Abstract
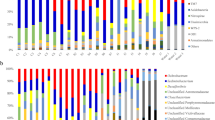
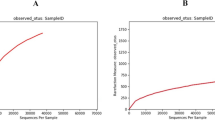
This study investigated the intestinal microbial community structure of Litopenaeus vannamei at six different stages during shrimp farming. Our goal was to elucidate the bacterial profile and the changes in the relative abundance of taxa during an atypical massive mortality event in Sonora, Mexico. High-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis showed that Vibrionaceae was persistent with high relative abundances in the intestine from cultivated shrimp during all the studied stages. The massive mortality observed at day 63 could be related to an overabundance of different Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) of Vibrio, Shewanella and Clostridium. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) showed variations in microbial structure at different culture times. These findings suggest that OTUs of different taxa contributed to the community switch from healthy to diseased individuals, questioning the hypothesis that single bacterial species is the cause of disease outbreaks. This study provided data to improve the understanding of disease outbreaks during shrimp farming.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thitamadee S, Prachumwat A, Srisala J, Jaroenlak P, Salachan PV, Sritunyalucksana K, Flegel TW, Itsathitphaisarn O (2016) Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 452:69–87
Xiong J, Dai W, Li C (2016) Advances, challenges, and directions in shrimp disease control: the guidelines from an ecological perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6947–6954
Xiong J, Zhu J, Dai W, Dong Ch, Qiu Q, Li Ch (2017) Integrating gut microbiota immaturity and disease-discriminatory taxa to diagnose the initiation and severity of shrimp disease. Environ Microbiol 19:1490–1501
Gao S, Pan L, Huang F, Song M, Tian CH, Zhang M (2019) Metagenomic insights into the structure and function of intestinal microbiota of the farmed Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 499:109–118
Gilbert JA, Quinn RA, Debelius J, Xu ZZ, Morton J, Garg N, Jansson JK, Dorrestein PC, Knight R (2016) Microbiome-wide association studies link dynamic microbial consortia to disease. Nature 535:94–103
Zeng S, Huang Z, Hou D, Liu J, Weng S, He J (2017) Composition, diversity and function of intestinal microbiota in pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) at different culture stages. PeerJ 5:e3986
Xiong J, Zhu J, Zhang D (2014) The application of bacterial indicator phylotypes to predict shrimp health status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8291–8299
Xiong J, Dai W, Qiu Q, Zhu J, Yang W, Li Ch (2018) Response of host-bacterial colonization in shrimp to developmental stage, environment and disease. Mol Ecol 27:3686–3699
Xiong J, Xuan L, Yu W, Zhu J, Qiu Q, Chen J (2019) Spatiotemporal successions of shrimp gut microbial colonization: high consistency despite distinct species pool. Environ Microbiol 21:1383–1394
Rungrassamee W, Klanchui A, Chaiyapechara S, Maibunkaew S, Tangphatsornruang S, Jiravanichpaisal P, Karoonuthaisiri N (2013) Bacterial population in intestines of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) under different growth stages. PLoS ONE 8:e60802
Zhang M, Sun Y, Chen K, Yu N, Zhou Z, Chen L, Du Z, Li E (2014) Characterization of the intestinal microbiota in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, fed diets with different lipid sources. Aquaculture 434:449–455
Li CC, Chen JC (2009) The immune response of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and its susceptibility to Vibrio alginolyticus under low and high pH stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:701–709
Zhou J, Fang W, Yang X, Zhou S, Hu L, Li X, Qi X, Su H, Xie L (2012) A Nonluminescent and highly virulent Vibrio harveyi strain is associated with “bacterial white tail disease” of Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp. PLoS ONE 7:e299
Vandenberghe J, Verdonck L, Robles-Arozarena R, Rivera G, Bolland A, Balladares M, Gomez-Gil B, Calderon J, Sorgeloos P, Swings J (1999) Vibrios Associated with Litopenaeus vannamei larvae, postlarvae, broodstock, and hatchery probionts. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2592–2597
Saulnier D, Haffner P, Goarant C, Levya P, Ansquera D (2000) Experimental infection models for shrimp vibriosis studies: a review. Aquaculture 191:133–144
