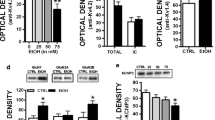
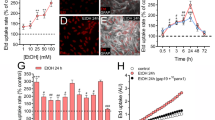
Abstract
Recent studies show that alcohol exposure can induce glial production of neuroimmune factors in the CNS. Of these, IL-6 has gained attention because it is involved in a number of important physiological and pathophysiological processes that could be affected by alcohol-induced CNS production of IL-6, particularly under conditions of excessive alcohol use. For example, IL-6 has been shown to play a role in hippocampal behaviors and synaptic plasticity (long-term potentiation; LTP) associated with memory and learning. Surprisingly, in our in vitro studies of LTP at the Schaffer collateral to CA1 pyramidal neuron synapse in hippocampus from transgenic mice that express elevated levels of astrocyte produced IL-6 (TG), LTP was not altered by the increased levels of IL-6. However, exposure to acute alcohol revealed neuroadaptive changes that served to protect LTP against the alcohol-induced reduction of LTP observed in hippocampus from non-transgenic control mice (WT). Here we examined the induction phase of LTP to assess if presynaptic neuroadaptive changes occurred in the hippocampus of TG mice that contributed to the resistance of LTP to alcohol. Results are consistent with a role for IL-6-induced neuroadaptive effects on presynaptic mechanisms involved in transmitter release in the resistance of LTP to alcohol in hippocampus from the TG mice. These actions are important with respect to a role for IL-6 in physiological and pathophysiological processes in the CNS and in CNS actions of alcohol, especially when excessive alcohol used is comorbid with conditions associated with elevated levels of IL-6 in the CNS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoglia AE, Sharko AC, Psilos KE, Holstein SE, Reid GT, Hodge CW (2015) Alcohol alters the activation of ERK1/2, a functional regulator of binge alcohol drinking in adult C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39(3):463–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12645
Alfonso-Loeches S, Pascual-Lucas M, Blanco AM, Sanchez-Vera I, Guerri C (2010) Pivotal role of TLR4 receptors in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and brain damage. J Neurosci 30(24):8285–8295. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0976-10.2010
Alleva E, Cirulli F, Bianchi M, Bondiolotti GP, Chiarotti F, De Acetis L, Panerai AE (1998) Behavioural characterization of interleukin-6 overexpressing or deficient mice during agonistic encounters. Eur J Neurosci 10(12):3664–3672
Anderson ML, Nokia MS, Govindaraju KP, Shors TJ (2012) Moderate drinking? Alcohol consumption significantly decreases neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Neuroscience 224:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.08.018
Aniszewska A, Chlodzinska N, Bartkowska K, Winnicka MM, Turlejski K, Djavadian RL (2015) The expression of interleukin-6 and its receptor in various brain regions and their roles in exploratory behavior and stress responses. J Neuroimmunol 284:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.05.001
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1999) Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 22(5):208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-2236(98)01349-6
Armario A, Hernandez J, Bluethmann H, Hidalgo J (1998) IL-6 deficiency leads to increased emotionality in mice: evidence in transgenic mice carrying a null mutation for IL-6. J Neuroimmunol 92(1–2):160–169
Baier PC, May U, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Schiffelholz T (2009) Impaired hippocampus-dependent and -independent learning in IL-6 deficient mice. Behav Brain Res 200(1):192–196
Balschun D, Wetzel W, Del Rey A, Pitossi F, Schneider H, Zuschratter W, Besedovsky HO (2004) Interleukin-6: a cytokine to forget. FASEB J 18(14):1788–1790. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-1625fje
Barney TM, Vore AS, Gano A, Mondello JE, Deak T (2019) The influence of central interleukin-6 on behavioral changes associated with acute alcohol intoxication in adult male rats. Alcohol 79:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.11.004
Baxter-Potter LN, Henricks AM, Berger AL, Bieniasz KV, Lugo JM, McLaughlin RJ (2017) Alcohol vapor exposure differentially impacts mesocorticolimbic cytokine expression in a sex-, region-, and duration-specific manner. Neuroscience 346:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.01.015
Becker HC (2000) Animal models of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Res Health 24(2):105–113
Blednov YA, Ponomarev I, Geil C, Bergeson S, Koob GF, Harris RA (2012) Neuroimmune regulation of alcohol consumption: behavioral validation of genes obtained from genomic studies. Addict Biol 17(1):108–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00284.x
Butterweck V, Prinz S, Schwaninger M (2003) The role of interleukin-6 in stress-induced hyperthermia and emotional behaviour in mice. Behav Brain Res 144(1–2):49–56
Campbell IL, Abraham CR, Masliah E, Kemper P, Inglis JD, Oldstone MB, Mucke L (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(21):10061–10065
