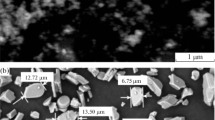
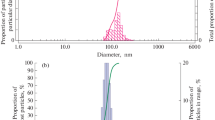
Abstract
Under a single 4 hour inhalation exposure to aerosol containing an aqueous suspension of calcium oxide nanoparticles (CaO) in an actual concentration of 6.68 mg/m3, the accumulation of calcium increased in the lungs (by 1.52 times), in the brain (by 1.55 times) and in the liver (by 1.25 times) relative to the control, while exposure to a microdispersed analog in a concentration of 6.37 mg/m3 resulted in an increase in the indicator only in the brain (by 1.27 times). At the same time, the calcium concentration in the brain of animals in the experimental group is higher than in the comparison group (by 1.22 times). After exposure to CaO nano- and microparticles a subarachnoid hemorrhage in the brain tissues was found. The development of pathomorphological changes in the form of lymphoid tissue hyperplasia, eosinophilia, acute arterial plethora, and hemorrhagic lung infarcts, as well as the hydropic and hyaline-drop dystrophy of parenchymal liver tissue was observed only after exposure to CaO nanoparticles. The identified features of the bioaccumulation and pathomorphological changes under inhalation exposure to CaO nanoparticles demonstrate that the studied nanomaterial has a higher level of toxicity in comparison to its microdispersed analog.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Benefits and Applications, National Nanotechnology Initiative. http://www.nano.gov/you/nanotechnology-benefits. Accessed January 21, 2020.
A. Sukhanova, S. Bozrova, P. Sokolov, et al., “Dependence of nanoparticle toxicity on their physical and chemical properties,” Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13 (44), 21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2457-x
S. Abraham and V. P. Saranthy, “Biomedical applications of calcium oxide nanoparticles - a spectroscopic study,” Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 49, 121 (2018).
C. Batt and M. Tortorello, Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed. (Academic, Elsevier, San Diego, 2014).
Calcium Oxide (CaO) Nanoparticles – Properties, Applications, AZoNano. 2013. http://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=3365. Accessed January 21, 2020.
H. Bai, X. Shen, X. Liu, et al., “Synthesis of porous CaO microsphere and its application in catalyzing transesterification reaction for biodiesel,” Trans. Nonferr. Met. 19, 674 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60130-6
S. Al-Shaibani, “The effect of calcium oxide-nanoparticles on the function of the kidney organ in the rats,” J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 13, 7689 (2018).
A. R. Butt, S. Ejaz, J. C. Baron, et al., “CaO nanoparticles as a potential drug delivery agent for biomedical applications,” Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 10, 799 (2015).
G. Gedda, S. Pandy, Y.-C. Lin, et al., “Antibacterial effect of calcium oxide nano-plates fabricated from shrimp shells,” Green Chem. 17, 3276 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC00615E
C. Bhavya, K. Yogendra, K. M. Mahadevan, et al., “Synthesis of calcium oxide nanoparticles and its mortality study on fresh water fish cyprinus carpio,” IOSR J. Environ. Sci., Toxicol. Food Technol. 10 (12), 55 (2016).
J. Kovrižnych, R. Sotnikova, D. Zeljenkova, et al., “Acute toxicity of 31 different nanoparticles to zebrafish (Danio rerio) tested in adulthood and in early life stages - comparative study,” Interdiscipl. Toxicol. 6 (2), 67 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2013-0012
Natl. Res. Council of the National Acad., Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Natl. Acad. Press, Washington, DC, 2011).
S. J. Goldstein, J. G. Sacks, C. Lee, et al., “Computed tomographic findings in cerebral arterial ectasia,” Am. J. Neuroradiol., No. 4, 501 (1983).
Kim Jung Hun, Kim Jin Hyoung, J. A. Park, S. W. Lee, et al., “Blood-neural barrier: intercellular communication at glio-vascular interface,” J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39, 339 (2006). https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2006.39.4.339
S. Liu, D. Agalliu, C. Yu, and M. Fisher, “The role of pericytes in blood-brain barrier function and stroke,” Curr. Pharm. Des. 18, 3653 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212802002706
C. Pease, T. Rucker, and T. Birk, “Review of the evidence from epidemiology, toxicology and lung bioavailability on the carcinogenicity of inhaled iron oxide particulates,” Chem. Res. Toxicol. 29, 237 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00448
B. N. Lambrecht and H. Hammad, “The immunology of asthma,” Nat. Immunol. 16, 45 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3049
I. Petrushanko, N. Bogdanov, E. Bulygina, et al., “Na-K-ATPase in rat cerebellar granule cells is redox sensitive,” Am. J. Physiol., Regul. Integr. Compar. Physiol. 290, R916 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00038.2005
Medical Biophysics: A textbook for Higher School, 3rd ed., Ed. by V. Samoilov (SpetsLit, St. Petersburg, 2013) [in Russian].
Pathological Anatomy: Textbook, 5th ed., Ed. by A. I. Strukov and V. V. Serov (Litterra, Moscow, 2010) [in Russian].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitseva, N.V., Zemlyanova, M.A., Stepankov, M.S. et al. Studying and Assessing the Toxicity of Calcium Oxide Nanoparticles under One-Time Inhalation Exposure. Nanotechnol Russia 14, 497–503 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019050148
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019050148