Abstract
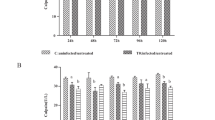
This study investigated the role of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway on host cell apoptosis in the early infection of Eimeria tenella. Chicken cecal epithelial cells were treated with apoptosis-inducer Actinomycin D (Act D) or PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibitor LY294002 and then infected with E. tenella. Results demonstrated that the E. tenella-infected group had less apoptosis 4–8 h after the infection and more apoptosis 12–20 h after the infection than the control group. At 4–20 h after the infection, the apoptotic/necrotic rate and the Caspase-3 activity in the Act D + E. tenella group were lower (P < 0.01) than those in the Act D-treated group. The p-Akt and NF-κB contents in the E. tenella-infected group were higher (P < 0.01) than those in the control group 4–12 h after the infection. However, the bad content and the Caspase-9/3 activity were lower (P < 0.05) in the E. tenella-infected group than in the control group. Compared with the E. tenella-infected group, the LY294002 + E. tenella group showed decreased p-Akt content and increased apoptotic/necrotic rate, bad content, NF-κB expression, membrane permeability transition pore (MPTP) openness, and Caspase-9/3 activity. Thus, the early development of E. tenella could inhibit host cell apoptosis by downregulating the Caspase-3 activity. Upregulating this activity promoted apoptosis. In addition, activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibited the apoptosis of E. tenella host cells in the early infection by reducing the expression of the bad content, limiting the MPTP opening, and decreasing the Caspase-9 and Caspase-3 activities.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand KV, Neelam A, Siera T, Iyer V, Christian S, Bin L, Liying W, Yon R (2011) Antioxidant c-FLIP inhibits Fas ligand-induced NF-κB activation in a PI3K/AKT-dependent manner[J]. J Immunol 187(6):3256–3266
Chen JZ (2012) Roles of the PI3K/Akt pathway in Epstein-Barr virus-induced cancers and therapeutic implications[J]. World J Virol 1(6):154–161
Chuenkova MV, Pereira MA (2000) A trypanosomal prote in synergizes with the cytokin esciliary neu rotrophic factor and leukemia inhibitory factor to prevent apoptosis of neuronal cells [J]. Mol Biol Cel 11:1487–1498
del Cacho E, Gallego M, López-Bernad F, Quílez J, Sánchez-Acedo C (2004) Expression of anti-apoptotic factors in cells parasitized by second-generation schizonts of Eimeria tenella and Eimeria necatrix[J]. Vet Parasitol 125(3–4):287–300
Duarte A, Silveira GG, Soave DF, João C, Oliveira P, Silva AR (2019) The Role of the LY294002 - A non-selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K) pathway- in cell survival and proliferation in cell line SCC-25.[J]. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev 20:3377–3383
Elizabeth S, Hannah G, Georgia W, Elizabeth M, Alexander L, Natasha A, Robert HI, Robert AS, Janet ML (2014) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition restores neutrophil accuracy in the elderly: toward targeted treatments for immunosenescence[J]. Blood 9(123):239–248
Gu SP, Zheng MX, Li BJ, Han KG (2010) Analysis on apoptosis of chicken Cecal epithelial cells infected by E. tenella.[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal & Veterinary Sciences 41(10):1322–1327
Juhaszova M, Zorov DB, Kim SH, Pepe S, Fu Q, Fishbein KW, Ziman BD, Wang S, Ytrehus K, Antos CL, Olson EN, Sollott SJ (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta mediates convergence of protection signaling to inhibit the mitochondrial permeability transition pore[J]. J Clin Invest 113:1535–1549
Karch J, Kwong JQ, Burr AR, Sargent MA, Elrod JW, Peixoto PM, Martinez-Caballero S, Osinska H, Cheng EH, Robbins J, Kinnally KW, Molkentin JD (2013) Bax and Bak function as the outer membrane component of the mitochondrial permeability pore in regulating necrotic cell death in mice[J]. Elife. 2(2):e00772
Kim L, Denkers EY (2006) Toxplasma gondii triggers Gi-dependent P13-kinase signaling required for inhibition of host cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Cell Science 119(10)):2119–2126
Kim NH, Kim K, Park WS, Son HS, Bae Y (2007) PKB/Akt inhibits ceramide induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells by blocking apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) translocation[J]. Cell Bioehem 102(5):1160–1170
