Abstract
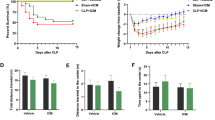
This study was designed to test whether the Cronobacter sakazakii infection-impaired contextual learning and memory are mediated by the activation of the complement system; subsequent activation of inflammatory signals leads to alternations in serotonin transporter (SERT). To test this, rat pups (postnatal day, PND 15) were treated with either C. sakazakii (107 CFU) or Escherichia coli OP50 (107 CFU) or Luria bertani broth (100 μL) through oral gavage and allowed to stay with their mothers until PND 24. Experimental groups’ rats were allowed to explore (PNDs 31–35) and then trained in contextual learning task (PNDs 36–43). Five days after training, individuals were tested for memory retention (PNDs 49–56). Observed behavioural data showed that C. sakazakii infection impaired contextual-associative learning and memory. Furthermore, our analysis showed that C. sakazakii infection activates complement system complement anaphylatoxin (C5a) (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS1)) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase1 (MEKK1). Subsequently, MEKK1 induces pro-inflammatory signals possibly through apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK-1), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1/3) and protein kinase B gamma (AKT-3). In parallel, activated nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer B cells (NF-κB) induces interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IFNα-1, which may alter the level of serotonin transporter (SERT). Observed results suggest that impaired contextual learning and memory could be correlated with C5a-mediated NF-κβ and ASK1 pathways.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All datasets generated for this study are included in the manuscript.
References
Akira S, Takeda T (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4(7):499–511
Arthur JS, Ley SC (2013) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13:679–692
Bai XZ, Zhang JL, Liu Y, Zhang W, Li XQ, Wang KJ, Cao MY, Zhang JN, Han F, Shi JH, Hu DH (2018) MicroRNA-138 aggravates inflammatory responses of macrophages by targeting SIRT1 and regulating the NF-κB and AKT pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 49:489–500
Balk RA (2014) Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Virulence 5(1):20–26
Belmer A, Klenowski PM, Patkar OL, Barlett SE (2017) Mapping the connectivity of serotonin transporter immunoreactive axons to excitatory and inhibitory neurochemical synapses in the mouse limbic brain. Brain Struct Funct 222:1297–1314
Beurel E, Jope RS (2009) Lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 production is controlled by glycogen synthase kinase-3 and STAT3 in the brain. J Neuroinflammation 6:9
Bhaskar K, Miller M, Chludzinski A, Herrup K, Zagorski M, Lamb BT (2009) The PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway regulates Abeta oligomer induced neuronal cell cycle events. Mol Neurodegener 4:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-4-14
Bosmann M, Patel VR, Russkamp NF, Pache F, Zetoune FS, Sarma JV, Ward PV (2011) MyD88-dependent production of IL-17F is modulated by the anaphylatoxin C5a via the Akt signalling pathway. FASEB J 25(12):4222–4232
Bifrare YD, Gianinzzi C, Imboden H, Leib SL, Täuber MG (2003) Bacterial meningitis causes two distinct forms of cellular damage in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in infant rats. Hippocampus 13(4):481–488
Bozza FA, Salluh JL, Japiassu AM, Soares M, Assis EF, Gomes RN, Bozza MT, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Bozza TB (2007) Cytokine profiles as markers of disease severity in sepsis: a multiplex analysis. Crit Care 11(2):R49
Bravo J, Dina ATG, Cryan JF (2014) Early-life stress induces persistent alterations in 5-HT1A receptor and serotonin transporter mRNA expression in adult rat brain. Front Mol Neurosci 7(24):1–9
Brouwer MC, de Gans J, Heckenberg SG, Zwinderman AH, van der Poll T, van de Beek D (2009) Host genetic susceptibility to pneumococcal and meningococcal disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 9(1):31–44
Campbell IL, Abraham CR, Masliah E, Kemper P, Inglis JD, Oldstone MB, Mucke L (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(21):10061–10065
Cuadrado A, Nabreda AR (2014) Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J 429:403–417
Czermak BJ, Sarma V, Pierson CL, Warner RL, Huber-Lang M, Bless NM, Schmal H, Friedl HP, Ward PA (1995) Protective effects of C5a blockade in sepsis. Nat Med 5:788–792
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):46–56
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Lawson MA, Kelley WK (2011) Inflammation-associated depression: from seroton into kynurenine. Pshychoneuroendocronlogy 36:426–436
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM et al (2012) Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Med 39(2):165–228
de Wit J, Ghosh A (2016) Specification of synaptic connectivity by cell surface interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:22–35
Dinel A-L, Joffre C, Trifilieff P, Aubert A, Foury A, Le Ruyet P, Laye´ S (2014) Inflammation early in life is a vulnerable factor for emotional behavior at adolescence and for lipopolysaccharideinduced spatial memory and neurogenesis alterations at adulthood. J Neuroinflammation 11:155.
