Abstract
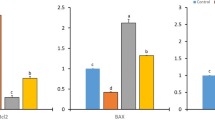
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of zinc and melatonin administration on interleukin-6, lipid peroxidation parameters, and element metabolism in DMBA-induced breast cancer in female rats. A total of 42 recently weaned Wistar rats were divided into 5 groups as follows: control (group 1), DMBA control (group 2), DMBA + zinc (group 3), DMBA + melatonin (group 4), and DMBA + melatonin and zinc (group 5). Malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH) levels in breast tissue and blood samples were determined via spectrophotometric methods. In addition, iron, magnesium, zinc, and copper levels in serum samples were determined by atomic emission, and plasma interleukin-6 levels were determined by ELISA method. The highest tissue and plasma MDA and the lowest tissue and erythrocyte GSH levels found in the study were in group 2; the highest tissue and erythrocyte GSH levels and the lowest tissue and plasma MDA levels are in group 5 (P < 0.05). Iron, magnesium, and zinc levels of groups 3, 4, and 5 were higher than the DMBA group without administration (group 2), but the copper values were significantly lower (P < 0.05). The highest IL-6 levels were determined in group 2 while IL-6 levels in the DMBA group (G5) treated with combined melatonin and zinc were lower than all other breast cancer groups (P < 0.05). According to the findings obtained in this presented study, combined zinc and melatonin therapy can contribute to the prevention of tumor growth by improving the disruption in element metabolism and suppressing IL-6 levels and reducing tissue damage that causes the cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubatka P, Zubor P, Busselberg D, Kwon TK, Adamek M, Petrovic D, Opatrilova R, Gazdikova K, Caprnda M, Rodrigo L, Danko J, Kruzliak P (2018) Melatonin and breast cancer: evidences from preclinical and human studies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 122:133–143
Dodda BR, Bondi CD, Hasan M, Clafshenkel WP, Gallagher KM, Kotlarczyk MP, Sethi S, Buszko E, Latimer JJ, Cline JM, Witt-Enderby PA, Davis VL (2019) Co-administering melatonin with an estradiol-progesterone menopausal hormone therapy represses mammary cancer development in a mouse model of HER2-positive breast cancer. Front Oncol 9:525
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Tan DX, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Qin L, Yang SF, Xu K (2017) Melatonin, a full service anti cancer agent: inhibition of initiation, progression and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 18(4):E843
Bondy SC, Campbell A (2018) Mechanisms underlying tumor suppressive properties of melatonin. Int J Mol Sci 19:E2205
Talib WH (2018) Melatonin and cancer hallmarks. Molecules 23:E518
da Cruz RS, Andrade FO, Carioni VMO, Rosim MP, Miranda MLP, Fontelles CC, de Oliveira PV, Barbisan LF, Castro IA, Ong TP (2019) Dietary zinc deficiency or supplementation during gestation increases breast cancer susceptibility in adult female mice offspring following a J-shaped pattern and through distinct mechanisms. Food Chem Toxicol 134:110813
Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Baltaci SB (2019) Review: The role of zinc in the endocrine system. Pak J Pharm Sci 32(1):231–239
Baltaci SB, Mogulkoc R, Baltaci AK, Emsen A, Artac H (2018) The effect of zinc and melatonin supplementation on immunity parameters in breast cancer induced by DMBA in rats. Arch Physiol Biochem 124(3):247–252
Kampan NC, Xiang SD, McNally OM, Stephens AN, Quinn MA, Plebanski M (2018) Immunotherapeutic Interleukin-6 or Interleukin-6 receptor blockade in cancer: challenges and opportunities. Curr Med Chem 25(36):4785–4806
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A, Bhatt AN (2016) Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour Biol 37(9):11553–11572
Zarogoulidis P, Yarmus L, Darwiche K, Walter R, Huang H, Li Z, Zaric B, Tsakiridis K, Zarogoulidis K (2013) Interleukin-6 cytokine: a multifunctional glycoprotein for cancer. Immunome Res 9(62):16535