Li YY, Popivanova BK, Nagai Y, Ishikura H, Fujii C, Mukaida N (2006) Pim-3, a proto-oncogene with serine/threonine kinase activity, is aberrantly expressed in human pancreatic cancer and phosphorylates bad to block bad-mediated apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cell lines [J]. Cancer Res 66(13):6741–6747
Li S, Zheng MX, Xu HC, Cui XZ, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yang SS, Xu ZY, Bai R, Sun XG (2016) Mitochondrial pathways are involved in Eimeria tenella-induced apoptosis of chick embryo cecal epithelial cells[J]. Parasitol Res 116(3):1–11
Parajuli B, Lee HG, Kwon SH, Cha SD, Shin SJ, Lee GH, Bae I, Cho CH (2013) Salinomycin inhibits Akt/NF-kB and induces apoptosis in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells [J]. Cancer Epidemiology 37:512–517
Pengtao C, Guiji W, Yingxin P, Liuxing W, Xiangying W, Renyin C (2008) The exploration of the effect of PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002 on improving chemotherapeutic sensitivity [J]. Journal of Basic and Clinical Oncology 21(1):10–12
Qasem MAA, Dkhil MA, Al-Shaebi EM, Murshed M, Mares M, Al-Quraishy S (2020) Rumex nervosus leaf extracts enhance the regulation of goblet cells and the inflammatory response during infection of chickens with Eimeria tenella[J]. J King Saud University-Science 32(3)
Shaw RJ, Cantley LC (2006) PI3K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth [J]. Nature 441(7092):424–430
Shuho S, Nanami I, Masafumi I, Masaru H, Mitsunori Y (2002) The in vitro and in vivo effects of 2-(4-Morpholinyl) -8-phenylchromone(LY294002), a specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, in human Colon Cancer cells[J]. Clinical Cancer Research 8:1957–1963
Wang R, Yang J, Peng J, Zhao J, Mu N, Huang J, Lazarovici P, Chen H, Zheng W (2015) Gardenamide a attenuated cell apoptosis induced by serum deprivation insult via the ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways[J]. Neuroscience 286:242–250
Wei L, Xiaoming Y (2008) Study of the interaction between Aktl and AIF[J]. Journal of Medical Molecular Biology 5(4):283–286
Xu J (2007) Study on the inhibition of host cell apoptosis by Toxoplasma gondii and its regulation mechanism [J]. Journal of Tropical Diseases and Parasitology 5(4):257–260
Xu ZY, Zheng MX, Zhang L, Gong X, Xi R, Cui XZ, Bai R (2017) Dynamic expression of death receptor adapter proteins tradd and fadd in Eimeria tenella-induced host cell apoptosis[J]. Poult Sci 96(5):1438–1444
Yang SS, Zheng MX, Xu HC, Cui XZ, Zhang Y, Zhao WL, Bai R (2015) The effect of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels on apoptosis of chick embryo cecal cells by Eimeria tenella.[J]. Research in Veterinary Science 99:188–195
Yoshiaki S, Masao Y, Toshiyuki M (2003) Caspase-8 and Caspase-10 activate NF-κB through RIP, NIK and IKKα kinases[J]. Immunnology. 7(33):1998–2006
Zhang Y, Zheng MX, Xu ZY, Xu HC, Cui XZ, Yang SS, Zhao WL, Li S, Lv QH, Bai R (2015) Relationship between Eimeria tenella development and host cell apoptosis in chickens.[J]. Poult Sci 94(12):2970–2979
Zhou W, Quan JH, Lee YH, Shin DW, Cha GH (2013) Toxoplasma gondii, proliferation require Down-regulation of host Nox4 expression via activation of PI3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway[J]. PLoS One 8(6):10454–10461
Zhu L, Derijar B, Krittalak C, Wang BS, Chen HZ, Hueber AO (2014) Synergism of PI3K/Akt inhibition and Fas activation on colon cancer cell death[J]. Cancer Letters 354:355–364
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972647).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All work involving animals was conducted in accordance with the national legislation on the protection of animal welfare and following the strict guidelines and approval of the Institution Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanxi Agricultural University, China.
Additional information
Section Editor: Berit Bangoura
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, S., Zheng, M. et al. Effects of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway on the apoptosis of early host cells infected with Eimeria tenella. Parasitol Res 119, 2549–2561 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06738-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06738-9