Abstract
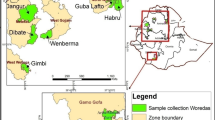
Due to the unique blue color and perennial growth habit, Muscari can be cultivated as a bedding plant, pot plant, or cut flower. Meanwhile, there is lack of information about genetic variations of Muscari neglectum Guss. ex Ten.; consequently, the diversity of nine populations (90 accessions) belonging to M. neglectum was evaluated by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) marker, start codon targeted (SCoT) marker and morphological marker. Ten ISSR primers used in this experiment amplified 142 reproducible bands with 137 (96.4%) polymorphism; and ten SCoT primers amplified 165 bands with 151 (91.12%) polymorphism. Both ISSR and SCoT analyses indicated a high level of genetic variation in the wild population of M. neglectum. Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) revealed a higher genetic diversity within the geographic group (0.69%) compared to the genetic variation among populations (0.31%). The gene flow between populations was low, while there was a greater gene flow between close areas. Morphological data divided nine populations into three clusters, while molecular data separated the populations into five groups, which were confirmed with structure analysis and discriminant analysis of principal component (DAPC) analysis. Our investigation showed that first, SCoT and ISSR markers are suitable for evaluation of genetic variation in Muscari genus, and there is appropriate genetic diversity among M. neglectum populations. Our results suggest some information to conserve the genetic resources and improve breeding program based on genetic data.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MA, Juraimi AS, Rafii MY, Hamid AA, Arolu IW, Abdul Latif M (2015) Genetic diversity analysis among collected purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) accessions using ISSR markers. CR Biol 338:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2014.10.007
Aras S, Cansaran D (2006) Isolation of DNA for sequence analysis from herbarium material of some lichen specimens. Turkish J Bot 30:449–453
Badfar-Chaleshtori S, Shiran B, Kohgard M, Mommeni H, Hafizi A, Khodambashi M, Mirakhorli N, Sorkheh K (2012) Assessment of genetic diversity and structure of imperial crown (Fritillaria imperialis L.) populations in the Zagros region of Iran using AFLP, ISSR and RAPD markers and implications for its conservation. Biochem Syst Ecol 42:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2011.12.027
Baliyan D, Sirohi A, Kumar M, Kumar V, Malik S, Sharma Shiveta, Sharma Shailendra (2014) Comparative genetic diversity analysis in chrysanthemum: a pilot study based on morpho-agronomic traits and ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 167:164–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.12.029
Bhattacharyya P, Kumaria S, Kumar S, Tandon P (2013) Start codon targeted (SCoT) marker reveals genetic diversity of Dendrobium nobile L., an endangered medicinal orchid species. Gene 529:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.096
Bor NL (1970) Gramineae-Festuceae. In: Rechinger KH (ed) Flora Iranica, vol 70. Akademische Druck-u. Verlagsanstalt, Graz, pp 450–452
Candido V, Castronuovo D, Fascetti S, Rosati L, Potenza G (2017) Seed-propagated Muscari comosum (L.) Mill.: effects of sowing date and growing conditions. Plant Biosyst An Int J Deal Asp Plant Biol 151:484–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2016.1194337
Collard BCY, Mackill DJ (2009) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: a simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-008-0060-5
De Hertogh A, Le Nard M (eds) (1993) The physiology of flower bulbs. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Earl DA, VonHoldt BM (2012) Structure harvester: a website and program for visualizing Structure output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Evans LT (1993) The physiology of flower induction - Paradigms lost and paradigms regained. Aust J Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP9930655
Garrido-Ramos MA, Jamilena M, De La Herrán R, Ruiz Rejón C, Camacho JPM, Ruiz Rejón M (1998) Inheritance and fitness effects of a pericentric inversion and a supernumerary chromosome segment in Muscari comosum (L.). Heredity 80:724–731. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.1998.00344.x
Ghahreman A (1984) Color atlas of Iranian plants, 5th edn. Institute of Forestries and Grasslands, Botany Division, Tehran
Guo W, Jeong J, Kim Z, Wang R, Kim E, Kim S (2011) Genetic diversity of Lilium tsingtauense in China and Korea revealed by ISSR markers and morphological characters. Biochem Syst Ecol 39:352–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2011.05.002
Jiménez JF, López-Romero C, Rosselló JA, Sánchez-Gómez P (2015) Genetic diversity of Narcissus tortifolius, an endangered endemic species from Southeastern Spain. Plant Biosyst An Int J Deal All Asp Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2015.1108937