Morales-Covarrubias MS, Cuéllar-Anjel J, Varela-Mejías A, Elisondo-Ovares C (2018) Shrimp bacterial infections in Latin America: a review. In: Asian Fisheries Society (ed) AHPND Acute hepatopancreatic disease. FAO Asian Fisheries Science, Rome, pp 76–87
Zhu J, Dai W, Qiu Q, Dong C, Zhang J, Xiong J (2016) Contrasting ecological processes and functional compositions between intestinal bacterial community in healthy and diseased shrimp. Microb Ecol 72:975–985
Zhu J, Miller MB, Vance RE, Dziejman M, Bassler BL, Mekalanos JJ (2002) Quorum-sensing regulators control virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:3129–3134
Hau HH, Gralnick JA (2007) Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:237–258
Xiong J, Dai W, Zhu J, Liu K, Dong C, Qiu Q (2017) The underlying ecological processes of gut microbiota among cohabitating retarded, overgrown and normal shrimp. Microb Ecol 73:988–999
Chaiyapechara S, Rungrassamee W, Suriyachay I, Kuncharin Y, Klanchui A, Karoonuthaisiri N, Jiravanichpaisal P (2012) Bacterial community associated with the intestinal tract of P. monodon in commercial farms. Microb Ecol 63:938–953
Gainza O, Ramírez C, Salinas Ramos A, Romero J (2017) Intestinal microbiota of white shrimp Penaeus vannamei under intensive cultivation conditions in Ecuador. Microb Ecol 75:562–568
CONAPESCA (2014) Anuario estadístico de acuacultura y pesca 2014. Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca, SAGARPA. Mazatlán, México
Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Wrighton KC, Zvenigorodsky N, Chen F, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P (2010) Experimental factors affecting PCR-based estimates of microbial species richness and evenness. ISME J 4:642–647
García-Maldonado JQ, Escobar-Zepeda A, Raggi L, Bebout BM, Sanchez-Flores A, López-Cortés A (2018) Bacterial and archaeal profiling of hypersaline microbial mats and endovaporites, under natural conditions and methanogenic microcosm experiments. Extremophiles 18:903–916
Andrew DR, Fitak RR, Munguia-Vega A, Racolta A, Martinson VG, Dontsova K (2012) Abiotic factors shape microbial diversity in Sonora desert soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7527–7537
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Gonzalez PA, Goodrich KJ, Gordon IJ, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–3336
Bragg L, Stone G, Imelfort M, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2012) Fast, accurate error-correction of amplicon pyrosequences using Acacia. Nat Methods 9:425–426
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E, Methé B, DeSantis TZ, The Human Microbiome Consortium, Petrosino JF, Knight R, Birren BW (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequencing PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucl Acids Res 41(D1):D590–D596
R Core Team (2018) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2009) FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol 26:1641–1650
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O'Hara R B, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2018) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.5-2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Lex A, Gehlenborg N, Strobelt H, Vuillemot R, Pfister H (2014) UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 20:1983–1992
Gómez-Gil B, Thompson CC, Matsumura Y, Sawabe T, Iida T, Christen R, Thompson F, Sawabe T (2014) The Family Vibrionaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 659–747
Katoh S (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML Version 8: A tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313
Matsen FA, Kodner RB, Armbrust E (2010) pplacer: linear time maximum-likelihood and Bayesian phylogenetic placement of sequences onto a fixed reference tree. BMC Bioinform 11(538):1–16
Letunic I, Bork P (2019) Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W256–259
Dabadé DS, Wolkers-Rooijackers JCM, Azokpota P, Hounhouigan DJ, Zwietering MH, Nout MJR, den Besten HMW (2016) Bacterial concentration and diversity in fresh tropical shrimps (Penaeus notialis) and surrounding brackish waters and sediment. Int J Food Microbiol 218:96–104