Chandler LJ, Sutton G (2005) Acute ethanol inhibits extracellular signal-regulated kinase, protein kinase B, and adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate response element binding protein activity in an age- and brain region-specific manner. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(4):672–682
Chi P, Greengard P, Ryan TA (2003) Synaptic vesicle mobilization is regulated by distinct synapsin I phosphorylation pathways at different frequencies. Neuron 38(1):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00151-x
Chourbaji S, Urani A, Inta I, Sanchis-Segura C, Brandwein C, Zink M, Schwaninger M, Gass P (2006) IL-6 knockout mice exhibit resistance to stress-induced development of depression-like behaviors. Neurobiol Dis 23(3):587–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.05.001
Citri A, Malenka RC (2008) Synaptic plasticity: multiple forms, functions, and mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(1):18–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301559
Cui C, Koob GF (2017) Titrating tipsy targets: the neurobiology of low-dose alcohol. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38(6):556–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.03.002
D'Arcangelo G, Tancredi V, Onofri F, D'Antuono M, Giovedi S, Benfenati F (2000) Interleukin-6 inhibits neurotransmitter release and the spread of excitation in the rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Neurosci 12(4):1241–1252. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00011.x
Dittman JS, Kreitzer AC, Regehr WG (2000) Interplay between facilitation, depression, and residual calcium at three presynaptic terminals. J Neurosci 20(4):1374–1385
Dobrunz LE, Stevens CF (1997) Heterogeneity of release probability, facilitation, and depletion at central synapses. Neuron 18(6):995–1008
Doremus-Fitzwater TL, Buck HM, Bordner K, Richey L, Jones ME, Deak T (2014) Intoxication- and withdrawal-dependent expression of central and peripheral cytokines following initial ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(8):2186–2198. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12481
Erta M, Giralt M, Esposito FL, Fernandez-Gayol O, Hidalgo J (2015) Astrocytic IL-6 mediates locomotor activity, exploration, anxiety, learning and social behavior. Horm Behav 73:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.06.016
Gano A, Doremus-Fitzwater TL, Deak T (2016) Sustained alterations in neuroimmune gene expression after daily, but not intermittent, alcohol exposure. Brain Res 1646:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.027
Gano A, Pautassi RM, Doremus-Fitzwater TL, Deak T (2017) Conditioned effects of ethanol on the immune system. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 242(7):718–730. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217694097
Gano A, Vore AS, Sammakia MN, Deak T (2019) Assessment of extracellular cytokines in the hippocampus of the awake behaving rat using large-molecule microdialysis combined with multiplex arrays after acute and chronic ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 43(4):640–654. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13963
Gill K, Deitrich RA (1998) Acute tolerance to the ataxic effects of ethanol in short-sleep (SS) and long-sleep (LS) mice. Psychopharmacology 136(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050543
Gioia DA, McCool B (2017) Strain-dependent effects of acute alcohol on synaptic vesicle recycling and post-tetanic potentiation in medial glutamate inputs to the mouse basolateral amygdala. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 41(4):735–746. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13343
Goncalves J, Martins T, Ferreira R, Milhazes N, Borges F, Ribeiro CF, Malva JO, Macedo TR, Silva AP (2008) Methamphetamine-induced early increase of IL-6 and TNF-alpha mRNA expression in the mouse brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1432.043
Gruol DL, Huitron-Resendiz S, Roberts AJ (2018) Altered brain activity during withdrawal from chronic alcohol is associated with changes in IL-6 signal transduction and GABAergic mechanisms in transgenic mice with increased astrocyte expression of IL-6. Neuropharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.05.024
Gruol DL, Melkonian C, Huitron-Resendiz S, Roberts AJ (2020) Alcohol alters IL-6 signal transduction in the CNS of transgenic mice with increased astrocyte expression of IL-6. Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00879-2
Gruol DL, Nelson TE (1997) Physiological and pathological roles of interleukin-6 in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 15(3):307–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02740665
Gundersen V, Storm-Mathisen J, Bergersen LH (2015) Neuroglial transmission. Physiol Rev 95(3):695–726. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00024.2014
Hao Y, Jing H, Bi Q, Zhang J, Qin L, Yang P (2014) Intra-amygdala microinfusion of IL-6 impairs the auditory fear conditioning of rats via JAK/STAT activation. Behav Brain Res 275:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.08.052
