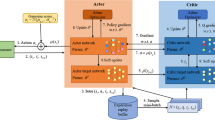
Abstract
In recent years, with the rapid development of Internet of Things (IoTs) and artificial intelligence, vehicular networks have transformed from simple interactive systems to smart integrated networks. The accompanying intelligent connected vehicles (ICVs) can communicate with each other and connect to the urban traffic information network, to support intelligent applications, i.e., autonomous driving, intelligent navigation, and in-vehicle entertainment services. These applications are usually delay-sensitive and compute-intensive, with the result that the computation resources of vehicles cannot meet the quality requirements of service for vehicles. To solve this problem, vehicular edge computing networks (VECNs) that utilize mobile edge computing offloading technology are seen as a promising paradigm. However, existing task offloading schemes lack consideration of the highly dynamic feature of vehicular networks, which makes them unable to give time-varying offloading decisions for dynamic changes in vehicular networks. Meanwhile, the current mobility model cannot truly reflect the actual road traffic situation. Toward this end, we study the task offloading problem in VECNs with the synchronized random walk model. Then, we propose a reinforcement learning-based scheme as our solution, and verify its superior performance in processing delay reduction and dynamic scene adaptability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-fuqaha A, Guizani M, Mohammadi M, et al. (2015) Internet of things: a survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 17(4):2347–2376. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2015.2444095
Siegel JE, Erb DC, Sarma SE (2018) A survey of the connected vehicle Landscape-Architectures, enabling technologies, applications, and development areas. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 19(8):2391–2406. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2017.2749459
Khelifi H, Luo S, Nour B et al (2019) Named Data Networking in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks: State-of-the-Art and Challenges
Zhang J, Wang F, Wang K, et al. (2011) Data-Driven Intelligent transportation systems: a survey. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 12:1624–1639. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2011.2158001
Han S, Huang Y, Meng W, et al (2019) Optimal power allocation for SCMA downlink systems based on maximum capacity. IEEE Trans Commun 67(2):1480–1489. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2877671
Zhang K, Mao Y, Leng S, et al (2016) Delay constrained offloading for mobile edge computing in Cloud-Enabled vehicular networks. In: Proc 2016 8th Int Work Resilient Networks Des Model RNDM, vol 2016, pp 288–294, https://doi.org/10.1109/RNDM.2016.7608300
Guo H, Zhang J, Liu J (2019) Fiwi-enhanced Vehicular Edge Computing networks: Collaborative Task Offloading. IEEE Veh Technol Mag 14(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1109/MVT.2018.2879537
Bisio I, Garibotto C, Lavagetto F, et al. (2019) Blind detection: Advanced Techniques for WiFi-Based Drone Surveillance. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(1):938–946. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2018.2884767
Sun F, Hou F, Cheng N, et al. (2018) Cooperative task scheduling for computation offloading in vehicular cloud. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(11):11049–11061. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2018.2868013
Guo H, Liu J, Zhang J (2018) Computation offloading for Multi-Access mobile edge computing in Ultra-Dense networks. IEEE Commun Mag 56(8):14–19. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701069
Guo H, Liu J, Zhang J (2018) Mobile-edge Computation Offloading for Ultradense IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J 5(6):4977–4988. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2838584
Mach P, Becvar Z (2017) Mobile edge computing: a survey on architecture and computation offloading. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 19(3):1628–1656. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2682318
Han S, Li Y, Meng W, et al. (2019) Indoor localization with a single Wi-Fi access point based on OFDM-MIMO. IEEE Syst J 13(1):964–972. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2018.2823358
Qiao G, Leng S, Zhang K, He Y (2018) Collaborative task offloading in vehicular edge Multi-Access networks. IEEE Commun Mag 56(8):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701130
Liu Y, Wang S, Huang J, Yang F (2018) A computation offloading algorithm based on game theory for vehicular edge networks
Du J, Yu FR, Chu X, et al. (2019) Computation offloading and resource allocation in vehicular networks based on Dual-Side cost minimization. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(2):1079–1092. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2018.2883156
Wang K, Yin H, Quan W, Min G (2018) Enabling collaborative edge computing for software defined vehicular networks. IEEE Netw 32(5):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1700364
Zhao J, Li Q, Gong Y, Zhang K (2019) Computation offloading and resource allocation for cloud assisted mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(8):7944–7956. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2917890
Serra J, Sanabria-russo L, Pubill D, Verikoukis C (2018) Scalable and Flexible IoT Data Analytics: When Machine Learning Meets SDN and Virtualization. In: 2018 IEEE 23rd Int Work Comput Aided Model Des Commun Links Networks 1–6
Ye H, Liang L, Li GY, et al. (2018) Machine learning for vehicular networks: recent advances and application examples. IEEE Veh Technol Mag 13(2):94–101. https://doi.org/10.1109/MVT.2018.2811185
Taherkhani N, Pierre S (2016) Centralized and localized data congestion control strategy for vehicular ad hoc networks using a machine learning clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 17 (11):3275–3285. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2016.2546555
Zhang Z, Mao G, Member S, et al. (2014) Stochastic Characterization of Information Propagation Process in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 15(1):122–135. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2013.2274274
Zarei M, Rahmani AM (2017) Analysis of vehicular mobility in a dynamic Free-Flow highway. Veh Commun 7:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2016.12.001
Wang S, Zhang X, Zhang Y, et al. (2017) A survey on mobile edge networks: convergence of computing, caching and communications. IEEE Access 5:6757–6779. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2685434
Ning Z, Dong P, Kong X, Xia F (2019) A cooperative partial computation offloading scheme for mobile edge computing enabled internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J 6(3):4804–4814. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2868616
You C, Huang K, Chae H, Kim BH (2017) Energy-Efficient Resource allocation for Mobile-Edge computation offloading. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 16 (3):1397–1411. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2016.2633522
Guo H, Liu J (2018) Collaborative computation offloading for multiaccess edge computing over Fiber-Wireless networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(5):4514–4526. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2018.2790421
Sun Y, Member S, Guo X, Song J (2019) Adaptive Learning-Based task offloading for vehicular edge computing systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(4):3061–3074. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2895593
Cao Y, Zhang L, Liao J (2019) Knowledge-Driven Service offloading decision for vehicular edge computing: a deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(5):4192–4203. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2894437
Yousefi S, Altman E, El-Azouzi R, Fathy M (2008) Analytical model for connectivity in vehicular Ad Hoc networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 57(6):3341–3356. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2008.2002957
Han S, Zhang Y, Meng W, et al (2019) Full-Duplex Relay-Assisted Macrocell with millimeter wave backhauls: framework and prospects. IEEE Netw 33(5):190–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2019.1800305
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61771374, 61771373, 61801360, and 61601357), in part by Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2020JC-15 and 2020JM-109), in part by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3102019PY005, 31020190QD040, and 31020200QD010), in part by Special Funds for Central Universities Construction of World-Class Universities (Disciplines) and Special Development Guidance (06390-20GH020114), and in part by China 111 Project (B16037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Guo, H. & Liu, J. Adaptive Task Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing Networks: a Reinforcement Learning Based Scheme. Mobile Netw Appl 25, 1736–1745 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01584-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01584-6