Abstract
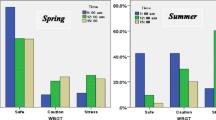
In this study, the spatio-temporal characteristics of the minimum rest time for the safety of South Korean outdoor workers during hot summer months (June to August) are examined based on the hourly wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT) across 27 weather stations in South Korea. The WBGT thresholds in the work-rest recommendation of the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency (KOSHA 2017) for the quantification of the minimum rest time are evaluated through a comparison of the given thresholds with the occurrences of occupational heat-related illness patients due to outdoor work during hot summer months in South Korea. The long-term (2009–2018) average of the hourly WBGT values during summer months shows that outdoor workers with a moderate workload are exposed to heat stress during approximately 30% of the entire daytime working hours (06:00–18:00). According to the WBGT thresholds modified from the KOSHA (2017) guidelines, the daily minimum rest time for a moderate workload noticeably increases up to 18% (11 min/h) in mid-summer (late July and early August). During mid-summer, the minimum rest time for a continuous moderate outdoor workload even increases up to 31% (18 min/h) between 12:00 and 13:00 and is regionally higher in the southwestern than in the southeastern regions of the Korean Peninsula. These results suggest that in summertime high-heat environments, a mandatory rest time must be provided according to appropriate heat management programs for the safety of workers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACGIH (2015) Threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents and biological exposures indices 2015. American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, Cincinnati
Alfano FRA, Malchaire J, Palella BI, Riccio G (2014) WBGT index revisited after 60 years of use. Ann Occup Hyg 58(8):955–970. https://doi.org/10.1093/annhyg/meu050
BLS (2017) Injuries, illnesses, and fatalities databases. Bureau of Labor Statistics. http://www.bls.gov/iif/. Accessed 11 Sep 2019
BSI (2017) Ergonomics of the thermal environment. Assessment of heat stress using the WBGT (wet bulb globe temperature) index. BS EN ISO 7243:2017, The British Standards Institution
Budd GM (2008) Wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT)—its history and its limitations. J Sci Med Sport 11(1):20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2007.07.003
CDC (2008) Heat-related deaths among crop workers–United States, 1992–2006. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 57(24):649–653
Chae H, Kim H, Oh Y, Lee K, Kim H, Kim K (2013) Evaluation of the farmers’ workload and thermal environments during chili harvest in the open field. Korean J Community Living Sci 24(4):543–552. https://doi.org/10.7856/kjcls.2013.24.4.543 (In Korean)
Choi G, Lee DE (2020) Changing human-sensible temperature in Korea under a warmer monsoon climate over the last 100 years. Int J Biometeorol 64:729–738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01862-8
Choi JW, Park JH (2007) Working clothes and working environment of workers at a construction site in summer. J Korean Soc Cloth Text 31(11):1520–1529. https://doi.org/10.5850/JKSCT.2007.31.11.1520 (In Korean)
Choi G, Choi J, Kwon HJ (2005) The impacts of high apparent temperature on increase of summertime disease-related mortality in Seoul: 1991-2000. J Prev Med Public Health 38(3):283–290 https://www.jpmph.org/upload/pdf/jpmph-38-3-283.pdf (In Korean)
Corleto RD, Firth I, Maté J (2013) A guide to managing heat stress: developed for use in the Australian environment, 2nd edn. The Australian Institute of Occupational Hygienists, Tullamarine
Dunne JP, Stouffer RJ, John JG (2013) Reductions in labour capacity from heat stress under climate warming. Nat Clim Chang 3:563–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1827
ESDC (2018) Thermal stress in the work place. Employment and Social Development Canada, LT-313-11-18E. https://www.canada.ca/en/employment-social-development/services/health-safety/reports/thermal-stress-work-place.html. Accessed 10 Sep 2019
Hale A, Borys D, Adams M (2015) Safety regulation: the lessons of workplace safety rule management for managing the regulatory burden. Saf Sci 71:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2013.11.012
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part A: global and sectoral aspects. Contribution of working group II to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. University Press, Cambridge, Cambridge
ISO (2017) Ergonomics of the thermal environment — assessment of heat stress using the WBGT (wet bulb globe temperature) index. ISO 7243:2017. International Standards Organization, Geneva
Jia AY, Rowlinson S, Loosemore M, Gilbert D, Ciccarelli M (2019) Institutional logics of processing safety in production: the case of heat stress management in a megaproject in Australia. Saf Sci 120:388–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.07.004
JSOH (2018) Recommendation of occupational exposure limits (2018–2019). J Occup Health 60(5):419–452. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.ROEL2018
Jung WS, Park JK, Kim EB, Song JH (2009) Study on the establishment of threshold criteria for heat health watch warning system in Korea; part II: improvement of criteria. J Environ Sci 18(7):781–796. https://doi.org/10.5322/JES.2009.18.7.781 (In Korean)
