Abstract
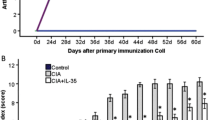
Dexamethasone (Dex) exhibits broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effects in chronic destructive rheumatoid arthritis. We present in vivo and in vitro evidence supporting the preventive effects and underlying mechanisms of Dex on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA)-induced synovial injuries. After successful induction of CIA, Wistar rats were administered Dex intraperitoneally (1 mg/kg) three times a week for more than 2 weeks. In vivo, paw swelling, arthritis scores, and histological evaluations were analyzed to determine the therapeutic effects of Dex on the progression of arthritis. In vitro, CIA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) were treated for 48 h with vehicle (control group), 10 ng/mL IL-1α (IL-1α group), 10 ng/mL IL-1α + 10 μM Dex (Dex group), or 10 ng/mL IL-1α + 10 μg/mL anti-CD147 antibody (anti-CD147 group). Evaluations of FLSs proliferation, cell cycle, migration, gene expression of Cyclin D1, p27, p57, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-17, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, CD147, CypB, matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), MMP-9, and MMP-13, ROS generation, protein expression of NF-κB and CD147, and translocation of NF-κB p65 were all conducted. The in vivo results showed that arthritis intensity was attenuated in the Dex-treated group. The in vitro findings demonstrated that treatment with Dex induced G0/G1 arrest and suppressed proliferation, migration, gene expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, TNF-α, CD147, CypB, MMP-3, MMP-9, and MMP-13, ROS generation and protein expression of NF-κB and CD147. Translocation of NF-κB p65 was inhibited by both Dex and anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody treatment. We offer molecular evidence of the anti-rheumatism efficacy Dex through hindrance to CD147, splendidly stabilization of the oxidative stress by downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang G, Chang CC, Yang Y, Yuan L, Xu L, Ho CT, Li S (2018) Resveratrol alleviates rheumatoid arthritis via reducing ROS and inflammation, inhibiting MAPK signaling pathways, and suppressing angiogenesis. J Agric Food Chem 66:12953–12960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05047
Winchester LJ, Veeranki S, Givvimani S, Tyagi SC (2015) Homocysteine elicits an M1 phenotype in murine macrophages through an EMMPRIN-mediated pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 93:577–584. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2014-0520
Schmidt R, Bültmann A, Fischel S, Gillitzer A, Cullen P, Walch A, Jost P, Ungerer M, Tolley ND, Lindemann S, Gawaz M, Schömig A, May AE (2008) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) is a novel receptor on platelets, activates platelets, and augments nuclear factor kappaB-dependent inflammation in monocytes. Circ Res 102:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.107.157990
Zhu P, Lu N, Shi ZG, Zhou J, Wu ZB, Yang Y, Ding J, Chen ZN (2006) CD147 overexpression on synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis enhances matrix metalloproteinase production and invasiveness of synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R44. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1899
Jia J, Wang C, Shi Z, Zhao J, Jia Y, Zhao-Hui Z, Li X, Chen Z, Zhu P (2009) Inhibitory effect of CD147/HAb18 monoclonal antibody on cartilage erosion and synovitis in the SCID mouse model for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:721–726. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep099
Wang CH, Dai JY, Wang L, Jia JF, Zheng ZH, Ding J, Chen ZN, Zhu P (2011) Expression of CD147 (EMMPRIN) on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis enhances chemotaxis, matrix metalloproteinase production and invasiveness of synoviocytes. J Cell Mol Med 15:850–860. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01084.x
Huang Z, Meng S, Wang L, Wang Y, Chen T, Wang C (2012) Suppression of oxLDL-induced MMP-9 and EMMPRIN expression by berberine via inhibition of NF-κB activation in human THP-1 macrophages. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 295:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.21489
Koenen M, Culemann S, Vettorazzi S, Caratti G, Frappart L, Baum W, Krönke G, Baschant U, Tuckermann JP (2018) Glucocorticoid receptor in stromal cells is essential for glucocorticoid-mediated suppression of inflammation in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 77:1610–1618. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212762
Song D, DuBois DC, Almon RR, Jusko WJ (2018) Modeling sex differences in anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone in arthritic rats. Pharm Res 35:203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-018-2483-5
