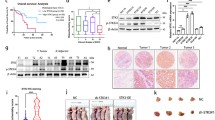
Abstract
In this study, the functional role of miR-550a-3 and its direct target nuclear factor IC (NFIC) in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC) cells were explored. Differential expression of miR-550a-3 in ESCC tissues was acquired from TCGA database, and Kaplan–Meier method was used to determine the relationship between miR-550a-3 expression and survival time of ESCC patients. Expression level of miR-550a-3 in several ESCC cell lines was measured by qRT-PCR. Two cell lines including Eca109 and JAR were used to perform proliferation, cloning, invasion and migration experiments. Targeted relationship between miR-550a-3 and NFIC was speculated by predication software and confirmed by dual luciferase assay. Additionally, potential relationship between miR-550a-3 and NFIC was analyzed by Spearman rank correlation analysis and western blot. Rescue assays were performed to explore the function of miR-550a-3/NFIC in ESCC cells biological behaviors. Expression levels of key proteins involved in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process were determined by western blot. By consulting TCGA database, we found that high expression of miR-550a-3 was positively connected with the poor prognosis of patients with ESCC. In addition, overexpression of miR-550a-3 promoted the proliferation, colony formation and metastasis of ESCC cells. Moreover, rescue assays revealed that overexpression of NFIC attenuated the promoting effects of miR-550a-3 on ESCC cells malignant behaviors. While the promoting effects of miR-550a-3 on EMT process were inhibited by NFIC. Our results illustrate the importance of miR-550a-3/NFIC in regulation of ESCC cells growth and metastasis, which could contribute to developing novel target for early diagnosis or neoteric therapeutic target for ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67:7–30
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD (2013) Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 381:400–412
Predescu D, Gheorghe M, Boeriu M, Constantin A, Iosif C, Anghel R, Constantinoiu S (2012) Molecular factors and criteria for predicting the response to neoadjuvant treatment in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)-responder/non-responder. Chirurgia (Bucur) 107:583–590
Murphy G, McCormack V, Abedi-Ardekani B, Arnold M, Camargo MC, Dar NA, Dawsey SM, Etemadi A, Fitzgerald RC, Fleischer DE, Freedman ND, Goldstein AM, Gopal S, Hashemian M, Hu N, Hyland PL, Kaimila B, Kamangar F, Malekzadeh R, Mathew CG, Menya D, Mulima G, Mwachiro MM, Mwasamwaja A, Pritchett N, Qiao YL, Ribeiro-Pinto LF, Ricciardone M, Schuz J, Sitas F, Taylor PR, Van Loon K, Wang SM, Wei WQ, Wild CP, Wu C, Abnet CC, Chanock SJ, Brennan P (2017) International cancer seminars: a focus on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 28:2086–2093
Khan S, Ayub H, Khan T, Wahid F (2019) MicroRNA biogenesis, gene silencing mechanisms and role in breast, ovarian and prostate cancer. Biochimie. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.09.001
Xu TJ, Qiu P, Zhang YB, Yu SY, Xu GM, Yang W (2019) MiR-148a inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioblastoma by targeting ITGA9. Hum Cell 32(4):548–556
Desvignes T, Batzel P, Berezikov E, Eilbeck K, Eppig JT, McAndrews MS, Singer A, Postlethwait JH (2015) miRNA nomenclature: a view incorporating genetic origins, biosynthetic pathways, and sequence variants. Trends Genet 31:613–626
Greene CM, Varley RB, Lawless MW (2013) MicroRNAs and liver cancer associated with iron overload: therapeutic targets unravelled. World J Gastroenterol 19:5212–5226
Shen J, Stass SA, Jiang F (2013) MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors. Cancer Lett 329:125–136
Han Y, Yang X, Zhao N, Peng J, Gao H, Qiu X (2016) Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating miR-370/PIM1 signaling. Am J Cancer Res 6:2755–2771
Liu W, Li M, Chen X, Zhang D, Wei L, Zhang Z, Wang S, Meng L, Zhu S, Li B (2016) MicroRNA-373 promotes migration and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting TIMP3 expression. Am J Cancer Res 6:1–14
Liu H, Ren G, Zhu L, Liu X, He X (2016) The upregulation of miRNA-146a inhibited biological behaviors of ESCC through inhibition of IRS2. Tumour Biol 37:4641–4647
Yang B, Liu Y, Li L, Deng H, Xian L (2020) MicroRNA-200a promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through extensive target genes. Mol Med Rep 21:2073–2084
Lu YF, Yu JR, Yang Z, Zhu GX, Gao P, Wang H, Chen SY, Zhang J, Liu MY, Niu Y, Wei XM, Wang W, Ye FJ, Zhang LX, Zhao Y, Sun GG (2018) Promoter hypomethylation mediated upregulation of MicroRNA-10b-3p targets FOXO3 to promote the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:301
