Abstract
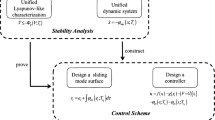
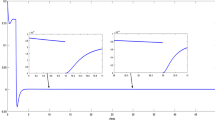
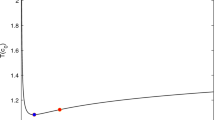
This paper considers the finite-time drive-response synchronization of stochastic nonlinear systems consisting of continuous-time and discrete-time subsystems. To save communication resources and reduce control cost, quantized controllers, which only work on continuous-time intervals, are designed. Owing to the hybrid characteristics of continuous- and discrete-time subsystems, existing finite-time stability theorems are not applicable. By developing novel analytical techniques, three criteria are derived to guarantee the finite-time synchronization. Moreover, the settling time is explicitly estimated. It is shown that the settling time is dependent not only on the control gains and systems’ initial conditions, but also on the control width and uncontrolled width. Numerical examples demonstrate the effectiveness of the theoretical analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis G M. A wavelet-based analysis of fractal image compression. IEEE Trans Image Process, 1998, 7: 141–154
Cao J D, Li R X. Fixed-time synchronization of delayed memristor-based recurrent neural networks. Sci China Inf Sci, 2017, 60: 032201
Wang Z X, Fan J B, Jiang G-P, et al. Consensus in nonlinear multi-agent systems with nonidentical nodes and sampled-data control. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 122203
Sundar S, Minai A A. Synchronization of randomly multiplexed chaotic systems with application to communication. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85: 5456–5459
Lang J, Tao R, Wang Y. The discrete multiple-parameter fractional Fourier transform. Sci China Inf Sci, 2010, 53: 2287–2299
Liu X, Chen T. Synchronization of complex networks via aperiodically intermittent pinning control. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2015, 60: 3316–3321
Zhong J, Lu J, Liu Y, et al. Synchronization in an array of output-coupled Boolean networks with time delay. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2014, 25: 2288–2294
Yang X, Lu J. Finite-time synchronization of coupled networks with Markovian topology and impulsive effects. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2016, 61: 2256–2261
Yao F Q, Deng F Q. Stability of impulsive stochastic functional differential systems in terms of two measures via comparison approach. Sci China Inf Sci, 2012, 55: 1313–1322
Yang X, Cao J. Exponential synchronization of delayed neural networks with discontinuous activations. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2013, 60: 2431–2439
Zhang W, Yang X, Xu C, et al. Finite-time synchronization of discontinuous neural networks with delays and mismatched parameters. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2018, 29: 3761–3771
Wan X, Yang X, Tang R, et al. Exponential synchronization of semi-Markovian coupled neural networks with mixed delays via tracker information and quantized output controller. Neural Netw, 2019, 118: 321–331
Yang X, Li X, Lu J, et al. Synchronization of time-delayed complex networks with switching topology via hybrid actuator fault and impulsive effects control. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2938217
Yang X, Ho D W C, Lu J, et al. Finite-time cluster synchronization of T-S fuzzy complex networks with discontinuous subsystems and random coupling delays. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2015, 23: 2302–2316
Bhat S P, Bernstein D S. Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM J Control Opt, 2000, 38: 751–766
Amato F, Ariola M, Dorato P. Finite-time control of linear systems subject to parametric uncertainties and disturbances. Automatica, 2001, 37: 1459–1463
Yang X, Lam J, Ho D W C, et al. Fixed-time synchronization of complex networks with impulsive effects via nonchattering control. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2017, 62: 5511–5521
Shi P, Su X, Li F. Dissipativity-based filtering for fuzzy switched systems with stochastic perturbation. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2016, 61: 1694–1699
Liu T, Jiang Z P. Further results on quantized stabilization of nonlinear cascaded systems with dynamic uncertainties. Sci China Inf Sci, 2016, 59: 072202
Yang X S, Cao J D, Xu C, et al. Finite-time stabilization of switched dynamical networks with quantized couplings via quantized controller. Sci China Technol Sci, 2018, 61: 299–308
Yang X, Lu J, Ho D W C, et al. Synchronization of uncertain hybrid switching and impulsive complex networks. Appl Math Model, 2018, 59: 379–392
Cao J D, Rakkiyappan R, Maheswari K, et al. Exponential H⋡ filtering analysis for discrete-time switched neural networks with random delays using sojourn probabilities. Sci China Technol Sci, 2016, 59: 387–402
Yang X, Feng Z, Feng J, et al. Synchronization of discrete-time neural networks with delays and Markov jump topologies based on tracker information. Neural Netw, 2017, 85: 157–164
