Abstract
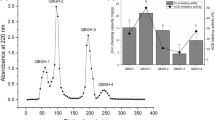
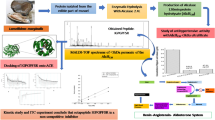
Hypertension is declared as the major risk factor of cardiovascular diseases and stroke, and the leading cause of premature deaths. ACE is a zinc dependent dipeptidyl peptidase and plays key role in controlling blood pressure via renin angiotensin system (RAS), and hence serves as the promising target for antihypertension drugs. Many food derived antihypertensive peptides have been identified recently. However, their ACE inhibitory activity, interactions and stability are not fully evaluated. Our work focused on combination of modern bioinformatics techniques for efficient evaluation of potent ACE inhibitory food peptides and understanding of interactions between ACE and inhibitory peptides. We reported novel antihypertensive peptide IQDVPS, LQPGS, VIP from date, salmon and soybean proteins respectively. Food proteins were digested in-silico to release peptides. Molecular docking studies revealed high binding affinities and interactions with ACE active site. MD simulations and Alanine Scanning were carried out to study the stability of these ACE-peptide complexes in cell like environment. The results showed that the suggested peptides competitively inhibit ACE by tightly binding to its active site, meanwhile maintaining the structural stability of the complex. ACE-LQPGS (Salmon) was found to have best binding with least structural fluctuations.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10093-9
References
Abdel-Rahman LH, Ismail NM, Ismael M, Abu-Dief AM, Ahmed EH (2017) Synthesis, characterization, DFT calculations and biological studies of Mn (II), Fe (II), Co (II) and Cd (II) complexes based on a tetradentate ONNO donor Schiff base ligand. J Mol Struct 1134:851–862
Adam A, Cugno M, Molinaro G, Perez M, Lepage Y, Agostoni A (2002) Aminopeptidase P in individuals with a history of angio-oedema on ACE inhibitors. Lancet 359:2088–2089
Aldeghi M, Heifetz A, Bodkin MJ, Knapp S, Biggin PC (2016) Accurate calculation of the absolute free energy of binding for drug molecules. Chem Sci 7:207–218
Bicket DP (2002) Using ACE inhibitors appropriately. Am Fam Phys 66:461–468
Carretero OA (2005) Novel mechanism of action of ACE and its inhibitors. Am J Physiol- Heart C 289(5):H1796–H1797
Chay SY, Salleh A, Sulaiman NF, Abidin NZ, Hanafi MA, Zarei M, Saari N (2018) Blood- pressure lowering efficacy of winged bean seed hydrolysate in spontaneously hypertensive rats, peptide characterization and a toxicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Funct 9(3):1657–1671
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ (2003) The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572
Cushman DW, Ondetti MA (1999) Design of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Nat Med 5:1110–1113
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh ewald: An N⋅ log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98:10089–10092
Esther CR, Marino EM, Howard TE, Machaud A, Corvol P, Capecchi MR, Bernstein KE (1997) The critical role of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme as revealed by gene targeting in mice. J Clin Invest 99:2375–2385
Falsafi-zadeh S, Karimi Z, Galehdari H (2012) VMD DisRg: new user-friendly implement for calculation distance andradius of gyration inVMD program. Bioinformation 8:7–9
Fanng L, Geng M, Liu C, Wang J, Min W, Liu J (2019) Structural and molecular basis of angiotensin-converting enzyme by computational modeling: insights into the mechanisms of different inhibitors. PLoS ONE 14(4):e0215609
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Wilkins M R, Appel R D, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In the proteomics protocols handbook Springer, pp. 571–607
Gu Y, Majumder K, Wu J (2011) QSAR-aided in silico approach in evaluation of food proteins as precursors of ACE inhibitory peptides. Food Res Int 44(8):2465–2474
Halgren TA (1996) Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J Comput Chem 17(5–6):490–519
Hoover WG (1985) Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys Rev A 31(3):1695
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(1):33–38
Jayakumar S, Mahendiran D, Viswanathan V, Velmurugan D, KalilurRahiman A (2017) Heteroscorpionate-based heteroleptic copper (II) complexes: antioxidant, molecular docking and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Appl Organomet Chem 31(11):e3809
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79(2):926–935
Keskin O, Gursoy A, Ma B, Nussinov R (2008) Principles of protein-protein interactions: what are the preferred ways for proteins to interact? Chem Rev 108:1225–1244