Mihara M, Uchiyama M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86(1):271–278
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman's reagent. Anal Biochem 25(1):192–205
Hadley M, Draper HH (1990) Isolation of a guanine-malondialdehyde adduct from rat and human urine. Lipids 25(2):82–85
Atroshi F, Sankari S, Osterberg S, Sandholm M (1981) Variation of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase activity in Finn sheep. Res Vet Sci 31(3):267–271
Gan H, Zhang Y, Zhou Q, Zheng L, Xie X, Veeraraghavan VP, Mohan SK (2019) Zingerone induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in MCF-7 cells and prevents 7,12-dimethylbenz(a) anthracene-induced mammary carcinogenesis in experimental rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 33(10):e22387
Rajendran J, Pachaiappan P, Subramaniyan S (2019) Dose-dependent chemopreventive effects of citronellol in DMBA-induced breast cancer among rats. Drug Dev Res 80(6):867–876
Zeweil MM, Sadek KM, Taha NM, El-Sayed Y, Menshawy S (2019) Graviola attenuates DMBA-induced breast cancer possibly through augmenting apoptosis and antioxidant pathway and downregulating estrogen receptors. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(15):15209–15217
Hecht F, Pessoa CF, Gentile LB, Rosenthal D, Carvalho DP, Fortunato RS (2016) The role of oxidative stress on breast cancer development and therapy. Tumour Biol 37(4):4281–4291
Gurer-Orhan H, Ince E, Konyar D, Saso L, Suzen S (2018) The role of oxidative stress modulators in breast cancer. Curr Med Chem 25(33):4084–4101
Borges de Araújo CG, Oliveira do Nascimento Holanda A, de Souza Rocha CV, Soares do Nascimento AP, Simplício Revoredo CM, Borges da Silva B, do Nascimento Nogueira N, do Nascimento Marreiro D (2015) Relationship between zincemia, superoxide dismutase activity and marker of oxidatıve stress in women with breast cancer. Nutr Hosp 32(2):785–791
Famurewa AC, Ekeleme-Egedigwe CA, David EE, Eleazu CO, Folawiyo AM, Obasi NA (2020) Zinc abrogates anticancer drug tamoxifen-induced hepatotoxicity by suppressing redox imbalance, NO/iNOS/NF-ĸB signaling, and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in female rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 30(2):115–123
Amin AH, El-Missiry MA, Othman AI, Ali DA, Gouida MS, Ismail AH (2019) Ameliorative effects of melatonin against solid Ehrlich carcinoma progression in female mice. J Pineal Res 67(2):e12585
Luo M, Shang L, Brooks MD, Jiagge E, Zhu Y, Buschhaus JM, Conley S, Fath MA, Davis A, Gheordunescu E, Wang Y, Harouaka R, Lozier A, Triner D, McDermott S, Merajver SD, Luker GD, Spitz DR, Wicha MS (2018) Targeting breast cancer stem cell state equilibrium through modulation of redox signaling. Cell Metab 28(1):69–86.e6
Didžiapetrienė J, Kazbarienė B, Tikuišis R, Dulskas A, Dabkevičienė D, Lukosevičienė V, Kontrimavičiūtė E, Sužiedėlis K, Ostapenko V (2020) Oxidant/antioxidant status of breast cancer patients in pre- and post-operative periods. Medicina (Kaunas) 56(2):E70
Gumulec J, Masarik M, Krizkova S, Adam V, Hubalek J, Hrabeta J, Eckschlager T, Stiborova M, Kizek R (2011) Insight to physiology and pathology of zinc(II) ions and their actions in breast and prostate carcinoma. Curr Med Chem 18(33):5041–5051
Al-Saran N, Subash-Babu P, Al-Nouri DM, Alfawaz HA, Alshatwi AA (2016) Zinc enhances CDKN2A, pRb1 expression and regulates functional apoptosis via upregulation of p53 and p21 expression in human breast cancer MCF-7 cell. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 47:19–27
Jarosz M, Olbert M, Wyszogrodzka G, Młyniec K, Librowski T (2017) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling. Inflammopharmacology 25(1):11–24
Li Y, Li S, Zhou Y, Meng X, Zhang JJ, Xu DP, Li HB (2017) Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 8(24):39896–39921
Hill SM, Belancio VP, Dauchy RT, Xiang S, Brimer S, Mao L, Hauch A, Lundberg PW, Summers W, Yuan L, Frasch T, Blask DE (2015) Melatonin: an inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 22(3):183–204
