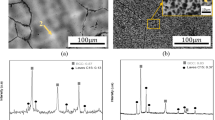
Optical and electron microscopy and x-ray spectral microanalysis are used to study the transformation of the phases present in the structure of cast refractory alloy HP40NbTi during prolonged high-temperature oxidation. It is established that during oxidation alloy phase chemical composition changes continuously and by complex laws in relation to the surroundings, temperature, and exposure duration, and there is rapid exchange of chemical elements between different phases. After prolonged exposure this process reaches a limiting condition.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here and subsequently through the text the element content is shown in weight fractions expressed as a %, with the exception of specially stipulated cases.
References
M. Garbiak, W. Jasinski, and B. Piekarski, “Materials for reformer furnace tubes. History of evolution,” Arch. Foundry Eng., 11, Special Issue 2, 47 – 52 (2011).
D. J. Tillack and J. E. Guthrie, “Wrought and cast heat-resistant stainless steels and nickel alloys for the refining and petrochemical industries,” Nickel Development Institute (Toronto), Technical Ser., No. 10, 71 – 85 (1998).
E. A. Kenik, P. J. Maziasz, R. W. Swindeman, et al., “Structure and phase stability in cast modified-HP austenite after long-term ageing,” Scr. Mater., 49(2), 117 – 122 (2003).
A. I. Rudskoy, A. S. Oryshchenko, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, et al., “Special features of structure and long-term strength of cast refractory alloy 45Kh26N33S2B2,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 55(3 – 4), 209 – 215 (2013).
A. I. Rudskoy, A. S. Oryshchenko, G. P. Anastasiadi, et al., “Transformation of the structure of refractory alloy 0.45C – 26Cr – 33Ni – 2Si – 2Nb during a long-term high-temperature hold,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 55(9 – 10), 517 – 525 (2014).
Antonello Alvino, Daniela Lega, Francesco Giacobbe, et al. “Damage characterization in two reformer heater tubes after nearly 10 years of service at different operative and maintenance conditions,” Eng. Failure Anal., 17(7 – 8), 1526 – 1541 (2010).
Zhichao Zhu, Congqian Cheng, Jie Zhao, and Lu Wang, “High temperature corrosion and microstructure deterioration of KHR35H radiant tubes in continuous annealing furnace,” Eng. Failure Anal., 21, 59 – 66 (2012).
A. A. Kaya, P. Krauklis, and D. J. Young, “Microstructure of HK40 alloy after high-temperature service in oxidizing carburizing environment: I. Oxidation phenomena and propagation of a crack,” Mater. Charact., 49(1), 11 – 21 (2002).
A. A. Kaya, “Microstructure of HK40 alloy after high-temperature service in oxidizing-carburizing environment: II. Carburization and carbide transformations,” Mater. Charact., 49(1), 23 – 34 (2002).
L. H. De Almeida, A. F. Ribeiro, and I. Le May, “Microstructural characterization of modified 25Cr – 35Ni centrifugally cast steel furnace tubes,” Mater. Charact., 49(3), 219 – 229 (2003).
F. C. Nunes, L. H. De Almeida, J. Dille, et al., “Microstructural changes caused by yttrium addition to NbTi-modified centrifugally cast HP-type stainless steels,” Mater. Charact., 58, 132 – 142 (2007).
A. I. Rudskoy, A. S. Oryshchenko, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, et al., “Mechanisms and kinetics of phase transformations in refractory alloy 45Kh26N33S2B2 in long-term high-temperature holds. Part 1,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 56(1 – 2), 3 – 8 (2014).
A. I. Rudskoy, S. Yu., Kondrat’ev, G. P. Anastasiadi, et al., “Mechanism and kinetics of phase transformations in refractory alloy 45Kh26N33S2B2 under long-term high-temperature holds. Part 2,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 56(3 – 4), 124 – 130 (2014).
L. S. Monobe and C. G. Schõn, “Microstructural and fractographic investigation of a centrifugally cast 20Cr32Ni + Nb alloy tube in the as cast and aged states,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2(2), 195 – 201 (2013).
K. G., Buchanan and M. V. Kral, “Crystallography and morphology of niobium carbide in as-cast HP-niobium reformer tubes,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 43A(6), 1760 – 1769 (2012).
K. G. Buchanan, M. V. Kral, and C. M. Bishop, “Crystallography and morphology of MC carbides in niobium-titanium modified as-cast HP alloys,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 45A(8), 3373 – 3385 (2014).
A. I. Rudskoi, G. P. Anastasiadi, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, et al., “Effect of electron factor (number of electron holes) on kinetics of nucleation, growth, and dissolution of phases during long-term high-temperature holdings of 0.45C – 26Cr – 33Ni – 2Si – 2Nb superalloy,” Phys. Met. Metallogr., 115(1), 1 – 11 (2014).
