L. S. Clesceri (2012) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 22nd ed. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington, USA.
Jayashree, C., S. Sweta, P. Arulazhagan, I. T. Yeom, M. I. I. Iqbal, and J. R. Banu (2015) Electricity generation from retting wastewater consisting of recalcitrant compounds using continuous upflow microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 20: 753–759.
Kondaveeti, S., S. H. Lee, H. D. Park, and B. Min (2014) Bacterial communities in a bioelectrochemical denitrification system: The effects of supplemental electron acceptors. Water Res. 51: 25–36.
Logan, B. E., B. Hamelers, R. Rozendal, U. Schrorder, J. Keller, S. Freguia, P. Aelterman, W. Verstraete, and K. Rabaey (2006) Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40: 5181–5192.
Kondaveeti, S., E. Kang, H. Liu, and B. Min (2019) Continuous autotrophic denitrification process for treating ammonium-rich leachate wastewater in bioelectrochemical denitrification system (BEDS). Bioelectrochemistry. 130: 107340.
Logan, B. E. (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7: 375–381.
Bernat, K., I. Wojnowska-Baryla, and A. Dobrzynska (2008) Denitrification with endogenous carbon source at low C/N and its effect on P(3HB) accumulation. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 2410–2418.
Wu, Y., Q. Yang, Q. Zeng, H. H. Ngo, W. Guo, and H. Zhang (2017) Enhanced low C/N nitrogen removal in an innovative microbial fuel cell (MFC) with electroconductivity aerated membrane (EAM) as biocathode. Chem. Eng. J. 316: 315–322.
Xie, X., M. Ye, P. C. Hsu, N. Liu, C. S. Criddle, and Y. Cui (2013) Microbial battery for efficient energy recovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110: 15925–15930.
Hou, L., J. Li, and Y. Liu (2019) Microbial communities variation analysis of denitrifying bacteria immobilized particles. Process Biochem. 87: 151–156.
Chan, Y. I., M. F. Chong, C. L. Law, and D. G. Hassell (2009) A review on anaerobic-aerobic treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 155: 1–18.
Rismani-Yazdi, H., S. M. Carver, A. D. Christy, and O. H. Tuovinen (2008) Cathodic limitations in microbial fuel cells: An overview. J. Power Sources. 180: 683–694.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (No.2017ZX07103-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
There are no conflicts of interest to declare. Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Lg., Yang, Qz. & Li, J. Electricity Effectively Utilization by Integrating Microbial Fuel Cells with Microbial Immobilization Technology for Denitrification. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 470–476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0470-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0470-2