KCDC (2018) Annual report on the notified patients with heat-related illness in Korea. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. http://www.cdc.go.kr/menu.es?mid=a20304010700. Accessed 12 June 2018 (In Korean)
KCWU (2018) Press conference urging the implementation of heat wave safety regulations at construction sites. Korean Construction Workers’ Union. Appendix 2: survey results of construction site during an extreme heat period. https://www.kcwu.or.kr/statement/63972. (In Korean)
Kim YH, Oh IB, Lee JH, Kim JH, Chung IS, Lim HJ, Park JK, Park JS (2016) Evaluation of heat stress and comparison of heat stress indices in outdoor work. J Environ Health Sci 42(2):85–91. https://doi.org/10.5668/JEHS.2016.42.2.85 (In Korean)
Kjellstrom T, Crowe J (2011) Climate change, workplace heat exposure, and occupational health and productivity in Central America. Int J Occup Environ Health 17(3):270–281. https://doi.org/10.1179/107735211799041931
Kjellstrom T, Holmer I, Lemke B (2009) Workplace heat stress, health and productivity – an increasing challenge for low and middle-income countries during climate change. Glob Health Action 2(1):2047. https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v2i0.2047
Kjellstrom T, Lemke B, Otto M (2013) Mapping occupational heat exposure and effects in South-East Asia: ongoing time trends 1980–2009 and future estimates to 2050. Ind Health 51:56–67. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.2012-0174
Kjellstrom T, Lemke B, Otto M, Hyatt O, Dear K (2014) Occupational heat stress: contribution to WHO project on “global assessment of the health impacts of climate change”, which started in 2009. Tech Rep 2014:4 http://www.climatechip.org/technical-reports.
Kjellstrom T, Briggs D, Freyberg C, Lemke B, Otto M, Hyatt O (2016) Heat, human performance, and occupational health: a key issue for the assessment of global climate change impacts. Annu Rev Public Health 37:97–112. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-032315-021740
KMA (2011) A white book of Changma. Korea Meteorological Administration. http://www.climate.go.kr/home/bbs/view.php?bname=publicity&category1=&category2&code=25&skind=&sword=&vcode=4462. Accessed I Jan 2017 (In Korean)
KOSHA (2017) Management guidelines of high-heated working environments. KOSHA guide W-12-2017, Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency. http://www.kosha.or.kr/kosha/data/guidanceW.do?mode=view&articleNo=263634&article.offset=10&articleLimit=10. Accessed 1 Jun 2018 (in Korean)
Lamarche DT, Meade RD, D'Souza AW, Flouris AD, Hardcastle SG, Sigal RJ, Boulay P, Kenny GP (2017) The recommended threshold limit values for heat exposure fail to maintain body core temperature within safe limits in older working adults. J Occup Environ Hyg 14(9):703–711. https://doi.org/10.1080/15459624.2017.1321844
Lee DH, Kim DS, Chung JW, Lee K, Lim HS (2018a) Status and awareness of excessive heat exposure among agricultural workers. J Agric Med Community Health 43(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.5393/JAMCH.2018.43.1.009 (In Korean)
Lee SW, Lee K, Lim B (2018b) Effects of climate change-related heat stress on labor productivity in South Korea. Int J Biometeorol 62:2119–2129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-018-1611-6
Lemke B, Kjellstrom T (2012) Calculating workplace WBGT from meteorological data: a tool for climate change assessment. Ind Health 50:267–278. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.MS1352
LHI (2014) A study on the method of estimating the construction duration for apartment to assure quality. Land and Housing Institute. https://lhi.lh.or.kr/web/atchFile/atchFileDownload.do?atchId=409. Accessed 1 Jun 2018 (In Korean)
Liljegren JC, Carhart RA, Lawday P, Tschopp S, Sharp R (2008) Modeling the wet bulb globe temperature using standard meteorological measurements. J Occup Environ Hyg 5:645–655. https://doi.org/10.1080/15459620802310770
Lim YH, Lee KS, Bae HJ, Kim D, Yoo H, Park S, Hong YC (2019) Estimation of heat-related deaths during heat wave episodes in South Korea (2006–2017). Int J Biometeorol 63:1621–1629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01774-2
Lucas RAI, Epstein Y, Kjellstrom T (2014) Excessive occupational heat exposure: a significant ergonomic challenge and health risk for current and future workers. Extrem Physiol Med 3:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-7648-3-14
Lundgren K, Kuklane K, Gao C, Holmer I (2013) Effects of heat stress on working populations when facing climate change. Ind Health 51:3–15. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.2012-0089
Ministry of Defence (2019) JSP 539: heat illness and cold injury: prevention and management, part 2 guidance. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/prevention-of-climatic-injuries-in-the-armed-forces-medical-policy. Accessed 10 Sep 2019
Morioka I, Miyai N, Miyashita K (2006) Hot environment and health problems of outdoor workers at a construction site. Ind Health 44(3):474–480. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.44.474
NIOSH (2016) NIOSH criteria for a recommended standard: occupational exposure to heat and hot environments. DHHS (NIOSH) Publication 2016-106. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2016-106.