Chang VC, Cotterchio M, Khoo E (2019) Iron intake, body iron status, and risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 19(1):543
Elliott RL, Head JF, McCoy JL (1994) Relationship of serum and tumor levels of iron and iron-binding proteins to lymphocyte immunity against tumor antigen in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 30(3):305–309
Rajizadeh A, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Zavar-Reza J, Shiryazdi SM (2017) Comparison of hematological parameters, iron levels, and oxidative stress in women with and without breast cancer: a case-control study. Med J Islam Repub Iran 31:114
Quintana Pacheco DA, Sookthai D, Graf ME, Schübel R, Johnson T, Katzke VA, Kaaks R, Kühn T (2018) Iron status in relation to cancer risk and mortality: findings from a population-based prospective study. Int J Cance 143(3):561–569
Hennigar SR, Kelley AM, McClung JP (2016) Metallothionein and zinc transporter expression in circulating human blood cells as biomarkers of zinc status: a systematic review. Adv Nutr 7(4):735–746
Jouybari L, Kiani F, Akbari A, Sanagoo A, Sayehmiri F, Aaseth J, Chartrand MS, Sayehmiri K, Chirumbolo S, Bjørklund G (2019) A meta-analysis of zinc levels in breast cancer. J Trace Elem Med Biol 56:90–99
Abdelgawad IA, El-Mously RH, Saber MM, Mansour OA, Shouman SA (2015) Significance of serum levels of vitamin D and some related minerals in breast cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(4):4074–4082
Choi R, Kim MJ, Sohn I, Kim S, Kim I, Ryu JM, Choi HJ, Kim JM, Lee SK, Yu J, Kim SW, Nam SJ, Lee JE, Lee SY (2018) Serum trace elements and their associations with breast cancer subgroups in Korean breast cancer patients. Nutrients 11(1):E37
Masjedi A, Hashemi V, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Ghalamfarsa G, Azizi G, Yousefi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F (2018) The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 108:1415–1424
Weng YS, Tseng HY, Chen YA, Shen PC, Al Haq AT, Chen LM, Tung YC, Hsu HL (2019) MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2 macrophage polarization in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer 18(1):42
González-González A, García Nieto E, González A, Sánchez-Fernández C, Alonso-González C, Menéndez-Menéndez J, Gómez-Arozamena J, Cos S, Martínez-Campa C (2019) Melatonin modulation of radiation and chemotherapeutics-induced changes on differentiation of breast fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci 20(16):E3935
Unver N, McAllister F (2018) IL-6 family cytokines: key inflammatory mediators as biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 41:10–17
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Projects Coordinatorship of Selcuk University (SUBAPK; project no. 16202035).
Data
Combined zinc and melatonin treatment may contribute to prevent tumor growth by improving impairment in element metabolism and suppressing IL-6 levels and increased tissue damage that causes acceleration of cancer development.
Funding
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Projects Coordinatorship of Selcuk University (SUBAPK; project no. 16202035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Informed Consent
This study was performed on Wistar type adult male rats.
Ethical Approval
Research meets ethical guidelines is a required field. The study protocol was approved by Selçuk University Experimental Medicine Research and Application Center Laboratory Animals Ethics Board (No: 2016-32).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulbahce-Mutlu, E., Baltaci, S.B., Menevse, E. et al. The Effect of Zinc and Melatonin Administration on Lipid Peroxidation, IL-6 Levels, and Element Metabolism in DMBA-Induced Breast Cancer in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 1044–1051 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02238-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02238-0