Abstract
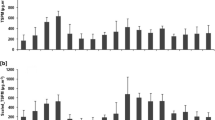
Size-fractionated particulate matter (PM), associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and their dry deposition fluxes were measured in a coastal urban environment of Mumbai, India. PM samples were collected using a variable configuration cascade impactor (VCCI) with 11 size fractionation stages. Dry deposition samples were collected using a round-bottomed PVC tray. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used for the identification and quantification of PAHs in samples. PM were observed to range between 58 and 130 μg m−3, with a mean dry deposition flux of 1298 mg m−2 day−1. Observed PM concentrations during the sampling period were found to be well above the WHO Air Quality Guidelines. A strong linear correlation was observed between the gravitational settling velocities and estimated dry deposition velocities for PM. Concentrations of PAHs associated with PM were observed to be in the range 101–145 ng m−3 while their dry deposition fluxes varied from 1008 to 1160 ng m−2 month−1. The molecular diagnostic ratios (MDRs) indicated that sources of PAHs in the study area were petrogenic as well as non-traffic. The dry deposition velocities calculated for PAHs were in the order of 10−4 cm s−1 to 10−3 cm s−1 in the entire size range.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Shafya HI, Mansour MSM (2016) A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt J Pet 25(1):107–123
Birgül A, Tasdemir Y, Cindoruk SS (2011) Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) determined using a modified sampler. Atmos Res 101:341–353
Burkart K, Nehls I, Win T, Endlicher W (2013) The carcinogenic risk and variability of particulate-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with consideration of meteorological conditions. Air Qual Atmos Health 6:27–38
Caffery PF (1997) Size distributions, sources, and dry deposition of atmospheric particles in Southern Lake Michigan. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park
Chate DM, Rao PSP, Naik MS, Momin GA, Safai PD, Ali K (2003) Scavenging of aerosols and their chemical species by rain. Atmos Environ 37:2477–2484
Cincinelli A, del Bubba M, Martellini T, Gambaro A, Lepri L (2007) Gas-particle concentration and distribution of n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmosphere of Prato (Italy). Chemosphere 68(3):472–478
Connan O, Maro D, HeÂbert D, Roupsard P, Goujon R, Letellier B et al (2013) Wet and dry deposition of particles associated metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Ni, Hg) in a rural wetland site, Marais Vernier, France. Atmos Environ 67:394–403
CPCB (2009) http://cpcb.nic.in/uploads/National_Ambient_Air_Quality_Standards.pdf (Accessed on April 30: 2019)
Dvorská A, Lammel G, Klánová J (2011) Use of diagnostic ratios for studying source apportionment and reactivity of ambient polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over Central Europe. Atmos Environ 45:420–427
Filippo PD, Riccardi C, Pomata D, Buiarelli F (2010) Concentrations of PAHs, and nitro-and methyl-derivatives associated with a size-segregated urban aerosol. Atmos Environ 44:2742–2749
Garrido A, Jimenez-Guerrero P, Ratola N (2014) Levels, trends and health concerns of atmospheric PAHs in Europe. Atmos Environ 99:474–484
Gnauk T, Muller K, Bruggemann E, Birmili W, Weinhold K, van Pinxteren D, Loschau G, Spindler G, Herrmann H (2011) A study to discriminate local, urban and regional source contributions to the particulate matter concentrations in the city of Dresden, Germany. J Atmos Chem 68:199–231
Golomb D, Barry E, Fischer G, Varanusupakul P, Koleda M, Rooney T (2001) Atmospheric deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons near new England coastal waters. Atmos Environ 35:6245–6258
Gupta S, Kumar K, Srivastava A, Srivastava A, Jain VK (2011) Size distribution and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in aerosol particle samples from the atmospheric environment of Delhi, India. Sci Total Environ 409:4674–4680
Hien TT, Thanh LT, Kameda T, Takenaka N, Bandow H (2007) Distribution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with particle size in urban aerosols at the roadside in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Atmos Environ 41:1575–1586
Hussein T, Smolik J, Kerminen V, Kulmala M (2012) Modeling dry deposition of aerosol particles onto rough surfaces. Aerosol Sci Technol 46(1):44–59
