Abstract
Backgrounds
Recent research has shown that stress has a significant influence on the functions of many organs.
Objective
The present study investigated the effect of acute or chronic restraint stress on physiological and psychological processes.
Results
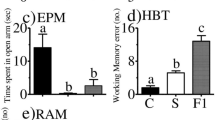
In the acute stress group, body weight and food intake did not change, but in the chronic stress group, food intake significantly increased and body weight was significantly inhibited. ALT and AST levels were significantly increased by both groups. Acute and chronic restraint stress led to different behavioral changes. Serum levels of corticosterone and cortisol were more increased in chronic stress than in acute stress. The levels of neurons and astrocyte in the hippocampus, and the NeuN-positive neuronal cells remained unaffected by acute stress, but were decreased by chronic stress. GFAP-positive astrocytes were increased by both groups.
Conclusion
In summary, our study provides evidence of a relationship between liver injury and behavioral change upon exposure to restraint stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin I et al (2004) The effect of chronic restraint stress on spatial learning and memory: relation to oxidant stress. Int J Neurosci 114:683–699. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207450490430543
Adachi S, Kawamura K, Takemoto K (1993) Oxidative damage of nuclear DNA in liver of rats exposed to psychological stress. Cancer Res 53:4153–4155
Amador-Noguez D et al (2007) Alterations in xenobiotic metabolism in the long-lived Little mice. Aging Cell 6:453–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00300.x
Bao L et al (2008) Protective effects of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) extract on restraint stress-induced liver damage in mice. J Agric Food Chem 56:7803–7807. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf800728m
Bao L et al (2010) Bilberry extract protect restraint stress-induced liver damage through attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction. Fitoterapia 81:1094–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2010.07.004
Bardin L, Malfetes N, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortere R (2009) Chronic restraint stress induces mechanical and cold allodynia, and enhances inflammatory pain in rat: relevance to human stress-associated painful pathologies. Behav Brain Res 205:360–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.07.005
Bhatnagar S, Vining C, Iyer V, Kinni V (2006) Changes in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function, body temperature, body weight and food intake with repeated social stress exposure in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 18:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2005.01375.x
Buynitsky T, Mostofsky DI (2009) Restraint stress in biobehavioral research: recent developments. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.05.004
Cao HJ et al (2012) Sarcandra glabra extract reduces the susceptibility and severity of influenza in restraint-stressed mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:236539. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/236539
Crane JW, French KR, Buller KM (2005) Patterns of neuronal activation in the rat brain and spinal cord in response to increasing durations of restraint stress. Stress 8:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/10253890500333817
Gagliano H, Fuentes S, Nadal R, Armario A (2008) Previous exposure to immobilisation and repeated exposure to a novel environment demonstrate a marked dissociation between behavioral and pituitary-adrenal responses. Behav Brain Res 187:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.09.006
Gong S et al (2015) Dynamics and correlation of serum cortisol and corticosterone under different physiological or stressful conditions in mice. PLoS ONE 10:e0117503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117503
Harris RB et al (1998) Effect of repeated stress on body weight and body composition of rats fed low- and high-fat diets. Am J Physiol 275:R1928–1938
Harris RB, Palmondon J, Leshin S, Flatt WP, Richard D (2006) Chronic disruption of body weight but not of stress peptides or receptors in rats exposed to repeated restraint stress. Horm Behav 49:615–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.12.001
He RR et al (2009) Effects of histamine on lipid metabolic disorder in mice loaded with restraint stress. J Pharmacol Sci 111:117–123
He RR et al (2011) Protective effect of apple polyphenols against stress-provoked influenza viral infection in restraint mice. J Agric Food Chem 59:3730–3737. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104982y
Hummel M, Lu P, Cummons TA, Whiteside GT (2008) The persistence of a long-term negative affective state following the induction of either acute or chronic pain. Pain 140:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.09.020
Jeong JY, Lee DH, Kang SS (2013) Effects of chronic restraint stress on body weight, food intake, and hypothalamic gene expressions in mice. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 28:288–296. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.4.288
Johnson EO, Kamilaris TC, Chrousos GP, Gold PW (1992) Mechanisms of stress: a dynamic overview of hormonal and behavioral homeostasis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 16:115–130
Kim JJ, Diamond DM (2002) The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn849
Kim HG, Lee JS, Lee JS, Han JM, Son CG (2012) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Myelophil on restraint stress-induced liver injury in BALB/c mice. J Ethnopharmacol 142:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.04.023
