Abstract
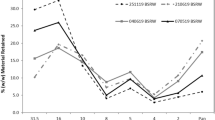
Fluorspar (CaF2) has been widely used to control the physicochemical properties of slag in steelmaking processes. However, it is very important to reduce the CaF2 consumption because it causes various environmental problems. In the current study, therefore, the effect of industrial waste materials such as red mud (RM) and ferromanganese slag (FMS) on the desulfurization behavior of molten steel was investigated to find potential substitutes for fluorspar. Compared to conventional 10 pct CaF2-containing ladle slag, when excess industrial wastes were added (i.e., more than 10 mass pct), the composition of the slag was dramatically changed (SiO2 increases, while FetO and MnO decrease). Therefore, the sulfide capacity of the slag decreased, and the viscosity of the slag increased. Thus, the desulfurization efficiency was also reduced. However, when the RM or FMS were added not more than 10 mass pct to lean-CaF2 (3 pct) slag, the sulfide capacity of the slag was equivalent to 10 pct CaF2-containing ladle slag; thus, the desulfurization efficiency was also equivalent with lower melting point and higher fraction of liquid phase. Consequently, it was confirmed that a small amount (less than 10 mass pct) of industrial wastes can be added as a desulfurization fluxing agent as a partial substitute for fluorspar.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Andersson and D. Sichen: Steel Research Int., 2009, vol. 80, pp. 544-51.
A. Putan, V. Putan, T. Heput and A. Socalici: Rev. Metall., 2013, vol. 49, pp. 31-44.
K. C. Mills: Slag Atlas, 2nd ed, Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Düsseldorf, 1995, p. 362.
J. H. Park and D. J. Min: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2004, vol. 337, pp. 150-56.
J. H. Park, D. J. Min and H. S. Song: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 38-43.
F. Shahbazian, D. Sichen, K. C. Mills and S. Seetharaman: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 1999, vol. 26, pp. 193-99.
P. Kozakevitch: Rev. Metall., 1954, 51, 569-87.
J. R. Maclean, P. W. Kingston, J. B. MacDonald and W. F. Caley: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 1997, 24, 406-11.
J. H. Park, D. J. Min and H. S. Song: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 33B, pp. 723-28.
T. S. Kim and J. H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 2031-38.
J. S. Han, J. G. Kang, J. H. Shin, Y. Chung and J. H. Park: Ceram. Int., 2018, vol. 44, pp. 13197-13204.
M. O. Suk and J. H. Park: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2009, vol. 92, pp. 717-23.
J. H. Park, M. O. Suk, I. H. Jung, M. Guo and B. Blanpain: Steel Res. Int., 2010, vol. 81, pp. 860-68.
A. I. Zaitsev, A. V. Leites, A. D. Litvina and B. M. Mogutnov: Steel Res., 1994, vol. 65, pp. 368-74.
A. S. B. Moreira, C. A. Silva and I. A. Silva: REM: Int. Eng. J, 2018, vol. 71, pp. 261-67.
Y. Kashiwaya and A. Cramb: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 401-07.
J. H. Park and D. J. Min: Steel Res. Int., 2004, vol. 75, pp. 807-11.
Fluorspar supply: trade trends & new sources (http://imformed.com/fluorspar-supply-trade-trends-new-sources/) accessed on 1st Feb 2020.
T. S. Tribe, P. W. Kingston, J. B. MacDonald and W. F. Caley: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 1994, vol. 21, pp. 145-49.
S. H. Amini, O. Ostrovski, and M. P. Brungs: Proc. of 7th Int. Conf. on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts, The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2004, pp. 595-99.
J. Y. Choi, D. J. Kim and H. G. Lee: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 3, pp. 216-24.
C. R. Borra, B. Blanpain, Y. Pontikes and K. Binnemans: J. Sustain. Metall, 2016, vol. 2, pp. 365-86.
K. Evans: J. Sustain. Metall, 2016, vol. 2, pp. 316-31.
Y. H. Park and Y. N. Jung: Magazine of RCR, 2017, vol. 12, pp. 22-27.
International Aluminium Institute (IAI): Bauxite ResidueManagement_Best Practice, July 2015, pp. 1–31.