Hernandez RV, Puro AC, Manos JC, Huitron-Resendiz S, Reyes KC, Liu K, Vo K, Roberts AJ, Gruol DL (2016) Transgenic mice with increased astrocyte expression of IL-6 show altered effects of acute ethanol on synaptic function. Neuropharmacology 103:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.12.015
Heyser CJ, Masliah E, Samimi A, Campbell IL, Gold LH (1997) Progressive decline in avoidance learning paralleled by inflammatory neurodegeneration in transgenic mice expressing interleukin 6 in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(4):1500–1505
Hilfiker S, Pieribone VA, Czernik AJ, Kao HT, Augustine GJ, Greengard P (1999) Synapsins as regulators of neurotransmitter release. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 354(1381):269–279. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1999.0378
Holma M, Holma I, Isometsa E (2020) Comorbid alcohol use disorder in psychiatric MDD patients: A five-year prospective study. J Affect Disord 267:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.02.024
Jankowsky JL, Derrick BE, Patterson PH (2000) Cytokine responses to LTP induction in the rat hippocampus: a comparison of in vitro and in vivo techniques. Learn Mem 7(6):400–412
Jovanovic JN, Czernik AJ, Fienberg AA, Greengard P, Sihra TS (2000) Synapsins as mediators of BDNF-enhanced neurotransmitter release. Nat Neurosci 3(4):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/73888
Kalluri HS, Ticku MK (2002) Ethanol-mediated inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol 439(1–3):53–58
Kalueff AV, Lehtimaki KA, Ylinen A, Honkaniemi J, Peltola J (2004) Intranasal administration of human IL-6 increases the severity of chemically induced seizures in rats. Neurosci Lett 365(2):106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.04.061
Kane CJ, Phelan KD, Douglas JC, Wagoner G, Johnson JW, Xu J, Drew PD (2013) Effects of ethanol on immune response in the brain: region-specific changes in aged mice. J Neuroinflammation 10:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-10-66
Kane CJ, Phelan KD, Douglas JC, Wagoner G, Johnson JW, Xu J, Phelan PS, Drew PD (2014) Effects of ethanol on immune response in the brain: region-specific changes in adolescent versus adult mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(2):384–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12244
Kushner SA, Elgersma Y, Murphy GG, Jaarsma D, van Woerden GM, Hojjati MR, Cui Y, LeBoutillier JC, Marrone DF, Choi ES, De Zeeuw CI, Petit TL, Pozzo-Miller L, Silva AJ (2005) Modulation of presynaptic plasticity and learning by the H-ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/synapsin I signaling pathway. J Neurosci 25(42):9721–9734. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2836-05.2005
Leenders AG, Sheng ZH (2005) Modulation of neurotransmitter release by the second messenger-activated protein kinases: implications for presynaptic plasticity. Pharmacol Ther 105(1):69–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.10.012
Li AJ, Katafuchi T, Oda S, Hori T, Oomura Y (1997) Interleukin-6 inhibits long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res 748(1–2):30–38
Lovinger DM (2018) Presynaptic ethanol actions: potential roles in ethanol seeking. Handb Exp Pharmacol 248:29–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2017_76
Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF (1990) NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic excitation selectively inhibited by ethanol in hippocampal slice from adult rat. J Neurosci 10(4):1372–1379
MacDougall MJ, Fine A (2014) The expression of long-term potentiation: reconciling the preists and the postivists. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369(1633):20130135. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0135
Mai HN, Chung YH, Shin EJ, Sharma N, Jeong JH, Jang CG, Saito K, Nabeshima T, Reglodi D, Kim HC (2018) IL-6 knockout mice are protected from cocaine-induced kindling behaviors; possible involvement of JAK2/STAT3 and PACAP signalings. Food Chem Toxicol 116(Pt B):249–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.04.031
Murata S, Usuda N, Okano A, Kobayashi S, Suzuki T (2000) Occurrence of a transcription factor, signal transducer and activators of transcription 3 (Stat3), in the postsynaptic density of the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 78(1–2):80–90
Nelson TE, Campbell IL, Gruol DL (1999) Altered physiology of Purkinje neurons in cerebellar slices from transgenic mice with chronic central nervous system expression of interleukin-6. Neuroscience 89(1):127–136
Nelson TE, Olde Engberink A, Hernandez R, Puro A, Huitron-Resendiz S, Hao C, De Graan PN, Gruol DL (2012) Altered synaptic transmission in the hippocampus of transgenic mice with enhanced central nervous systems expression of interleukin-6. Brain Behav Immun 26(6):959–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.05.005
Puglia MP, Valenzuela CF (2010) Ethanol acutely inhibits ionotropic glutamate receptor-mediated responses and long-term potentiation in the developing CA1 hippocampus. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34(4):594–606. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01128.x