Kim SH et al (2016) Silymarin prevents restraint stress-induced acute liver injury by ameliorating oxidative stress and reducing inflammatory response. Molecules 21:443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040443
Lau C, Simpson C (2004) Animal models for the study of the effect of prolonged stress on lactation in rats. Physiol Behav 82:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.05.004
Leite-Almeida H et al (2012) Differential effects of left/right neuropathy on rats’ anxiety and cognitive behavior. Pain 153:2218–2225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2012.07.007
Liu Y et al (2013) Protective effects of nizofenone administration on the cognitive impairments induced by chronic restraint stress in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:474–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2012.09.009
Liu HY et al (2018) Chronic minocycline treatment reduces the anxiety-like behaviors induced by repeated restraint stress through modulating neuroinflammation. Brain Res Bull 143:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.08.015
Masood A, Nadeem A, Mustafa SJ, O'Donnell JM (2008) Reversal of oxidative stress-induced anxiety by inhibition of phosphodiesterase-2 in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.137208
McEwen BS (2000) The neurobiology of stress: from serendipity to clinical relevance. Brain Res 886:172–189
Monteggia LM et al (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor conditional knockouts show gender differences in depression-related behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 61:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.021
Moore CJ, Cunningham SA (2012) Social position, psychological stress, and obesity: a systematic review. J Acad Nutr Diet 112:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2011.12.001
Norden DM, Trojanowski PJ, Villanueva E, Navarro E, Godbout JP (2016) Sequential activation of microglia and astrocyte cytokine expression precedes increased Iba-1 or GFAP immunoreactivity following systemic immune challenge. Glia 64:300–316. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22930
Ovejero R et al (2013) Do cortisol and corticosterone play the same role in coping with stressors? Measuring glucocorticoid serum in free-ranging guanacos (Lama guanicoe). J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol 319:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1833
Parent AJ et al (2012) Increased anxiety-like behaviors in rats experiencing chronic inflammatory pain. Behav Brain Res 229:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.01.001
Reid MB (2001) Nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and skeletal muscle contraction. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:371–376
Santha P et al (2015) Restraint stress-induced morphological changes at the blood-brain barrier in adult rats. Front Mol Neurosci 8:88. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00088
Sha J et al (2019) Dexmedetomidine improves acute stress-induced liver injury in rats by regulating MKP-1, inhibiting NF-κB pathway and cell apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 234:14068–14078. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28096
Steimer T (2011) Animal models of anxiety disorders in rats and mice: some conceptual issues. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 13:495–506
Stojanovich L, Marisavljevich D (2008) Stress as a trigger of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 7:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2007.11.007
Strohle A et al (2007) Physical activity and prevalence and incidence of mental disorders in adolescents and young adults. Psychol Med 37:1657–1666. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003329170700089X
Tsoi B et al (2011) Carnosine ameliorates stress-induced glucose metabolism disorder in restrained mice. J Pharmacol Sci 117:223–229
Tyng CM, Amin HU, Saad MNM, Malik AS (2017) The influences of emotion on learning and memory. Front Psychol 8:1454. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01454
Vere CC, Streba CT, Streba LM, Ionescu AG, Sima F (2009) Psychosocial stress and liver disease status. World J Gastroenterol 15:2980–2986
Yalcin I et al (2011) A time-dependent history of mood disorders in a murine model of neuropathic pain. Biol Psychiatry 70:946–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.07.017
Yun S et al (2016) Stress-induced anxiety- and depressive-like phenotype associated with transient reduction in neurogenesis in adult nestin-CreERT2/diphtheria toxin fragment a transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 11:e0147256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147256
Acknowledgements
This work was also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2017R1D1A1B03032284) and by a grant (No. K17830) from the Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KIP conceived and designed the study, and supported all materials. TWh, KYK, YWK and HJD performed the experiments, treatments/animal care and statistical analysis. TWO and KYK wrote the manuscript. KIP reviewed the literature, revised the manuscript and coordinated the study. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and animal rights
The experimental procedure followed the actual law of animal protection that was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, Korea.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, T.W., Kim, KY., Do, H.J. et al. Comparative analysis of acute and chronic stress-induced neurobehavioral alteration and liver injury in mice. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 16, 367–375 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-020-00094-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-020-00094-6