Abstract
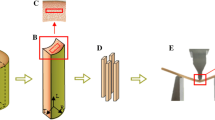
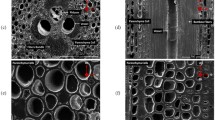
Bamboo based composite materials are widely used for structural components in building and textile industries. The structural hierarchy across different scales could enhance the strength and toughness of bamboo for load-bearing applications. Firstly, chemical components of bamboo fibril are described, and bamboo fibril specimens are fabricated through chemical solution processing; Secondly, functionally graded mechanical properties of macroscopic bamboo fibers are studied with tensile experiments, and relations between graded mechanical properties and microstructures are explored; Afterwards, hierarchical microstructure characterization of bamboo across different scales are performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and mechanical properties of bamboo fibrils are tested using homemade in-situ micro-tension setup. The results indicate that the elastic modulus, ultimate strain and strength of bamboo fibers are: 5.952 GPa, 0.0136 and 81.13 MPa respectively. The Young’s moduli, ultimate strains and fracture strengths of the five fibril samples located in (10.478, 12.285) GPa, (0.0172, 0.0217) and (181.87, 230.50) MPa, respectively. These experimental results suggest that the modulus and ultimate strength of bamboo fibril are higher than that of bamboo fibers which are attributed to several main factors including the ages of the bamboo, bamboo species, multi-lamella structures of the fibrils, geometry differences of fibrils, etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. P. Cottingham, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 136, 2283 (2014).
B. Sharma, A. Gatóo, M. Bock, and M. Ramage, Const. Build. Mater., 81, 66 (2015).
A. K. Ray, S. Mondai, S. K. Das, and P. Ramachandrarao, J. Mater. Sci., 40, 5249 (2005).
S. C. Burgess and D. Pasini, J. Eng. Des., 15, 177 (2004).
S. A. S. Zainathul Akhmar, M. Z. Nurul Aizan, A. Mohd Muhiddin, J. Siti Sarah, and Z. Nor Hazwani, Adv. Mater. Res., 812, 53 (2013).
C. Hong, Y. Yan, T. Zhong, Y. Wu, Y. Li, Z. Wu, and B. Fei, Cellulose, 24, 333 (2017).
X. Zhou, L. Chen, S. Huang, G. Su, and Y. Yu, Tran. Chin. Soc. Agr. Eng., 30, 287 (2014).
J. Xie, J. Qi, T. Hu, C. F. De Hoop, C. Y. Hse, and T. F. Shupe, J. Mater. Sci., 51, 7480 (2016).
S. Amada and S. Untao, Compos. Part B-Eng., 32, 451 (2001).
L. Zou, H. Jin, W. Y. Lu, and X. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 29, 1375 (2009).
S. Yang, X. Liu, B. Fei, Z. Jiang, X. Yang, and H. Shan, Chin. For. Sci. Technol., 3, 70 (2012).
N. S. V. Gupta, K. V. S. Rao, and D. S. A. Kumar, IOP Confer. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 149, 012093 (2016).
Y. Wang, G. Wang, H. Cheng, G. Tian, Z. Liu, Q. F. Xiao, X. Zhou, X. Han, and X. Gao, Text. Res. J., 80, 334 (2010).
L. Ma, H. He, C. Jiang, L. Zhou, Y. Luo, and D. Jia, J. Macromol. Sci. B, 51, 2232 (2012).
H. Chen, Y. Yu, T. Zhong, Y. Wu, Y. Li, Z. Wu, and B. Fei, Cellulose, 24, 333 (2017).
W. Wu, X. Li, and L. Liu, Rev. Sci. Instru., 80, 085107 (2009).
E. P. S. Tan, C. N. Goh, C. H. Sow, and C. T. Lim, Appl. Phys. Lett., 86, 073115 (2005).
R. Krishnaprasad, N. R. Veena, H. J. Maria, R. Rajan, M. Skrifvars, and K. Joseph, J. Polym. Environ., 17, 109 (2009).
P. K. Kushwahak and R. Kumar, J. Reinf. Plast. Comp., 30, 73 (2011).
B. Lybeer, J. Van Acker, and P. Goetghebeur, WoodSci. Technol., 40, 477 (2006).
W. Liese and G. Weiner, Wood Sci. Tech., 30, 77 (1996).
S. M. Yang, Z. H. Jiang, H. Q. Ren, B. H. Fei, and X. E. Liu, Spectrosc. Spect. Anal., 30, 3399 (2010).
Acknowledgments
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51874213) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, M., Jiang, X., Ke, H. et al. Experimental Investigations on the Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber and Fibril. Fibers Polym 21, 1382–1386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-9554-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-9554-z