T. Sourmail, “Precipitates in creep resistant austenitic stainless steels,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 17(1), 1 – 14 (2001).
G. F. Vander Voort, G. M. Lucas, and E. P. Manilova, “Metallography and Microstructures of Heat-Resistant Alloys,” in: J. R. Davis, at al. (eds.), ASM Handbook, Vol. 9. Metallography and Microstructures, ASM International (2004).
R. A. P. Ibanez, G. D. De Almeida Soares, L. H. De Almeida, and I. Le May, “Effects of Si content on the microstructure of modified-HP austenitic steels,” Mater. Charact., 30, 243 – 249 (1993).
G. P. Anastasiadi, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, and A. I. Rudskoy, “Selective high-temperature oxidation of phases in a cast refractory alloy of the 25Cr – 35Ni – Si – Nb – C system,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 56(7 – 8), 403 – 408 (2014).
S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, G. P. Anastasiadi, and A. I. Rudskoy, “Nanostructure mechanism of formation of oxide film in heat-resistant Fe – 25Cr – 35Ni superalloys,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 56(9 – 10), 531 – 536 (2015).
N. McIntyre, N. Chan, and C. Chen, “Characterization of oxide structures formed on nickel-chromium alloy during low pressure oxidation at 500 – 600°C,” Oxidation Met., 33(5 – 6), 458 – 479 (1990).
A. P. Babichev, N. A. Babushkina, A. M. Bratkovskaya, et al., Physical Values: Handbook [in Russian], Énergoaromizdat, Moscow (1991).
V. A. Ryabin, M. V. Kireeva, N. A. Berg, et al., Inorganic Chromium Compounds [in Russian], Khimiya, Leningrad (1981).
S. Yu., Kondrat’ev, E. V. Sviatysheva, G. P. Anastasiadi, and S. N. Petrov, “Fragmented structure of niobium carbide particles in as-cast modified HP alloys,” Acta Mater., 127, 267 – 276 (2017).
I. P. Fedorov, Chemical Encyclopedia. Vol. 5, Chromium Oxides [in Russian], Izd. Bol. Ross. Ents., Moscow (1999).
R. Zapa’a and B. Kalandyk, “Identification of scale formed on Cr – Ni cast steel,” Arch. Foundry Eng., 10(4), 217 – 220 (2010).
Raluca Voicu, Eric Andrieu, Dominique Poquillon, et al., “Microstructure evolution of HP40-Nb alloys during aging under air at 1000°C,” Mater. Charact., 60(9), 1020 – 1027 (2009).
S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, A. V. Ptashnik, G. P. Anastasiadi, and S. N. Petrov, “Analysis of transformations of carbide phases in alloy 25Cr35Ni by the method of quantitative electron microscope,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 57(7 – 8), 402 – 409 (2015).
L. H., Koopmans, D. B. Owen, and J. I. Rosenblatt, “Confidence intervals for the coefficient of variation for the normal and log normal distributions,” Biometrika, 51(1 – 2), 25 – 32 (1964).
J. K. Patel, N. M. Patel, and R. I. Shiyani, “Coefficient of variation in field experiments and yardstick thereof — An empirical study,” Current Sci., 81(9 – 10), 1163 – 1164 (2001).
A. M. Babakr, A. Al-Ahmari, K. Al-Jumayiah, and F. Habiby, “Sigma phase formation and embrittlement of cast iron-chromium- nickel (Fe – Cr – Ni) alloys,” J. Miner. Mater. Char. Eng., 7, 127 – 145 (2008).
S. Y. Kondrat’ev, G. P. Anastasiadi, S. N. Petrov, and A. V. Ptashnik, “Kinetics of the formation of intermetallic phases in HP-type heat-resistant alloys at long-term high-temperature exposure,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A: Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 48(1), 482 – 492 (2017).
R. F. Voitovich and É. A Pugach, Refractory Compound Oxidation: Handbook [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1978).
Experimental research was conducted on equipment of the Center for Collective Usage of Scientific Equipment “Composition, structure, and properties of structural and functional materials” of the NITs Kurchatov Institute – TsNII KM Prometei with financial support Of the Russian Ministry of Education and Science within the scope of agreement No. 14.595.21.0004, unique identifier RFMEF159517X0004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 1, pp. 47 – 56, January, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondrat’ev, S.Y., Petrov, S.N., Anastasiadi, G.P. et al. Structural Features of Cast Refractory Alloy HP40NbTi High-Temperature Oxidation. Part 2. Microstructure and Phase Composition Evolution. Met Sci Heat Treat 62, 46–54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00511-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00511-6