P. E. Tsakiridis, S. Agatzini-Leonardou and P. Oustadakis: J. Hazard. Mater., 2004, vol. B116, pp. 103-10.
M. Singh, S. N. Upadhayay and P. M. Prasad: Waste Manage., 1996, vol. 16, pp. 665-70.
X. Liu and N. Zhang: Waste Manage. & Res., 2010, vol. 29, pp. 1053-63.
J. Yang and B. Xiao: Constr. Build. Mater., 2008, vol. 22, pp. 2299-2307.
D. D. Arhin, D. S. Konadu, E. Annan, F. P. Buabeng, A. Yaya and B. A. Tuffour: Am. J. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 3, pp. 110-19.
S. E. Olsen, M. Tangstad, T. Lindstad: FeMn: Production of Manganese Ferroalloys, SINTEF and Tapir Academin Press, Trondheim, Norway, 2007.
D. R. Groot, D. M. Kazadi, H. Pollmann, J. P. R. de Villiers, T. Redtmann and J. Steenkamp: Proc. INFACON XIII, The Thirteenth International Ferroalloys Congress, June 9–13, Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2013, pp. 1051–60.
J. H. Heo, Y. Chung, J. H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1154-61.
J. Safarian, G. Tranell, L. Kolbeinsen, M. Tangstad, S. Gaal and J. Kaczorowski: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 702-12.
J. Safarian, L. Kolbeinsen, M. Tangstad and G. Tranell: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 929-39.
J. K. Kang, J. H. Shin, Y. Chung and J. H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48B, pp. 2123-35.
B. Deo and R. Boom: Fundamentals of Steelmaking Metallurgy, Prentice Fall, New York, NY, 1993.
J. K. Jung and J. J. Pak: J. Kor. Inst. Met. Mater, 2000, vol. 38, pp. 585-90.
X. Chushao and T. Xin: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 1081-83.
E. Oktay and R. J. Fruehan: Steel Res., 1995, vol. 66, pp. 93-95.
N. Bannenberg, H. Lachmund and B. Prothmann: ISS Steelmaking Conf. Proc., 1994, vol. 77, pp. 135-43.
H. Lachmund and Y. Xie: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2003, vol. 30, pp. 125-29.
K. Takahashi, K. Utagawa, H. Shibata, S. Kitamura, N. Kikuchi and Y.Kishimoto: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 10-17.
D. Lindstrom and D. Sichen: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 83-92.
C. J. B. Fincham and F. D. Richardson: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 1954, vol. 223, pp. 40-62.
Y. B. Kang and A. D. Pelton: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 979-94.
A. Einstein: Ann. Phys, 1906, vol. 19, pp. 289-306.
R. Roscoe: Br. J. Appl. Phys, 1952, vol. 3, pp. 267-69.
S. H. Seok, S. M. Jung, Y. S. Lee and D. J. Min: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 1090-96.
J. H. Heo, J. S. Yoo, Y. Chung and J. H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 903-13.
J. H. Heo and J. H. Park: Calphad, 2017, vol. 58, pp. 219-28.
J. H. Heo and J. H. Park: Calphad, 2017, vol. 58, pp. 229-38.
J. H. Park: Steel Res. Int., 2013, vol. 84, pp. 664-69.
G. H. Park, Y. B. Kang and J. H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1375-82.
Y. B. Kang and J. H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 1211-17.
J. H. Park and G. H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 764-69.
J. H. Park: Met. Mater. Int., 2013, vol. 19, pp. 577-84.
S. J. Jeong, T. S. Kim and J. H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48B, pp. 545-53.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the Industrial Strategic Technology Development program (Grant Number 10063056) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE), Korea. In addition, this research was partly funded by the Competency Development Program for Industry Specialists (Grant Number P0002019) of the MOTIE, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted February 16, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, T.S., Park, J.H. Effect of Fluorspar and Industrial Wastes (Red Mud and Ferromanganese Slag) on Desulfurization Efficiency of Molten Steel. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2309–2320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01889-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01889-7