Abstract
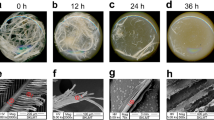
A fibroin-degrading bacterium was isolated in a medium containing fibroin as a sole nitrogen source, and then identified and characterized. The strain was designated Bacillus subtilis strain Bs5C, and the culture medium containing the extracellular proteolytic enzymes was found to hydrolyze cocoon fiber. A decomposition rate of 35% was achieved with the culture medium in optimized cocoon-degrading condition. In a second round of decomposition performed on the same fibers with additional culture medium, the decomposition rate reached 45.9%. To investigate the proteolytic enzymes degrading cocoon, the enzymes was purified from culture medium using ion exchange column and identified using LC-MS/MS analysis system. As a result, it was uncovered that the cocoon degradation was due to the neutral protease NprE of the strain Bs5C. Moreover, the cocoon fibers treated with semi-purified NprE enzyme solution were clearly split and degraded, as assessed by SEM, and solubilized peptides from fibroin and sericin were detected by LC-MS/MS. In conclusion, this study is the first report that peptides could be produced from cocoon by cultured medium of B. subtilis, and the newly isolated strain Bs5C and the NprE protease from the strain Bs5C could clearly be valuable for the production of silk peptides, which have various pharmacological and industrial applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jung, H., Y. Y. Kim, B. Kim, H. Nam, and J. G. Suh (2017) Improving glycemic control in model mice with type 2 diabetes by increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity using silk fibroin hydrolysate (SFH). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 493: 115–119.
Do, S. G., J. H. Park, H. Nam, J. B. Kim, J. Y. Lee, Y. S. Oh, and J. G. Suh (2012) Silk fibroin hydrolysate exerts an anti-diabetic effect by increasing pancreatic β cell mass in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. J. Vet. Sci. 13: 339–344.
Lapphanichayakool, P., M. Sutheerawattananonda, and N. Limpeanchob (2017) Hypocholesterolemic effect of sericin-derived oligopeptides in high-cholesterol fed rats. J. Nat. Med. 71: 208–215.
Deori, M., D. Devi, S. Kumari, A. Hazarika, H. Kalita, R. Sarma, and R. Devi (2016) Antioxidant effect of sericin in brain and peripheral tissues of oxidative stress induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Front. Pharmacol. 7: 319.
Kato, N., S. Sato, A. Yamanaka, H. Yamada, N. Fuwa, and M. Nomura (1998) Silk protein, sericin, inhibits lipid peroxidation and tyrosinase activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 62: 145–147.
Selvaraj, S. and N. N. Fathima (2017) Fenugreek incorporated silk fibroin nanofibers-a potential antioxidant scaffold for enhanced wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interaces. 9: 5916–5926.
Dash, R., C. Acharya, P. C. Bindu, and S. C. Kundu (2008) Antioxidant potential of silk protein sericin against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in skin fibroblasts. BMB Rep. 41: 236–241.
Cha, Y., S. H. Lee, S. K. Jang, H. Guo, Y. H. Ban, D. Park, G. Y Jang, S. Yeon, J. Y. Lee, E. K. Choi, S. S. Joo, H. S. Jeong, and Y. B. Kim (2017) A silk peptide fraction restores cognitive function in AF64A-induced Alzheimer disease model rats by increasing expression of choline acetyltransferase gene. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 314: 48–54.
Altman, G. H., F. Diaz, C. Jakuba, T. Calabro, R. L. Horan, J. Chen, H. Lu, J. Richmond, and D. L. Kaplan (2003) Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials. 24: 401–416.
Kim, B. K., O. H. Kwon, W. H. Park, and D. Cho (2016) Thermal, mechanical, impact, and water absorption properties of novel silk fibroin fiber reinforced poly(butylene succinate) biocomposites. Macromol. Res. 24: 734–740.
Horan, R. L., K. Antle, A. L. Collette, Y. Wang, J. Huang, J. E. Moreau, V. Volloch, D. L. Kaplan, and G. H. Altman (2005) In vitro degradation of silk fibroin. Biomaterials. 26: 3385–3393.
Vepari, C. and D. L. Kaplan (2007) Silk as a biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 32: 991–1007.
Drnovšek, N., R. Kocen, A. Gantar, M. Drobnič-Košorok, A. Leonardi, I. Križaj, A. Rečnik, and S. Novak (2016) Size of silk fibroin β-sheet domains affected by Ca2+. J. Mater. Chem. B. 4: 6597–6608.