Porchas-Cornejo MA, Martínez-Porchas M, Vargas-Albores F, Gollas-Galvan T, Martínez-Córdova LR, Vazquez-Euan R, Peña-Messina E (2017) High-resolution detection of bacterial profile of ocean water, before and after being used by shrimp farms. Aquacult Int 25:1833–1843
Vargas-Albores F, Porchas-Cornejo MA, Martínez-Porchas M, Villalpando-Canchola E, Gollas-Galván T, Martínez-Córdova LR (2017) Bacterial biota of shrimp intestine is significantly modified by the use of a probiotic mixture: a high throughput sequencing approach. Helg Mar Res 71:1–10
Cornejo-Granados F, Lopez-Zavala AA, Gallardo-Becerra L, Mendoza-Vargas A, Sánchez F, Vichido R, Brieba LG, Viana MT, Sotelo-Mundo RR, Ochoa-Leyva A (2017) Microbiome of Pacific whiteleg shrimp reveals differential bacterial community composition between wild, aquacultured and AHPND/EMS outbreak conditions. Sci Rep 7:11783
Kriem MR, Banni B, El Bouchtaoui H, Hamama A, El Marrakchi A, Chaouqy N, Robert-Pillot A, Quilici ML (2015) Prevalence of Vibrio spp. in raw shrimps (Parapenaeus longirostris) and performance of a chromogenic medium for the isolation of Vibrio strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 61:224–230
Kondo H, Tinwongger S, Proespraiwong P, Mavichak R, Unajak S, Nozaki R, Hirono I (2014) Draft genome sequences of six strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from early mortality syndrome/acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease shrimp in Thailand. Genome Announc 2:e00221–e1214
Garibay-Valdez E, Martínez-Porchas M, Calderón K, Vargas-Albores F, Gollas-Galván G, Martínez-Córdova L (2020) Taxonomic and functional changes in the microbiota of the white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) associated with postlarval ontogenetic development. Aquaculture 518:734842
MacDonell MT, Colwell RR (1985) Phylogeny of the Vibrionaceae and recommendation for two new genera, Listonella and Shewanella. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:171–182
Kita-Tsukamoto K, Oyaizu H, Namba K, Simidu U (1993) Phylogenetic relationships of marine bacteria, mainly members of the Family Vibrionaceae, determined on the basis of 16S rRNA sequences. Int J Syst Bact 43:8–19
Cai J, Chen H, Thompson KD, Li C (2006) Isolation and identification of Shewanella algae and its pathogenic effects on post-larvae of abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta. J Fish Dis 29:505–508
Chang Ch, Chaoqun H, Xiaoyan Ch, Luping Z (2003) Identification and characterization of Shewanella algae as a novel pathogen of ulcer disease of fish Scinenops ocellata. Oceano Limnol Sin 34:1–8
Md Zoqratt MZH, Han Eng WW, Thai BT, Austin ChM, Gang HM (2018) Microbiome analysis of Pacific white shrimp gut and rearing water from Malaysia and Vietnam: implications for aquaculture research and management. PeerJ 6:e5826
Giraffa G (2003) Functionality of enterococci in dairy products. Int J Food Microbiol 88:215–222
Gerritsen J, Fuentes S, Grievink W, van Niftrik L, Tindall BJ, Timmerman HM, Rijkers GT, Smidt H (2014) Characterization of Romboutsia ilealis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gastro-intestinal tract of a rat, and proposal for the reclassification of five closely related members of the genus Clostridium into the genera Romboutsia gen. nov., Intestinibacter gen. nov., Terrisporobacter gen. nov. and Asaccharospora gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1600–1616
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, Grants 175268 (FINNOVA 2012–2014) and 178664 (PROINNOVA 2012–2013) to ALC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author performed the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by JQG-M, AM-V, MM and HL-B. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AL-C and all authors participated in drafting the sections of the manuscript and commented on previous versions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
The specimens are aquaculture animals. The animals were handled under the best practices and for sampling, the principles of Replacement, Reduction and Refinement (3Rs) were applied.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Cortés, A., Latisnere-Barragán, H., García-Maldonado, J.Q. et al. Intestinal Microbiota Analyses of Litopenaeus vannamei During a Case of Atypical Massive Mortality in Northwestern Mexico. Curr Microbiol 77, 2312–2321 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02079-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02079-z