IARC (1991) International Agency for Research on Cancer. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Lyon(FR) 1991:43–53
Katsoyiannis A, Sweetman AJ, Jones KC (2011) PAH molecular diagnostic ratios applied to atmospheric sources: a critical evaluation using two decades of source inventory and air concentration data from the UK. Environmental Science & Technology 45:8897–8906
Kaupps H, McLachlan MS (1999) Atmospheric particle size distributions of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their implications for wet and dry deposition. Atmos Environ 33:85–95
Kawanaka Y, Matsumoto E, Sakamoto K, Wang N, Yun SJ (2004) Size distributions of mutagenic compounds and mutagenicity in atmospheric particulate matter collected with a low-pressure cascade impactor. Atmos Environ 38:2125–2132
Khaiwal R, Sokhi R, Grieken R (2008) Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos Environ 42:2895–2921
Kim K, Ara S, Kabir E, Brown RJC (2013) A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ Int 60:71–80
Koulouri E, Saarikoski S, Theodosi C, Markaki Z, Gerasopoulos E, Kouvarakis G, Makela T, Hillamo R, Mihalopoulos N (2008) Chemical composition and sources of fine and coarse aerosol particles in the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Environ 42:6542–6550
Lee JY, Shin HJ, Bae SY, Kim YP, Kan CH (2008) Seasonal variation of particle size distributions of PAHs at Seoul, Korea. Air Qual Atmos Health 1:57–68
Li X, Tao S, Liu W, Li X, Chen H, Wu S (2010) Dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its influence on surface soil contamination in Tianjin, China. J Environ Monit 12:952–957
Lv Y, Li X, Xu TT, Cheng TT, Yang X, Chen JM, Iinuma Y, Herrmann H (2016) Size distributions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban atmosphere: sorption mechanism and source contributions to respiratory deposition. Atmos Chem Phys 16:2971–2983
Mohan SM (2016) An overview of particulate dry deposition: measuring methods, deposition velocity and controlling factors. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:387–402
Ncube S, Madikizela L, Cukrowska E, Chimuk L (2018) Recent advances in the adsorbents for isolation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from environmental sample solutions. Trends Anal Chem 99:101–116
Nsibande SA, Montaseri H, Forbes PBC (2019) Advances in the application of nanomaterial-based sensors for detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aquatic systems. Trends Anal Chem 115:52–69
Odabasi M, Sofuoglu A, Vardar N, Tasdemir Y, Holsen TM (1999) Measurement of dry deposition and air-water exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with the water surface sampler. Environ Sci Technol 33:426–434
Pacyna JM (2008) Atmospheric deposition. Ecological Process:275–285
Phoothiwut S, Junyapoon S (2013) Size distribution of atmospheric particulates and particulate-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and characteristics of PAHs during haze period in Lampang Province, Northern Thailand. Air Qual Atmos Health 6:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-012-0194-3
Police S, Sahu SK, Tiwari M, Pandit GG (2018) Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Trombay (Mumbai, India), a coastal industrial area. Particuology 37:143–153
Pooltawee J, Pimpunchat B, Junyapoon S (2017) Size distribution, characterization and risk assessment of particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during haze periods in Phayao Province, northern Thailand. Air Qual Atmos Health 10:1097–1112
Pryor S, Gallagher M, Sievering H, Larsen SE, Barthelmie RJ, Birsan F, Nemitz E, Rinne J, Kulmala M, Grönholm T (2008) A review of measurement and modelling results of particle atmosphere–surface exchange. Tellus B 60:42–75
Radke M, Willsch H, Welte DH (1980) Preparative hydrocarbon group type determination by automated medium pressure liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 52(3):406–411
Sahu SK, Pandit GG, Puranik VD (2008) Dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with atmospheric particulate matters in an urban site, Mumbai, India. Aerosol Air Qual Res 8(4):437–446
Sahu SK, Pandit GG and Sadasivan S (2004) Precipitation Scavenging of Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Mumbai. Sci Total Environ 318 (1-3): 245-249.