Wongnarat, C. and P. Srihanam, (2013) Degradation behaviors of Thai bombyx mori silk fibroins exposure to protease enzymes. Engineering. 5: 61–66.
Joung, J. A., M. N. Park, J. Y. You, B. J. Song, and J. H. Choi (2018) Application of food-grade proteolytic enzyme for the hydrolysis of regenerated silk fibroin from Bombyx mori. J. Chem. 2018: 1285823.
Eom, S. J., N. H. Lee, M. C. Kang, Y. H. Kim, T. G. Lim, and K. M. Song (2020) Silk peptide production from whole silkworm cocoon using ultrasound and enzymatic treatment and its suppression of solar ultraviolet-induced skin inflammation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 61: 104803.
Forlani, G., A. M. Seves, and O. Ciferri (2000) A bacterial extracellular proteinase degrading silk fibroin. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation. 46: 271–275.
Suwannaphan, S., E. Fufeungsombut, A. Promboon, and P. Chimanage (2017) A serine protease from newly isolated Bacillus sp. for efficient silk degumming, sericin degrading and colour bleaching activities. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation. 117: 141–149
Thompson, J. D., T. J. Gibson, F. Plewniak, F. Jeanmougin, and D. G. Higgins (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 4876–4882.
Kumar, S., G. Stecher, and K. Tamura (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33: 1870–1874.
Choi, N. S., D. M. Chung, C. H. Ryu, K. S. Yoon, P. J. Maeng, and S. H. Kim (2006) Identification of three extracellular proteases from Bacillus subtilis KCTC 3014. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16: 457–464.
Shin, S., S. Yeon, D. Park, J. Oh, H. Kang, S. Kim, S. S. Joo, W. T. Lim, J. Y. Lee, K. C. Choi, K. Y. Kim, S. U. Kim, J. C. Kim, and Y. B. Kim (2010) Silk amino acids improve physical stamina and male reproductive function of mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 33: 273–278.
Kim, T. K., D. Park, S. Yeon, S. H. Lee, Y. J. Choi, D. K. Bae, Y. H. Yang, G. Yang, S. S. Joo, W. T. Lim, J. Y. Lee, J. S. Lee, H. S. Jeong, S. Y. Hwang, and Y. B. Kim (2011) Tyrosine-fortified silk amino acids improve physical function of Parkinson’s disease rats. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 20: 79–84.
Park, S., T. Zhang, J. Y. Qiu, and X. Wu (2019) The combination of mulberry extracts and silk amino acids alleviated high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis by improving hepatic insulin signaling and normalizing gut microbiome dysbiosis in rats. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2019: 8063121.
Mahmoodi, N. M., M. Arami, F. Mazaheri, and S. Rahimi (2010) Degradation of sericin (degumming) of Persian silk by ultrasound and enzymes as a cleaner and environmentally friendly process. J. Clean. Prod. 18: 146–151.
Hadjidj, R., A. Badis, S. Mechri, K. Eddouaouda, L. Khelouia, R. Annane, M. El Hattab, and B. Jaouadi (2018) Purification, biochemical, and molecular characterization of novel protease from Bacillus licheniformis strain K7A. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 114: 1033–1048.
Wang, L. F., S. M. Ekkel, and R. J. Devenish (1990) Expression in Escherichia coli of the Bacillus subtilis neutral protease gene (NPRE) lacking its ribosome binding site. Biochem. Int. 22: 1085–1093.
Wang, H., L. Yang, Y. Ping, Y. Bai, H. Luo, H. Huang, and B. Yao (2016) Engineering of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain with high neutral protease producing capacity and optimization of its fermentation conditions. PLoS One. 11: e0146373.
Rajkhowa, R., X. Hu, T. Tsuzuki, D. L. Kaplan, and X. Wang (2012) Structure and biodegradation mechanism of milled Bombyx mori silk particles. Biomacromolecules. 13: 2503–2512.
Lu, Q., B. Zhang, M. Li, B. Zuo, D. L. Kaplan, Y. Huang, and H. Zhud (2011) Degradation mechanism and control of silk fibroin. Biomacromolecules. 12: 1080–1086.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) Research Initiative Program.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, H.D., Cho, M.S., Kim, JS. et al. Identification and Characterization of a Cocoon Degradable Enzyme from the Isolated Strain Bacillus subtilis Bs5C. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 442–449 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0399-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0399-5