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ, Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR, Greenberg ME (1997) Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science 275:661–665
Faix JD (2013) Biomarkers of sepsis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 50(1):23–36
Fan L-W, Tien L-T, Zheng B, Pang Y, Lin RCS, Simpson KL, Ma T, Rhodes PG, Cai Z (2011) Dopaminergic neuronal injury in the adult rat brain following neonatal exposure to lipopolysaccharide and the silent neurotoxicity. Brain Behav Immun 25:286–297
Feng X, Yu S, Hou H, Zou Y, Chen J, Guo L (2019) Rapamycin reduces degeneration of neurons by inhibiting Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway and restoring autophagy in EAE mice. Int J Clin Exp Med 11(4):3504–3513
Frick A, Fredrik AHS, Engman J, Jonasson M, Alaie I, Björkstrand J, Frans Ö, Faria V, Linnman C, Appel L, Walhstedt K, Lubberink M, Fredrikson M, Fumark T (2015) Serotonin synthesis and reuptake in social anxiety disorder: a positron emission tomography study. JAMA Psychiatry 72(8):794–802
Giri CP, Shima K, Tall BD, Curtis S, Sathyamoorthy V, Hanisch B, Kim KS, Kopecko DJ (2012) Cronobacter spp. (previously Enterobacter sakazakii) invade and translocate across both cultured human intestinal epithelial cells and human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microb Pathog 52(2):140–147
Green RL, Scott K, Minaga A, Conrad S (2004) Sepsis associated encephalopathy (SAE): a review. Front Biosci 9:1637–1641
Guo RF, Riedemann NC, Ward PA (2004) Role of C5a-C5aR interaction in sepsis Shock 21:1-7 Guo RF, and Ward PA (2005) Role of C5a in inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol 23:821–852
Guo X, Harada C, Namekata K, Matsuzawa A, Camps M, Ji H, Swinnen D, Jorand-Lebrun C, Muzerelle M, Vitte PA, Rückle T, Kimura A, Kohyama K, Matsumoto Y, Ichijo H, Harada T (2010) Regulation of the severity of neuroinflammation and demyelination by TLR-ASK1-p38 pathway. EMBO Mol Med 12:504–515. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201000103
Heyser CJ, Masliah E, Samimi A, Campbell IL, Gold LH (1993) Progressive decline in avoidance learning paralleled by inflammatory neurodegeneration in transgenic mice expressing interleukin 6 in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(4):1500–1505
Hjorth OR, Frick A, Gingnell M, Hoppe MJ, Faria V, Hultberg S, Alaie I, Mansson KNT, Walhstedt K, Jonasson M, Lubberink M, Antoni G, Fredrikson M, Fumark T (2019) Expression and co-expression of serotonin and dopamine transporters in social anxiety disorder: a multitracer positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0618-7
Hoesel LM, Gao H, Ward PA (2006) New insights into cellular mechanisms during sepsis. Immunol Res 34:133–141
Hu X, Weng Z, Chu CT, Zhang L, Cao G, Gao Y, Signore A, Zhu J, Hastings T, Greenamyre JT, Chen J (2011) Peroxiredoxin-2 protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration via attenuation of the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK1) signaling cascade. J Neurosci 31(1):247–261. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4589-10.2011
Huber-Lang MS, Sarma VJ, Lu KT, McGuire SR, Padgaonkar VA, Guo RF, Younkin EM, Kunkel RG, Ding J, Erickson R, Curnette JT, Ward PA (2001) Role of C5a in multiorgan failure during sepsis. J Immunol 166:1193–1199
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, Takagi M, Matsumoto K, Miyazono K, Gotoh Y (1997) Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 275(5296):90–94
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Su L (2020, 2020 May 15) MiR-539-5p decreases amyloid β-protein production, hyperphosphorylation of Tau and memory impairment by regulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathways in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Neurotox Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00217-w
Johnson GL, Lapadat R (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298(5600):1911–1912
