Abstract
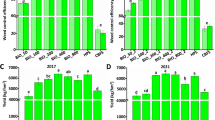
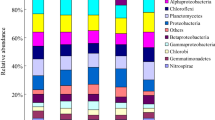
Among karst mountain agricultural fertilization measures, the partial replacement of chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers is important for protecting its vulnerable mountain environment and developing ecologically-friendly agriculture. In this study, we investigated the effects of short-term organic fertilizer application on the bacterial diversity of maize soil in karst areas and the potential of using organic fertilizer as a partial substitute for chemical fertilizers. Two maize fields with different parent materials in a karst region were selected for a short-term field control experiment using chemical fertilizer and organic fertilizer treatment, combined with the high-throughput sequencing method of 16S rDNA gene amplicons. (i) The soil physicochemical properties and bacterial diversity of different parent material soil are different, but the main dominant bacterial types are similar. (ii) Short-term organic fertilizer treatment, rather than chemical fertilizer treatment, increased the bacterial richness significantly, especially for some functional bacteria (such as Nitrospira, Gemmatimonas). (iii) Analysis of the correlation between environmental factors and bacterial diversity indicated that soil pH and total P had the most significant effects on bacterial community structure (r = 0.91, p = 0.001; r = 0.33, p = 0.001). This study showed that it is an effective method to maintain a richer bacterial community and increasing the abundance of some functional bacteria by increasing organic fertilizers and reducing chemical fertilizers in the farm soil in karst regions, which could also be applied to other fragile agricultural ecosystems in the world.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anda M, Suryani E, Husnain, Subardja D (2015) Strategy to reduce fertilizer application in volcanic paddy soils: nutrient reserves approach from parent materials. Soil Tillage Res 150:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.01.005
Baker B, Sheik C, Taylor C, Jain S, Bhasi A, Cavalcoli J, Dick G (2013) Community transcriptomic assembly reveals microbes that contribute to deep-sea carbon and nitrogen cycling. ISME J 7:2060. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.85
Blanchet G, Gavazov K, Bragazza L, Sinaj S (2016) Responses of soil properties and crop yields to different inorganic and organic amendments in a Swiss conventional farming system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 230:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.05.032
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bronick CJ, Lal R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.03.005
Calò F, Parise M (2006) Evaluating the human disturbance to karst environments in southern Italy. Acta Carsologica 35(2):47–56. https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v35i2-3.227
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Cardelli V, Cocco S, Agnelli A, Nardi S, Pizzeghello D, Fernández-Sanjurjo M, Corti G (2017) Chemical and biochemical properties of soils developed from different lithologies in northwestern Spain (Galicia). Forests 8:135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8040135
Cardinale BJ, Srivastava DS, Emmett Duffy J, Wright JP, Downing AL, Sankaran M, Jouseau C (2006) Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature 443:989–992. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05202
Cesarano G, De Filippis F, La Storia A, Scala F, Bonanomi G (2017) Organic amendment type and application frequency affect crop yields, soil fertility and microbiome composition. Appl Soil Ecol 120:254–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.08.017
Chen W, Teng Y, Li Z, Liu W, Ren W, Luo Y, Christie P (2018) Mechanisms by which organic fertilizer and effective microbes mitigate peanut continuous cropping yield constraints in a red soil of South China. Appl Soil Ecol 128:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.03.018
Chu HY, Lin XG, Fujii T, Morimoto S, Yagi K, Hu JL, Zhang J (2007) Soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, bacterial community structure in response to long-term fertilizer management. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2971–2976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.05.031
Chu HY, Fierer N, Lauber CL, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Grogan P (2010) Soil bacterial diversity in the Arctic is not fundamentally different from that found in other biomes. Environ Microbiol 12:2998–3006. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02277.x
Dai JZ, Yan RR, Wei ZJ, Bai YT, Zhang S, Wang TL, Sun SX (2017) Effects of short-term fertilization on soil microorganisms in a mown Leymus chinensis meadow. Chin J Ecol 36(9):2431–2437 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.201709.036
De Angelis KM, Silver WL, Thompson AW, Firestone MK (2010) Microbial communities acclimate to recurring changes in soil redox potential status. Environ Microbiol 12:3137–3149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02286.x
Diacono M, Montemurro F (2011) Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. In: Lichtfouse E, Hamelin M, Navarrete M, Debaeke P (eds) Sustainable agriculture volume 2. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 761–786
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10(10):996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/NMETH.2604
Fadrosh DW, Ma B, Gajer P, Sengamalay N, Ott S, Brotman RM, Ravel J (2014) An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-2618-2-6
Feng M, Adams JM, Fan K, Shi Y, Sun R, Wang D, Guo X, Chu H (2018) Long-term fertilization influences community assembly processes of soil diazotrophs. Soil Biol Biochem 126:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.08.021
Franke-Whittle IH, Manici LM, Insam H, Stres B (2015) Rhizosphere bacteria and fungi associated with plant growth in soils of three replanted apple orchards. Plant Soil 395:317–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2562-x