Kitts DD, Weiler K (2003) Bioactive proteins and peptides from food sources, applications of bioprocesses used in isolation and recovery. J Curr Pharm Des 9(16):1309–1323
Laskowski RA, Swindells MB (2011) LigPlot+: multiple ligand—protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J Chem Inf Model 51(10):2778–2786
Liu X, Peng L, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Zhang JZ (2018) Computational alanine scanning with interaction entropy for protein–ligand binding free energies. J Chem Theor Comput 14(3):1772–1780
Lobanov MY, Bogatyreva NS, Galzitskaya OV (2008) Radius of gyration as an indicator of protein structure compactness. Mol Biol 42(4):623–628
MacKerell AD Jr, Bashford D, Bellott M, Dunbrack RL Jr, Evanseck JD, Field MJ et al (1998) All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J Phys Chem B 102(18):3586–3616
Meena J, Archana D, Santhy KS (2018) In silico analysis of Cyclea peltata (Lam.) Hook. f. & Thomson root extract for docking studies of the compound β-estradiol. Indian J Tradit Knowl 17(1):162–167
Natesh R, Schwager SLU, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR (2003) Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme–lisinopril complex. Nature 421(6922):551
Patchett AA, Cordes EH (1985) The design and properties of N-carboxyalkyldipeptide inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 57:1–84
Phillips JC, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J, Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel RD, Kale L, Schulten K (2005) Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem 26(16):1781–1802
Pires DEV, Ascher DB, Blundell TL (2013) mCSM: predicting the effects of mutations in proteins using graph-based signatures. Bioinformatics 30(3):335–342
Qiao L, Li B, Chen Y, Li L, Chen X, Wang L, Lu F, Luo G, Li G, Zhang Y (2016) Discovery of anti-hypertensive oligopeptides from adlay based on in silico proteolysis and virtual screening. Int J Mol Sci 17(12):2099
Rotmensch HH, Vlasses PH, Ferguson RK (1988) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Med Clin North Am 72:399–425
Seeliger D, de Groot BL (2010) Conformational transitions upon ligand binding: holo- structure prediction from apo conformations. PLoS Comput Biol 6(1):e1000634
Shattuck TW (2011) Colby college molecular mechanics exercises MOE (Molecular Operating Environment) exercises. Chemical Computing Group ULC, Montreal, QC
Soubrier F, Alhenc-Gelas F, Hubert C, Allegrini J, John M, Tregear G, Corvol P (1988) Two putative active centers in human angiotensin I-converting enzyme revealed by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85(24):9386–9390
Walther B, Sieber R (2011) Bioactive proteins and peptides in foods. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 81:181–191
Wang X, Wu S, Xu D, Xie D, Guo H (2011) Inhibitor and substrate binding by angiotensin- converting enzyme: quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical molecular dynamics studies. J Chem Info Model 51(5):1074–1108
Wang B (2009) Drug design of zinc-enzyme inhibitors: functional, structural, and disease applications vol. 14. Wiley, New Jersey
Wei L, Clauser E, Alhenc-Gelas F, Corvol P (1992) The two homologous domains of human angiotensin I-converting enzyme interact differently with competitive inhibitors. J Biol Chem 267(19):13398–13405
Wong J, Patel RA, Kowey PR (2004) The clinical use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 47:116–130
Worth CL, Preissner R, Blundell TL (2011) SDM—a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability and malfunction. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl 2):W215–W222
Wu J, Aluko RE, Nakai S (2006) Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: quantitative structure- activity relationship study of di-and tripeptides. J Agric Food Chem 54(3):732–738
Funding
No funding has been obtained for current project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable. It is computational research no animal subject has been used.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: Error in author name Muhammad Wasim Sajid has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousafi, Q., Batool, J., Khan, M.S. et al. In Silico Evaluation of Food Derived Bioactive Peptides as Inhibitors of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE). Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 341–349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10090-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10090-y