Jia M, Deng C, Luo J, Zhang P, Sun X, Zhang Z, Gong T (2018) A novel dexamethasone-loaded liposome alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Int J Pharm 540:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.02.001
Wang QS, Wang TY (2018) Research progress of role of glucocorticoids in rheumatioid arthritis. Chin Pharmacol Bull 34:1647–1651
Wu J, Zhao FT, Fan KJ, Zhang J, Xu BX, Wang QS, Tang TT, Wang TY (2019) Dihydromyricetin inhibits inflammation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through regulation of nuclear factor-κB signaling in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 368:218–228. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.118.253369
Tang Y, Wang B, Sun X, Li H, Ouyang X, Wei J, Dai B, Zhang Y, Li X (2017) Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes co-cultured with PBMC increased peripheral CD4(+) CXCR5(+) ICOS(+) T cell numbers. Clin Exp Immunol 190:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13025
Xu S, Xiao Y, Zeng S, Zou Y, Qiu Q, Huang M, Zhan Z, Liang L, Yang X, Xu H (2018) Piperlongumine inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res 67:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1112-9
Wu Q, Wang Y, Wang Q, Yu D, Wang Y, Song L, Liu Z, Ye X, Xu P, Cao H, Li D, Ren G (2016) The bispecific antibody aimed at the vicious circle of IL-1β and IL-17A, is beneficial for the collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis of mice through NF-κB signaling pathway. Immunol Lett 179:68–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2016.09.001
Wu J, Li Q, Jin L, Qu Y, Liang BB, Zhu XT, Du HY, Jie LG, Yu QH (2019) Kirenol inhibits the function and inflammation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis in vitro and in vivo. Front Immunol 10:1304. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01304
Hong R, Sur B, Yeom M, Lee B, Kim KS, Rodriguez JP, Lee S, Kang KS, Huh CK, Lee SC, Hahm DH (2018) Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of the ethanolic extract of Aralia continentalis Kitag. in IL-1β-stimulated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and rodent models of polyarthritis and nociception. Phytomedicine 38:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2017.10.016
Zhang J, Chen Q, Wang S, Li T, Xiao Z, Lan W, Huang G, Cai X (2017) α-Mangostin, a natural xanthone, induces apoptosis and ROS accumulation in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. Curr Mol Med 17:375–380. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524018666171205123220
Phull AR, Nasir B, Haq IU, Kim SJ (2018) Oxidative stress, consequences and ROS mediated cellular signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Chem Biol Interact 281:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.12.024
Mateen S, Moin S, Khan AQ, Zafar A, Fatima N (2016) Increased reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 11:e0152925. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152925
Zhai KF, Duan H, Khan GJ, Xu H, Han FK, Cao WG, Gao GZ, Shan LL, Wei ZJ (2018) Salicin from Alangium chinense ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by modulating the Nrf2-HO-1-ROS pathways. J Agric Food Chem 66:6073–6082. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02241
Baldwin AS (2012) Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-κB: critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol Rev 246:327–345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01095.x
Cai P, Lu Z, Jiang T, Wang Z, Yang Y, Zheng L, Zhao J (2020) Syndecan-4 involves in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the inflammatory response and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Cell Physiol 235:1746–1758. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29093
Herlitz-Cifuentes H, Vejar C, Flores A, Jara P, Bustos P, Castro I, Poblete E, Saez K, Opazo M, Gajardo J, Aguayo C, Nova-Lamperti E, Lamperti L (2019) Plasma from patients with rheumatoid arthritis reduces nitric oxide synthesis and induces reactive oxygen species in A cell-based biosensor. Biosensors (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010032
Mateen S, Moin S, Shahzad S, Khan AQ (2017) Level of inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: correlation with 25-hydroxy vitamin D and reactive oxygen species. PLoS ONE 12:e0178879. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178879
Glennon-Alty L, Hackett AP, Chapman EA, Wright HL (2018) Neutrophils and redox stress in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Free Radic Biol Med 125:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.049
Morgan MJ, Liu ZG (2011) Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res 21:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.178