Chen KS, Lim JWC, Richards LJ, Bunt J (2017) The convergent roles of the nuclear factor I transcription factors in development and cancer. Cancer Lett 410:124–138
Zhang Y, Xu Y, Li Z, Zhu Y, Wen S, Wang M, Lv H, Zhang F, Tian Z (2018) Identification of the key transcription factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Dis 10:148–161
Mei LL, Qiu YT, Zhang B, Shi ZZ (2017) MicroRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cancer Biomark 19:1–9
Chen Z, Zhao L, Zhao F, Yang G, Wang J (2016) MicroRNA-26b regulates cancer proliferation migration and cell cycle transition by suppressing TRAF5 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res 8:1957–1970
Luo H, Guo W, Wang F, You Y, Wang J, Chen X, Wang J, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X, Xue C, Song G, Wang F (2015) miR-1291 targets mucin 1 inhibiting cell proliferation and invasion to promote cell apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 34:2665–2673
Tian Q, Liang L, Ding J, Zha R, Shi H, Wang Q, Huang S, Guo W, Ge C, Chen T, Li J, He X (2012) MicroRNA-550a acts as a pro-metastatic gene and directly targets cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 7:e48958
Yang JZ, Bian L, Hou JG, Wang HY (2018) MiR-550a-3p promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through down-regulating TIMP2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:4156–4165
Ho JY, Hsu RJ, Wu CH, Liao GS, Gao HW, Wang TH, Yu CP (2016) Reduced miR-550a-3p leads to breast cancer initiation, growth, and metastasis by increasing levels of ERK1 and 2. Oncotarget 7:53853–53868
Hong H, Liu T, Wu H, Zhang J, Shi X, Le X, Chen AM, Mo H, Huang Q, Zhou H, Rao X (2019) MicroRNA-550a is associated with muscle system conferring poorer survival for esophageal cancer. Biosci Rep 39(5):BSR20181173
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 9:287–314
Hausser J, Zavolan M (2014) Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions–beyond repression of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 15:599–612
Mason S, Piper M, Gronostajski RM, Richards LJ (2009) Nuclear factor one transcription factors in CNS development. Mol Neurobiol 39:10–23
Yang B, Zhou ZH, Chen L, Cui X, Hou JY, Fan KJ, Han SH, Li P, Yi SQ, Liu Y (2018) Prognostic significance of NFIA and NFIB in esophageal squamous carcinoma and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med 7:1756–1765
Mao Y, Liu J, Zhang D, Li B (2015) MiR-1290 promotes cancer progression by targeting nuclear factor I/X(NFIX) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Biomed Pharmacother 76:82–93
Lee HK, Lee DS, Park JC (2015) Nuclear factor I-C regulates E-cadherin via control of KLF4 in breast cancer. BMC cancer 15:113
Satoh K, Hamada S, Shimosegawa T (2015) Involvement of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in the development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol 50:140–146
Liao TT, Yang MH (2017) Revisiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: the connection between epithelial plasticity and stemness. Mol Oncol 11:792–804
Gomes LR, Terra LF, Sogayar MC, Labriola L (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: implications in cancer progression and metastasis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 12:1881–1890
Loret N, Denys H, Tummers P, Berx G (2019) The role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal plasticity in ovarian cancer progression and therapy resistance. Cancers (Basel). 11(6):838
Bastid J (2012) EMT in carcinoma progression and dissemination: facts, unanswered questions, and clinical considerations. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31:277–283
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA, Weinberg RA (2018) EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18:128–134
Grabowska MM, Elliott AD, DeGraff DJ, Anderson PD, Anumanthan G, Yamashita H, Sun Q, Friedman DB, Hachey DL, Yu X, Sheehan JH, Ahn JM, Raj GV, Piston DW, Gronostajski RM, Matusik RJ (2014) NFI transcription factors interact with FOXA1 to regulate prostate-specific gene expression. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, MD). 28:949–964
Nilsson J, Helou K, Kovács A, Bendahl PO, Bjursell G, Fernö M, Carlsson P, Kannius-Janson M (2010) Nuclear Janus-activated kinase 2/nuclear factor 1–C2 suppresses tumorigenesis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by repressing Forkhead box F1. Can Res 70:2020–2029
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Shi, X. & Wu, S. miR-550a-3/NFIC plays a driving role in esophageal squamous cell cancer cells proliferation and metastasis partly through EMT process. Mol Cell Biochem 472, 115–123 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03790-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03790-y