Quintana A, Molinero A, Borup R, Nielsen FC, Campbell IL, Penkowa M, Hidalgo J (2008) Effect of astrocyte-targeted production of IL-6 on traumatic brain injury and its impact on the cortical transcriptome. Dev Neurobiol 68(2):195–208. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.20584
Roberto M, Nelson TE, Ur CL, Brunelli M, Sanna PP, Gruol DL (2003) The transient depression of hippocampal CA1 LTP induced by chronic intermittent ethanol exposure is associated with an inhibition of the MAP kinase pathway. Eur J Neurosci 17(8):1646–1654
Roberts AJ, Khom S, Bajo M, Vlkolinsky R, Polis I, Cates-Gatto C, Roberto M, Gruol DL (2019) Increased IL-6 expression in astrocytes is associated with emotionality, alterations in central amygdala GABAergic transmission, and excitability during alcohol withdrawal. Brain Behav Immun 82:188–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.08.185
Rosenbloom MJ, Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A (2010) Focus on the brain: HIV infection and alcoholism: comorbidity effects on brain structure and function. Alcohol Res Health 33(3):247–257
Rothaug M, Becker-Pauly C, Rose-John S (2016) The role of interleukin-6 signaling in nervous tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863(6):1218–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.03.018
Sparkman NL, Buchanan JB, Heyen JR, Chen J, Beverly JL, Johnson RW (2006) Interleukin-6 facilitates lipopolysaccharide-induced disruption in working memory and expression of other proinflammatory cytokines in hippocampal neuronal cell layers. J Neurosci 26(42):10709–10716. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3376-06.2006
Sukoff Rizzo SJ, Neal SJ, Hughes ZA, Beyna M, Rosenzweig-Lipson S, Moss SJ, Brandon NJ (2012) Evidence for sustained elevation of IL-6 in the CNS as a key contributor of depressive-like phenotypes. Translational psychiatry 2:e199. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2012.120
Tancredi V, D'Antuono M, Cafe C, Giovedi S, Bue MC, D'Arcangelo G, Onofri F, Benfenati F (2000) The inhibitory effects of interleukin-6 on synaptic plasticity in the rat hippocampus are associated with an inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK. J Neurochem 75(2):634–643
Turner KM, Burgoyne RD, Morgan A (1999) Protein phosphorylation and the regulation of synaptic membrane traffic. Trends Neurosci 22(10):459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01436-8
Wei H, Alberts I, Li X (2013) Brain IL-6 and autism. Neuroscience 252:320–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.025
Weil ZM, Corrigan JD, Karelina K (2018) Alcohol use disorder and traumatic brain injury. Alcohol Res 39(2):171–180
Yamagata Y (2003) New aspects of neurotransmitter release and exocytosis: dynamic and differential regulation of synapsin I phosphorylation by acute neuronal excitation in vivo. J Pharmacol Sci 93(1):22–29. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.93.22
Yang L, Xin X, Zhang J, Zhang L, Dong Y, Zhang Y, Mao J, Xie Z (2014) Inflammatory pain may induce cognitive impairment through an interlukin-6-dependent and postsynaptic density-95-associated mechanism. Anesth Analg 119(2):471–480. https://doi.org/10.1213/ane.0000000000000279
Zhang Y, Wei G, Di Z, Zhao Q (2014) miR-339-5p inhibits alcohol-induced brain inflammation through regulating NF-kappaB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 452(3):450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.092
Zorumski CF, Mennerick S, Izumi Y (2014) Acute and chronic effects of ethanol on learning-related synaptic plasticity. Alcohol 48(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.09.045
Zucker RS (1996) Exocytosis: a molecular and physiological perspective. Neuron 17(6):1049–1055
Zucker RS, Regehr WG (2002) Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Physiol 64:355–405. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.64.092501.114547
Acknowledgements
We thank Alana C. Puro, Jessica C. Manos, and Kenneth C. Reyes for performing some of the experiments.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants AA024484 and the Integrated Neuroscience Initiative on Alcoholism (INIA)-West Grant AA020893, and The Scripps Research Institute’s Mouse Behavioral Assessment Core.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DLG and AJR conceived of the project and designed the experiments. DLG analyzed and interpreted the data with support from RH. RH carried out the experiments. All authors contributed to manuscript preparation and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Animals
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guideline for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Animal facilities and experimental protocols were in accordance with the Association for the Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care.
Informed Consent
NA.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gruol, D.L., Hernandez, R.V. & Roberts, A. Alcohol Enhances Responses to High Frequency Stimulation in Hippocampus from Transgenic Mice with Increased Astrocyte Expression of IL-6. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 1299–1310 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00902-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00902-6