Abstract
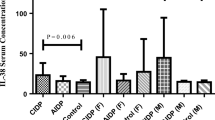
Interleukin (IL)-34 is ligand for the colony-stimulating factor (CSF)-1 receptor. This cytokine has fundamental roles the pathogenesis of a number of autoimmune and neurologic disorders. However, its role in the pathogenesis of acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies (AIDP and CIDP) has not been assessed yet. We measured serum levels of IL-34 33 CIDP cases, 16 AIDP cases, and 33 control subjects using commercial ELISA kits. IL-34 levels were significantly higher in both AIDP (44.87 ± 4.38) and CIDP (44.87 ± 4.38) groups compared with healthy subjects (30.10 ± 1.05) (P = 0.046 and P = 0.01, respectively). Differences between female subgroups were insignificant. However, levels of this cytokine were significantly higher in male subjects with CIDP compared with male controls (P = 0.042). Thus, levels of this cytokine might be regarded as biomarkers for these kinds of autoimmune disorders. Future studies are needed to verify these results and find the molecular mechanism of participation of IL-34 in the pathogenesis of AIDP/CIDP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali ZPM, Ghafouri-Fard S, Komaki A, Mazdeh M, Taheri M, Eftekharian MM (2020a) Assessment of IL-38 levels in patients with acquired immune-mediated polyneuropathies. J Molec Neurosci:1–4
Ali ZPM, Taheri M, Sangsefidi S, Arsang-Jang S, Mazdeh M, Zamani A, Ghafouri-Fard S, Eftekharian MM (2020b) Evaluation of expression of STAT genes in immune-mediated polyneuropathies. J Molec Neurosci:1–8
Arnold, M. (n.d.) AIDP/CIDP Part 1: Evaluation and Diagnosis
Bézie S, Picarda E, Ossart J, Tesson L, Usal C, Renaudin K, Anegon I, Guillonneau C (2015) IL-34 is a Treg-specific cytokine and mediates transplant tolerance. J Clin Invest 125:3952–3964
Boström EA, Lundberg P (2013) The newly discovered cytokine IL-34 is expressed in gingival fibroblasts, shows enhanced expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines, and stimulates osteoclast differentiation. PloS One 8
Boulakirba S, Pfeifer A, Mhaidly R, Obba S, Goulard M, Schmitt T, Chaintreuil P, Calleja A, Furstoss N, Orange F (2018) IL-34 and CSF-1 display an equivalent macrophage differentiation ability but a different polarization potential. Sci Rep 8:1–11
Chen, H., Ende, N. & Souayah, N. 2012. The cytokine profile of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (P06. 134) AAN Enterprises
Chi LJ, Xu WH, Zhang ZW, Huang HT, Zhang LM, Zhou J (2010) Distribution of Th17 cells and Th1 cells in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:345–356
Ciccia F, Alessandro R, Rodolico V, Guggino G, Raimondo S, Guarnotta C, Giardina A, Sireci G, Campisi G, DE Leo G (2013) IL-34 is overexpressed in the inflamed salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome and is associated with the local expansion of pro-inflammatory CD14brightCD16+ monocytes. Rheumatology 52:1009–1017
Clavel G, Thiolat A, Boissier M-C (2013) Interleukin newcomers creating new numbers in rheumatology: IL-34 to IL-38. Joint Bone Spine 80:449–453
Debnath M, Nagappa M, Subbanna M, Sundaravadivel P, Talukdar PM, Shivakumar V, Wahatule R, Dutta D, Binukumar B, Sinha S (2018) Th17 pathway signatures in a large Indian cohort of Guillain Barre syndrome. J Neuroimmunol 323:125–130
Dumitru, D., Amato, A. A. & Zwarts, M. J. 2002. Electrodiagnostic medicine, Hanley & Belfus Philadelphia
Eda H, Shimada H, Beidler DR, Monahan JB (2011) Proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNF-α, induce expression of interleukin-34 mRNA via JNK-and p44/42 MAPK-NF-κB pathway but not p38 pathway in osteoblasts. Rheumatol Int 31:1525–1530
Franzè E, Monteleone I, Cupi ML, Mancia P, Caprioli F, Marafini I, Colantoni A, Ortenzi A, Laudisi F, Sica G (2015) Interleukin-34 sustains inflammatory pathways in the gut. Clin Sci 129:271–280
Ge Y, Huang M, Yao Y-M (2019) Immunomodulation of Interleukin-34 and its potential significance as a disease biomarker and therapeutic target. Int J Biol Sci 15:1835
Köller H, Kieseier BC, Jander S, Hartung H-P (2005) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N Engl J Med 352:1343–1356
Lin H, Lee E, Hestir K, Leo C, Huang M, Bosch E, Halenbeck R, Wu G, Zhou A, Behrens D (2008) Discovery of a cytokine and its receptor by functional screening of the extracellular proteome. Science 320:807–811
Lindau R, Mehta RB, Lash G, Papapavlou G, Boij R, Berg G, Jenmalm M, Ernerudh J, Svensson-Arvelund J (2018) Interleukin-34 is present at the fetal–maternal interface and induces immunoregulatory macrophages of a decidual phenotype in vitro. Hum Reprod 33:588–599
Nandi S, Cioce M, Yeung Y-G, Nieves E, Tesfa L, Lin H, Hsu AW, Halenbeck R, Cheng H-Y, Gokhan S (2013) Receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase ζ is a functional receptor for interleukin-34. J Biol Chem 288:21972–21986
Nyati KK, Prasad KN (2014) Role of cytokines and toll-like receptors in the immunopathogenesis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Mediat Inflamm 2014:758639–758639
Sangsefidi S, Ghafouri-Fard S, Komaki A, Mazdeh M, Taheri M, Eftekharian MM (2020) High levels of Il-19 in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Mol Neurosci
Segaliny AI, Brion R, Mortier E, Maillasson M, Chérel M, Jacques Y, Le Goff B, Heymann D (2015) Syndecan-1 regulates the biological activities of interleukin-34. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molec Cell Res 1853:1010–1021
Sivieri S, Ferrarini A, Lolli F, Matà S, Pinto F, Tavolato B, Gallo P (1997) Cytokine pattern in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with GBS and CIDP. J Neurol Sci 147:93–95
Tian Y, Shen H, Xia L, Lu J (2013) Elevated serum and synovial fluid levels of interleukin-34 in rheumatoid arthritis: possible association with disease progression via interleukin-17 production. J Interf Cytokine Res 33:398–401
van der Meche FG, van Doorn PA, Meulstee J, Jennekens FG (2001) Diagnostic and classification criteria for the Guillain-Barre syndrome. Eur Neurol 45:133–139
Walker DG, Tang TM, Lue L-F (2017) Studies on colony stimulating factor receptor-1 and ligands colony stimulating factor-1 and interleukin-34 in Alzheimer’s disease brains and human microglia. Front Aging Neurosci 9:244
Wang Y, Szretter KJ, Vermi W, Gilfillan S, Rossini C, Cella M, Barrow AD, Diamond MS, Colonna M (2012) IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia. Nat Immunol 13:753–760
Yuki N, Hartung H-P (2012) Guillain–Barré syndrome. N Engl J Med 366:2294–2304
Funding
The current study was supported by a grant number 9712218216 from Hamadan University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The study protocol was approved by ethical committee of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (IR.UMSHA.REC.1397.948).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, S., Ghafouri-Fard, S., Komaki, A. et al. Increased Levels of IL-34 in Acquired Immune-Mediated Neuropathies. J Mol Neurosci 71, 137–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01634-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01634-4