NMC (2019) Statistics of emergency medical. National Medical Center. http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=411&tblId=DT_41104_411&conn_path=I3. Accessed 22 Nov 2019 (In Korean)
OSHA (2013) OSHA technical manual, section III: health hazards, chapter 4. Heat stress. OSHA Instruction TED 01-00-015, Occupational Safety and Health Administration. https://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/otm_iii/otm_iii_4.html.
OSHRI (2013) A study on research on the actual condition about the right of work suspension in workplace. Occupational Safety and Health Research Institute. http://kosha.or.kr/kosha/researchField/researchReportSearch.do?mode=download&articleNo=63320&attachNo=57163. Accessed 20 June 2018 (In Korean)
OSHRI (2016) A study of determining an appropriate construction duration of residential and tunnel projects. Occupational Safety and Health Research Institute. http://oshri.kosha.or.kr/oshri/publication/researchReportSearch.do?mode=download&articleNo=63586&attachNo=57432. Accessed 1 June 2018 (In Korean)
Park JK, Jung WS, Kim EB (2008a) A study on development of the extreme heat standard in Korea. J Environ Sci 17(6):657–669. https://doi.org/10.5322/JES.2008.17.6.657 (In Korean)
Park JK, Jung WS, Kim EB (2008b) A study on the influence of extreme heat on daily mortality. J Korea Soc Atmos Environ 24(5):523–537. https://doi.org/10.5572/KOSAE.2008.24.5.523 (In Korean)
Park JK, Jung WS, Kim EB (2009) Study on the establishment of threshold criteria for heat health watch warning system in Korea; part I: establishment of criteria and verification. J Environ Sci 18(7):767–780. https://doi.org/10.5322/JES.2009.18.7.767 (In Korean)
Parsons K (2003) Human thermal environments: the effects of hot, moderate and cold environments on human health, comfort and performance, 2nd edn. Taylor & Francis, London
Patel T, Mullen SP, Santee WR (2013) Comparison of methods for estimating wet-bulb globe temperature index from standard meteorological measurements. Mil Med 178:926–933. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-13-00117
Sahu S, Sett M, Kjellstrom T (2013) Heat exposure, cardiovascular stress and work productivity in rice harvesters in India: implications for a climate change future. Ind Health 51:424–431. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.2013-0006
Seo DI, Byun HR (2002) Definition of period and occurrence factors of summer and autumn rainy seasons on the Korean Peninsula. Atmos 12(3):402–405 http://www.dbpia.co.kr/journal/articleDetail?nodeId=NODE00943146
Wästerlund DS (1998) A review of heat stress research with application to forestry. Appl Ergon 29(3):179–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-6870(97)00063-X
Xiang J, Bi P, Pisaniello D, Hansen A, Sullivan T (2014) Association between high temperature and work-related injuries in Adelaide, South Australia, 2001–2010. Occup Environ Med 71(4):246–252. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2013-101584
Yaglou CP, Minard D (1956) Prevention of heat casualties at marine corps training centers. Final report under Contract No. N 50RI-07665. Office of Naval Research Physiology Branch, Washington DC
Yi W, Chan APC (2013) Optimizing work–rest schedule for construction rebar workers in hot and humid environment. Build Environ 61:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.12.012
Yi W, Chan APC (2017) Effects of heat stress on construction labor productivity in Hong Kong: a case study of rebar workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14091055
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Korea Meteorological Administration and the Korea Centers for Disease Control for the support in providing climate data for the WBGT calculation and heat-related illness data, respectively.
Funding
This work was funded by the Korea Meteorological Administration Research and Development Program “Support to Use of Meteorological Information and Value Creation” under grant (KMA2018-00122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5.40 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SW., Kim, IG., Kim, HM. et al. Spatio-temporal patterns of the minimum rest time for outdoor workers exposed to summer heat stress in South Korea. Int J Biometeorol 64, 1755–1765 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01956-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01956-3