Geisseler D, Scow KM (2014) Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 75:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.03.023
Geisseler D, Linquist BA, Lazicki PA (2017) Effect of fertilization on soil microorganisms in paddy rice systems—a meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 115:452–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.09.018
Gong X, Liu C, Li J, Luo Y, Yang Q, Zhang W, Yang P, Feng B (2019) Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercropping patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res 195:104355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104355
Gu SS, Hu QL, Cheng YQ, Bai LY, Liu ZH, Xiao WJ, Gong Z, Wu Y, Feng K, Deng Y, Tan L (2019) Application of organic fertilizer improves microbial community diversity and alters microbial network structure in tea (Camellia sinensis) plantation soils. Soil Tillage Res 195:104356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104356
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Goulding KWT, Vitousek PM, Zhang FS (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327(5968):1008–1010. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1182570
Han G, Chen Q, Zhang S, Li G, Yi X, Feng C, Wang X, Yu C, Lan J (2019) Biochar effects on bacterial community and metabolic pathways in continuously cotton-cropped soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:249–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-0014-z
Huang Q, Wang JL, Wang C, Wang Q (2019) The 19-years inorganic fertilization increased bacterial diversity and altered bacterial community composition and potential functions in a paddy soil. Appl Soil Ecol 144:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.07.009
Islam MR, Singh Chauhan P, Kim Y, Kim M, Sa T (2011) Community level functional diversity and enzyme activities in paddy soils under different long-term fertilizer management practices. Biol Fertil Soils 47:599–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0524-2
Jones R, Robeson M, Lauber C, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J 3:442–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2008.127
Karlen D, Mausbach MJ, Doran JW, Cline RG, Harris R, Schuman GE (1997) Soil quality: a concept, definition, and framework for evaluation (a guest editorial). Soil Soc Am J 61:4–10. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1997.03615995006100010001x
Khalil UR, Zhang Y, Shahla A, Zhao J, Erinle KO (2016) Short term influence of organic and inorganic fertilizer on soil microbial biomass and DNA in summer and spring. J Northeast Agric Univ (Engl Ed) 23(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-8104(16)30028-9
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microb 75:5111–5120. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00335-09
Lentendu G, Wubet T, Chatzinotas A, Wilhelm C, Buscot F, Schlegel M (2014) Effects of long-term differential fertilization on eukaryotic microbial communities in an arable soil: a multiple barcoding approach. Mol Ecol 23(13):3341–3355. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12819
Li Y, Shao X, Guan W, Ren L, Liu J, Wang J, Wu Q (2016) Nitrogen-decreasing and yield-increasing effects of combined applications of organic and inorganic fertilizers under controlled irrigation in a paddy field. Pol J Environ Stud 25(2):673–680. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/61530
Li H, Feng W, He X, Zhu P, Gao H, Sun N, Xu M (2017) Chemical fertilizers could be completely replaced by manure to maintain high maize yield and soil organic carbon (SOC) when SOC reaches a threshold in the Northeast China Plain. J Integr Agric 16:937–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61559-9
Li C, Ma S, Shao Y, Ma S, Zhang L (2018) Effects of long-term organic fertilization on soil microbiologic characteristics, yield and sustainable production of winter wheat. J Integr Agric 17:210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61740-4
Liu J, Sui Y, Yu Z, Shi Y, Chu H, Jin J, Liu X, Wang G (2014) High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of Northeast China. Soil Biol Biochem 70:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.12.014
Liu L, Wu Y, Hu G, Zhang Z, Cheng A, Wang S, Ni J (2016) Biomass of karst evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest in Central Guizhou Province, southwestern China: a comprehensive inventory of a 2 ha plot. Silva Fennica 50(3):1492. https://doi.org/10.14214/sf.1492
Liu JL, Dang P, Gao Y, Zhu HL, Zhu HN, Zhao F, Zhao Z (2018) Effects of tree species and soil properties on the composition and diversity of the soil bacterial community following afforestation. For Ecol Manag 427:342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.06.017
Liu Y, Lu M, Zhang X, Sun Q, Liu R, Lian B (2019) Shift of the microbial communities from exposed sandstone rocks to forest soils during pedogenesis. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 140:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.03.006
Liu X, Li Y, Ren X, Chen B, Zhang Y, Shen C, Wang F, Wu D (2020) Long-term greenhouse cucumber production alters soil bacterial community structure. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:306–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00109-9
Lu RK (1999) Methods of agrochemical soil analysis vol. China Agricultural Science Press, Beijing
Ma XX, Wang LL, Li QH, Li H, Zhang SL, Sun BH, Yang XY (2012) Effects of longterm fertilization on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities during maize growing season. Acta Ecol Sin 32:5502–5511 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201110191555
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Marcos MS, Bertiller MB, Olivera NL (2019) Microbial community composition and network analyses in arid soils of the Patagonian Monte under grazing disturbance reveal an important response of the community to soil particle size. Appl Soil Ecol 138:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.03.001