Yang G, Li S, Yuan L, Yang Y, Pan MH (2017) Effect of nobiletin on the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in the synovial membrane of rats with arthritis induced by collagen. Food Funct 8:4668–4674. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo01311f
Ye J, Jiang Z, Chen X, Liu M, Li J, Liu N (2016) Electron transport chain inhibitors induce microglia activation through enhancing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. Exp Cell Res 340:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.10.026
Yuan W, Ge H, He B (2010) Pro-inflammatory activities induced by CyPA-EMMPRIN interaction in monocytes. Atherosclerosis 213:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.09.033
López-Acosta O et al (2018) Reactive oxygen species from nadph oxidase and mitochondria participate in the proliferation of aortic smooth muscle cells from a model of metabolic syndrome. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:5835072. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5835072
Siwik DA, Kuster GM, Brahmbhatt JV, Zaidi Z, Malik J, Ooi H, Ghorayeb G (2008) EMMPRIN mediates beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase activity in cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.07.054
Wierstra I (2013) Cyclin D1/Cdk4 increases the transcriptional activity of FOXM1c without phosphorylating FOXM1c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431:753–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.037
Yan J, Chen Y, He C, Yang ZZ, Lü C, Chen XS (2012) Andrographolide induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol 28:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-011-9204-8
Zhang X, Feng H, Du J, Sun J, Li D, Hasegawa T, Amizuka N, Li M (2018) Aspirin promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation by blocking G0/G1 into S phase in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via downregulation of JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 42:3135–3148. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3883
de Andrés MC, Takahashi A, Oreffo RO (2016) Demethylation of an NF-κB enhancer element orchestrates iNOS induction in osteoarthritis and is associated with altered chondrocyte cell cycle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 24:1951–1960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2016.06.002
Jhou RS, Sun KH, Sun GH, Wang HH, Chang CI, Huang HC, Lu SY, Tang SJ (2009) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by olomoucine and roscovitine reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses via down-regulation of nuclear factor kappaB. Cell Prolif 42:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2184.2009.00584.x
Yu B, Zhang Y, Wu K, Wang L, Jiang Y, Chen W, Yan M (2019) CD147 promotes progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via NF-kappa B signaling. J Cell Mol Med 23:954–966. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13996
Sun WH, He F, Zhang NN, Zhao ZA, Chen HS (2018) Time dependent neuroprotection of dexamethasone in experimental focal cerebral ischemia: the involvement of NF-κB pathways. Brain Res 1701:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.029
Wang Q, Jiang H, Li Y, Chen W, Li H, Peng K, Zhang Z, Sun X (2017) Targeting NF-kB signaling with polymeric hybrid micelles that co-deliver siRNA and dexamethasone for arthritis therapy. Biomaterials 122:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.008
Jain S, Dash P, Minz AP, Satpathi S, Samal AG, Behera PK, Satpathi PS, Senapati S (2019) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) enhances prostate cancer metastasis potentially through NF-κB activation and recurrent dexamethasone administration fails to suppress it in vivo. Prostate 79:168–182. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23722
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81874011, 81572104 and 81301531) and the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Innovation Grant Nos. 18140903502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed the study conceptualization and design. Methodology, project administration, validation and data curation were performed by QW, BX, KF and JW. Original draft preparation was written by QW and review and editing were conducted by TW. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All animal experiment procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Xu, B., Fan, K. et al. Inflammation suppression by dexamethasone via inhibition of CD147-mediated NF-κB pathway in collagen-induced arthritis rats. Mol Cell Biochem 473, 63–76 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03808-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03808-5