Kalin NH, Takahashi KL, Chen FL (1994) Restraint stress increases corticotrophin-releasing hormone mRNA content in the amygdale and paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res 656(1):182–186
Kawai T, Akira S (2009) The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int Immunol 21(4):317–337
Kim HA, Yano H, Cho H, Meyer D, Monks B, Margolis B, Birnbaum MJ, Chao MV (2002a) Akt reugulates a JNK scaffold during exitotoxic apoptosis. Neuron 35:697–709
Kim DH, Feinbaum R, Alloing G, Emerson FE, Garsin DA, Inoue H, Tanaka-Hino M, Hisamoto N, Matsumoto K, Tan MW, Ausubel FM (2002b) A conserved p38 MAP kinase pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity. Science 297(5581):623–626. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1073759
Kim H, Lim G, Sung B, Warg S, McCabe F, Rusanescu G et al (2012) Brain Indolamine2,3-dioxygenase contributes to the comorbidity of pain and depression. J Clin Invset 122:2940–2954
Kitagishi Y, Wada Y, Matsuda S (2014) Roles of PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway in the pathogenesis of parkinson’s disease and the neuropsychiatric symptoms. Int Neuropsychiatr Dis J 1:1–12
Kong F, Han F, Xu Y, Shi Y (2017) Molecular mechanisms of IRE1α-ASK1 pathway reactions to unfolded protein response in DRN neurons of post-traumatic stress disorder rats. J Mol Neurosci 61(4):531–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0895-z
Kumar V, Zhang MX, Swank MW, Kunz J, Wu GY (2005) Regulation of dendritic morphogenesis by Ras-PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Ras-MAPK signaling pathways. J Neurosci 25:11288–11299
Kuperberg SJ, Wadgaonkar R (2017) Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: the blood-brain barrier and the sphingolipid rheostat. Front Immunol 8:597
Ishii KJ, Koyama S, Nakagawa A, Coban C, Akira S (2008) Host innate immune receptors and beyond: making sense of microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe. 3(6):352–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2008.05.003
Lakhani SA, Bogue CW (2003) Toll-like receptor signalling in sepsis. Curr Opin Pediatr 15:278–282
Lan KP, Wang CJ, Hsu JD, Chen KM, Lai SC, Lee HH (2004) Induced eosinophilia and proliferation in Angiostrongylus cantonensis-infected mouse brain are associated with the induction of JAK/STAT1, IAP/NF-kappaB and MEKK1/JNK signals. J Helminthol. 78(4):311–317
Laudes IJ, Chu JC, Sikranth S, Huber-Lang M, Guo RF, Riedemann N et al (2012) Anti-c5a ameliorates coagulation/fibrinolytic protein changes in a rat model of sepsis. Am J Pathol 160:1867–1875
Leach PT, Kenney JW, Gould TJ (2015) Stronger learning recruits additional cell-signaling cascades: c-Jun-N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) is necessary for expression of stronger contextual fear conditioning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 118:162–166
Leach PT, Kenney JW, Gould TJ (2016) c-Jun-N-terminal kinase 1 is necessary for nicotine-induced enhancement of contextual fear conditioning. Neurosci Lett. 627:61–64
Ledo JH, Azevedo EP, Beckman D, Ribeiro FC, Santos LE, Razolli DS, Kincheski GC, Melo HM, Bellio M, Teixeira AL, Velloso LA, Foguel D, de Felice FG, Ferreira ST (2016) Cross-talk between brain innate immunity and serotonin signalling underlies depressive-like behaviour induced by Alzheimer’s amloid-β oligomers in mice. J Neurosci 36(48):12106–12116
Leib SL, Heimgartner C, Bifrare YD, Loeffler JM, Täuber MG (2003) Dexamethasone aggravates hippocampal apoptosis and learning deficiency in pneumococcal meningitis in infant rats. Pediatric Research 54(3):353–357
Lerolle N, Nochy D, Geurot E, Bruneval P, Diebl JY et al (2010) Histopathology of septic shock induced acute kidney injury apoptosis and leukocytic infiltration. Intensive Care Med 36:471–478