Zhai G, Lin H, Michel A N, et al. Stability analysis for switched systems with continuous-time and discrete-time subsystems. In: Proceedings of the 2004 American Control Conference, Boston, 2004. 4555–4560
Zhai G, Lin H, Xu X, et al. Stability analysis and design of switched normal systems. In: Proceedings of the 43rd IEEE Conference Decision and Control, Atlantis, 2004. 3253–3258
Zhai G S, Liu D R, Imae J, et al. Lie algebraic stability analysis for switched systems with continuous-time and discrete-time subsystems. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2006, 53: 152–156
Zheng Y, Wang L. Consensus of switched multiagent systems. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2016, 63: 314–318
Lin X, Zheng Y. Finite-time consensus of switched multiagent systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, 2017, 47: 1535–1545
Yang X, Cao J. Stochastic synchronization of coupled neural networks with intermittent control. Phys Lett A, 2009, 373: 3259–3272
Huang T, Li C, Yu W, et al. Synchronization of delayed chaotic systems with parameter mismatches by using intermittent linear state feedback. Nonlinearity, 2009, 22: 569–584
Pan L, Cao J. Stochastic quasi-synchronization for delayed dynamical networks via intermittent control. Commun Nonlin Sci Numer Simul, 2012, 17: 1332–1343
Zhang W, Li C, Huang T, et al. Stability and synchronization of memristor-based coupling neural networks with time-varying delays via intermittent control. Neurocomputing, 2016, 173: 1066–1072
Liu L, Perc M, Cao J D. Aperiodically intermittent stochastic stabilization via discrete time or delay feedback control. Sci China Inf Sci, 2019, 62: 072201
Zhang W, Huang J, Wei P. Weak synchronization of chaotic neural networks with parameter mismatch via periodically intermittent control. Appl Math Model, 2011, 35: 612–620
Xu C, Yang X, Lu J, et al. Finite-time synchronization of networks via quantized intermittent pinning control. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2018, 48: 3021–3027
Nesic D, Liberzon D. A unified framework for design and analysis of networked and quantized control systems. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2009, 54: 732–747
Wang Z, Shen B, Shu H, et al. Quantized H∞ control for nonlinear stochastic time-delay systems with missing measurements. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2012, 57: 1431–1444
Xiao X, Zhou L, Zhang Z. Synchronization of chaotic Lur’e systems with quantized sampled-data controller. Commun Nonlin Sci Numer Simulat, 2014, 19: 2039–2047
Liu Z, Wang F, Zhang Y, et al. Fuzzy adaptive quantized control for a class of stochastic nonlinear uncertain systems. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2016, 46: 524–534
Yang X, Zhu Q, Huang C. Lag stochastic synchronization of chaotic mixed time-delayed neural networks with uncertain parameters or perturbations. Neurocomputing, 2011, 74: 1617–1625
Yang X, Cao J, Lu J. Stochastic synchronization of complex networks with nonidentical nodes via hybrid adaptive and impulsive control. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2012, 59: 371–384
Tang Z, Park J H, Lee T H, et al. Mean square exponential synchronization for impulsive coupled neural networks with time-varying delays and stochastic disturbances. Complexity, 2016, 21: 190–202
Zhang W, Li C, Huang T, et al. Fixed-time synchronization of complex networks with nonidentical nodes and stochastic noise perturbations. Phys A-Stat Mech Appl, 2018, 492: 1531–1542
Liang J L, Wang Z D, Liu Y R, et al. Robust synchronization of an array of coupled stochastic discrete-time delayed neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw, 2008, 19: 1910–1921
Tang Y, Fang J, Xia M, et al. Synchronization of Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy stochastic discrete-time complex networks with mixed time-varying delays. Appl Math Model, 2010, 34: 843–855
Wang Z D, Wang Y, Liu Y R. Global synchronization for discrete-time stochastic complex networks with randomly occurred nonlinearities and mixed time delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw, 2010, 21: 11–25
Yang X, Cao J, Lu J. Synchronization of randomly coupled neural networks with Markovian jumping and time-delay. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2013, 60: 363–376
Yang X, Cao J. Finite-time stochastic synchronization of complex networks. Appl Math Model, 2010, 34: 3631–3641
Tang Y. Terminal sliding mode control for rigid robots. Automatica, 1998, 34: 51–56
Matsumoto T, Chua L, Komuro M. The double scroll. IEEE Trans Circ Syst, 1985, 32: 797–818
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61673078, 61833005), Bowang Scholar Program of Chongqing Normal University, and Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. cstc2018jcyjAX0369).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, X., Yang, X., Cao, J. et al. Finite-time control for a class of hybrid systems via quantized intermittent control. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 63, 192201 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-018-2727-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-018-2727-5