Nacke H, Thürmer A, Wollherr A, Will C, Hodac L, Herold N, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Daniel R (2011) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of bacterial community structure along different management types in German forest and grassland soils. PLoS One 6(2):e17000. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017000
Okur N, Altindisli A, Cengel M, Gocmez S, Kayikcioglu HH (2009) Microbial biomass and enzyme activity in vineyard soils under organic and conventional farming systems. Turk J Agric For 33(4):413–423. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-0806-23
Pan Y, Cassman N, de Hollander M, Mendes LW, Korevaar H, Geerts RHEM, van Veen JA, Kuramae EE (2014) Impact of long-term N, P, K, and NPK fertilization on the composition and potential functions of the bacterial community in grassland soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12384
Parfitt RL, Yeates GW, Ross DJ, Mackay AD, Budding PJ (2005) Relationships between soil biota, nitrogen and phosphorus availability, and pasture growth under organic and conventional management. Appl Soil Ecol 28:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2004.07.001
Qin LY, Bai XY, Wang SJ, Zhou DQ, Luo GJ, Zhang SY, Li PL, Li Y (2014) Landscape pattern evolution of typical karst plateau in Puding, Guizhou during last 40 years. Chin J Ecol 33(12):3349–3357 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.2014.0299
Ren C, Zhao F, Kang D, Yang G, Han X, Tong X, Feng Y, Ren G (2016) Linkages of C:N:P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. For Ecol Manag 376:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.06.004
Rousk J, Bååth E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340–1351. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.58
Sakai M, Hosoda A, Ogura K, Ikenaga M (2014) The growth of Steroidobacter agariperforans sp nov., a novel agar-degrading bacterium isolated from soil, is enhanced by the diffusible metabolites produced by bacteria belonging to Rhizobiales. Microbes Environ 29:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME13169
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 75(23):7537–7541. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Guo JF, Ray JL, He JZ (2010) Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in Northeast China. Appl Soil Ecol 46(1):119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.06.015
Singh H, Verma A, Ansari MW, Shukla A (2014) Physiological response of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes to elevated nitrogen applied under field conditions. Plant Signal Behav 9:e29015. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.29015
Soil Survey Staff (2010) Keys to soil taxonomy, 11th edn. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington DC
Tang J, Tang XX, Qin YM, He QS, Yi Y, Ji ZL (2019) Karst rocky desertification progress: soil calcium as a possible driving force. Sci Total Environ 649:1250–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.242
Wang QF, Jiang X, Guan DW, Wei D, Zhao BS, Ma MC, Chen S, Li L, Cao F, Li J (2018) Long-term fertilization changes bacterial diversity and bacterial communities in the maize rhizosphere of Chinese Mollisols. Appl Soil Ecol 125:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.12.007
Yang Y, Shameer S, Mao S, Li Q, Ge F, Lian B, Lu CM (2020) Bioorganic–mineral fertilizer can remediate chemical fertilizer-oversupplied soil: purslane planting as an example. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00175-4
Zhang CH, Qi XK, Wang KL, Zhang MY, Yue YM (2017) The application of geospatial techniques in monitoring karst vegetation recovery in Southwest China: a review. Prog Phys Geogr Earth Environ 41(4):450–477. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133317714246
Zhao J, Ni T, Li Y, Xiong W, Ran W, Shen B, Shen Q, Zhang R (2014a) Responses of bacterial communities in arable soils in a rice-wheat cropping system to different fertilizer regimes and sampling times. PLoS One 9(1):e85301. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085301
Zhao J, Zhang R, Xue C, Xun W, Sun L, Xu Y, Shen Q (2014b) Pyrosequencing reveals contrasting soil bacterial diversity and community structure of two main winter wheat cropping systems in China. Microb Ecol 67:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0322-0
Zhao J, Ni T, Li J, Lu Q, Fang Z, Huang Q, Zhang R, Li R, Shen B, Shen Q (2016) Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl Soil Ecol 99:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.11.006
Zhou J, Guan D, Zhou B, Zhao B, Ma M, Qin J, Jiang X, Chen S, Cao F, Shen D, Li J (2015) Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in Northeast China. Soil Biol Biochem 90:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.005
Zhu J, Peng H, Ji XH, Li CJ, Li SN (2019) Effects of reduced inorganic fertilization and rice straw recovery on soil enzyme activities and bacterial community in double-rice paddy soils. Eur J Soil Biol 94:103116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2019.103116
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their gratitude to the three anonymous reviewers and editor for their insightful comments and kind suggestions.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by grants from the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA23060102) and the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0502305).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOC 2.97 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, L. et al. Effects of Short-Term Application of Chemical and Organic Fertilizers on Bacterial Diversity of Cornfield Soil in a Karst Area. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 2048–2058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00274-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00274-2