Sahu SK, Bhangare RC, Ajmal PY, Sharma S, Pandit GG, Puranik VD (2009) Characterization and quantification of persistent organic pollutants in fly ash from coal fueled thermal power stations in India. Microchem J 92:92–96
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (2006) Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change, pp 900-931 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN-13: 978-0-471-72018-8
Shahin U, Yi SM, Paodes RD, Holsen T (2010) Long-term elemental dry deposition fluxes measured around Lake Michigan with an automated dry deposition sampler. Environ Sci Technol 10(35):1887–1892
Shannigrahi AS, Fukusima T, Ozaki N (2005) Comparison of different methods for measuring dry deposition fluxes of particulate matter and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the ambient air. Atmos Environ 35:653–662
Shen G, Wang W, Yang Y, Ding J, Xue M, Min Y, Zhu C, Shen H, Li W, Wang B, Wang R, Wang X, Tao S, Russell AG (2011) Emissions of PAHs from indoor crop residue burning in a typical rural stove: emission factors, size Distributions, and Gas-Particle Partitioning. Environ Sci Technol 45:1206–1212
Sheu HL, Lee WJ, Lin SJ, Fang GC, Chang HC, You WC (1997) Particle-bound PAH content in ambient air. Environ Pollut 96(3):369–382
Shi JH, Zhang J, Gao HW, Tan SC, Yao XH, Ren JL (2013) Concentration, solubility and deposition flux of atmospheric particulate nutrients over Yellow Sea. Deep-Sea Res II 97:43–50
Shi GL, Zhou XY, Jiang SY, Tian YG, Liu GR, Feng YC, Chen G, Liang YK (2015) Further insights into the composition, source, and toxicity of PAHs in size-resolved particulate matter in a megacity in China. Environ Chem 34(3):480–487
Singh S, Sapra BK, Khan A, Kothalkar PK, Mayya YS (2010) Development of variable configuration cascade impactor for aerosol size distribution measurement. Atmos Environ 44:795–802
Stull RB (2012) An introduction to boundary layer meteorology, Springer Science & Business Media, Dordrecht, the Netherlands
Tasdemir Y, Esen F (2007) Dry deposition fluxes and deposition velocities of PAHs at an urban site in Turkey. Atmos Environ 41:1288–1301
Terzi E, Samara C (2005) Dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban and rural sites of Western Greece. Atmos Environ 39:6261–6270
Tiwari M, Sahu SK, Bhangare RC, Ajmal PY, Pandit GG (2013) Estimation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with size segregated combustion aerosols generated from household fuels. Microchem J 106:79–86
Tiwari M, Sahu SK, Pandit GG (2017) PAHs in size fractionate mainstream cigarette smoke, predictive deposition and associated inhalation risk. Aerosol Air Qual Res 17:176–186
Tiwari M, Sahu SK, Pandit GG (2017a) Distribution of PAHs in different compartment of creek ecosystem: ecotoxicological concern and human health risk. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 50:58–66
Tiwari M, Sahu SK, Pandit GG (2019) Environmental distribution and ecotoxicological concerns of phthalic acid esters in creek ecosystem. J Environ Sci Health A 54(4):328–336
Tong X, Chen XC, Chuang HC, Cao JJ, Ho SSH, Lui KH, Ho KF (2019) Characteristics and cytotoxicity of indoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Hong Kong. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health 12:1459–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00762-0
Wang G, Kawamura K, Xie M, Hu S, Gao S, Cao J, An Z, Wang Z (2009) Size-distributions of n-alkanes, PAHs and hopanes and their sources in the urban, mountain and marine atmospheres over East Asia. Atmos Chem Phys 9:8869–8882
Wang X, Liu S, Zhao J, Zuo Q, Liu W, Li B, Tao S (2014) Deposition flux of aerosol particles and 15 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the north China plain. Environ Toxicol Chem 33(4):753–760
WHO (2018) https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health ()
Wu D, Wang Z, Chen J, Kong S, Fu X, Deng H, Shao G, Wu G (2014) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in atmospheric PM2.5 and PM10 at a coal-based industrial city: implication for PAH control at industrial agglomeration regions, China. Atmos Res 149:217–229
Wu Y, Liu J, Zhai J, Cong L, Wang Y, Ma W, Zhang Z, Li C (2018) Comparison of dry and wet deposition of particulate matter in near-surface waters during summer. PLoS One 13(6):e0199241. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199241
Yi SM, Totten LA, Thota S, Yan S, Offenberg JH, Eisenreich SJ, Garney J, Holsen TM (2006) Atmospheric dry deposition of trace elements measured around the urban and industrially impacted NY–NJ harbor. Atmos Environ 40:6626–6637
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser river basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH sources and composition. Org Geochem 33:489–515
Zhang L, Gong S, Padro J, Barrie L (2001) A size-segregated particle dry deposition scheme for an atmospheric aerosol module. Atmos Environ 35:49–560
Zhang K, Zhang BZ, Li SM, Wong CS, Zeng EY (2012) Calculated respiratory exposure to indoor size-fractioned polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in an urban environment. Sci Total Environ 431:245–251
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr. Admir Créso Targino of Federal University of Technology - Paraná/Brazil (UTFPR) for their help in English and content of the present manuscript.
Funding
This work is funded under the plan project of the Government of India at Bhabha Atomic Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 123 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, M., Sahu, S.K., Rathod, T. et al. Measurement of size-fractionated atmospheric particulate matter and associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Mumbai, India, and their dry deposition fluxes. Air Qual Atmos Health 13, 939–949 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00849-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00849-z