Jombart T (2008) adegenet: a R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 24:1403–1405. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn129
Kamenetsky R, Okubo H (2012) Ornamental geophytes. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/b12881
Kubitzki K (1998) The families and genera of vascular plants, flowering plants, monocotyledons, Lilianae (except Orchidaceae), vol III. Springer, Berlin
Li G, Ra W-H, Park J-W, Kwon S-W, Lee J-H, Park C-B, Park Y-J (2011) Developing EST-SSR markers to study molecular diversity in Liriope and Ophiopogon. Biochem Syst Ecol 39:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2011.08.012
Lim TK (2016) Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants, edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7276-1
Lopez Alonso D, Pascual Reguera L (1989) Population structure and pattern of geographic variation in Muscari comosum along its range of distribution. Genetica 78:39–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058673
Mahboubi M, Taghizadeh M (2016) The antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of Muscari neglectum flower ethanol extract. Herba Polonica 62:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1515/hepo-2016-0021
Naik PK, Alam MA, Singh H, Goyal V, Parida S, Kalia S, Mohapatra T (2010) Assessment of genetic diversity through RAPD, ISSR and AFLP markers in Podophyllum hexandrum: a medicinal herb from the Northwestern Himalayan region. Physiol Mol Biol Plants An Int J Funct Plant Biol 16:135–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0015-9
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106–949:283–292
Parsa A (1949) Flore de l’Iran. Tehran University Press, Tehran
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research–an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software. http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis Wayne. Mol Breed 2(3):225–238
Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051046
Qiu Y-X, Hong D-Y, Fu C-X, Cameron KM (2004) Genetic variation in the endangered and endemic species Changium smyrnioides (Apiaceae). Biochem Syst Ecol 32:583–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2003.08.004
Rahimi M, Nazari L, Kordrostami M, Safari P (2018) SCoT marker diversity among Iranian Plantago ecotypes and their possible association with agronomic traits. Sci Hortic 233:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.01.009
Rohollahi I, Khoshkholghsima NA, Yamada T, Kafi M, Hoshino Y, Liaghat A, Jafari AA (2015) Evaluation of seedling emergence and relative DNA content under dry soil conditions of wild Festuca arundinacea populations collected in Iran. Grassl Sci 61:6–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/grs.12074
Ruiz-Rejon M, Oliver JL (1981) Genetic variability in Muscari comosum (Liliaceae). I. A comparative analysis of chromosome polymorphisms in Spanish and Aegean populations. Heredity 47:403–407. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1981.101
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): comparisons with data from RFLPS and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050544
R Core Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statictical Copmuting, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Vemmos SN (2005) Characterisation of genetic relationships in pansy (Viola wittrockiana) inbred lines using morphological traits and RAPD markers. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 80:529–536. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2005.11511974
Yang S, Xue S, Kang W, Qian Z, Yi Z (2019) Genetic diversity and population structure of Miscanthus lutarioriparius, an endemic plant of China. PLoS ONE 14:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211471
Ye YM, Zhang JW, Ning GG, Bao MZ (2008) A comparative analysis of the genetic diversity between inbred lines of Zinnia elegans using morphological traits and RAPD and ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 118:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2008.05.025
Yeh FC, Young RC, Boyle T (1999) Microsoft window-based freeware for population genetic analysis
Zeng B, Zhang Y, Huang L, Jiang X, Luo D, Yin G (2014) Genetic diversity of orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.) germplasms with resistance to rust diseases revealed by start codon targeted (SCoT) markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 54:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2013.12.028
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests. All the authors read and approved the manuscript in its final form.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
labbaf, N., Rohollahi, I. & Naji, A.M. Genetic diversity and population structure of wild Persian grape hyacinths (Muscari neglectum Guss. ex Ten.) assessed by morphological and molecular markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 67, 1481–1492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00922-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00922-7