Liu J, Li G, Xie WJ, Wung L, Zhang R, Huang KS et al (2007) Lipopolysaccharide stimulates surfactant protein-A in human rental epithelial HK-2 cells through upregulating toll-like receptor 4 dependent MEK1/2-ERK1/2-NF-kappaB pathway. Chin Med J 130(10):1236–1243
MacRae M, Kenkel W, Kentner AC (2015a) Social rejection following neonatal inflammation is mediated by olfactory scent cues. Brain Behav. Immun. 49:43–48
MacRae M, Macrina T, Khoury A, Migliore MM, Kentner AC (2015b) Tracing the trajectory of behavioral impairments and oxidative stress in an animal model of neonatal inflammation. Neuroscience 298:455–466
Matsuda S, Ikeda Y, Murakami M, Nakagawa Y, Tsuji A, Kitagishi Y (2019) Roles of PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway involved in psychiatric illness. Diseases 7:22–33
Matsuzawa A, Saegusa K, Noguchi T, Sadamitsu C, Nishitoh H, Nagai S, Koyasu S, Matsumoto K, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2005) ROS-dependent activation of the TRAF6-ASK1-p38 pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity. Nat Immunol 6:587–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1200
Moulton RA, Mashruwala MA, Smith AK, Lindsey DR, Wetsel RA, Haviland DL, Hunter RL, Jagannath C (2007) Complement C5a anaphylatoxin is an innate determinant of dendritic cell-induced Th1 immunity to Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in mice. J Leukoc Biol 82:956–967
Nazir S, Kumar A, Chatterjee I, Anbazhagan AN, Gujral T, Priyamvada S et al (2015) Mechanisms of intestinal serotonin transporter (SERT) upregulation by TGF-β1 induced non-Smad pathways. PLoS One 10(5):e0120447
Panta GR, Karur S, Cavin LG, Cortés ML, Mercurio F, Lothstein L, Sweatman TW, Israel M, Arsura M (2004) ATM and the catalytic subunit of DNA-dependent protein kinase activate NF-κB through a common MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/p90rsk signaling pathway in response to distinct forms of DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24(5):1823–1835
Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC, Mos RF, Tighe D, Bennett ED (2008) Pathophysiology of septic encephalopathy: a review. Crit Care Med 28(8):3019–3024
Rajji T, Chapman D, Eichenbaum H, Greene G (2006) The role of CA3 hippocampal NMDA receptors in paired associate learning. J Neurosci 26(3):908–1015
Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA (2003) The enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest. 112(4):460–467. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI19523
Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Hollmann TJ, Gao H, Neff TA, Reuben JS, Speyer CL, Sarma JV, Wetsel RA, Zetoune FS, Ward PA (2004) Regulatory role of C5a in LPS-induced IL-6 production by neutrophils during sepsis. FASEB J 18:370–372
Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Nadeau BA, Day DE, Huber-Lang M, Mackay CR, Zetoune FS, Gerard NP, Cianflone K, Köhl J, Gerard C, Sarma JV, Ward PA (2008) Functional roles for C5a receptors in sepsis. Nat Med 14:551–557
Sarma JV, Ward PA (2012) New developments in C5a receptor signalling. Cell Health Cytoskelet 4:73–82
Scholz W, McClurg MR, Cardenas GJ, Smith M, Noonan DJ, Hugli TE et al (1990) C5a-mediated release of interleukin 6 by human monocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 57:297–307
Semmler A, Frisch C, Debeir T, Ramanathan M, Okulla T, Klockgether T, Heneka MT (2007) Long-term cognitive impairment, neuronal loss and reduced cortical cholinergic innervation after recovery from sepsis in a rodent model. Exp Neurol 204(2):733–740
Serón MV, Ferwerda B, Engelen-Lee J, Geldhoff M, Jaspers V, Zwinderman AH, Tanck MW, Baas F, van der Ende A, Brouwer MC, van de Beek D (2016) V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 3(AKT3) contributes to poor disease outcome in humans and mice with Pneumococcal meningitis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 4(1):50
Shaulian E, Karin M (2004) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4:E131–E136
Shihab PK, Al-Roub A, Al-Ghanim M, Al-Mass A, Behbehani K, Ahmad R (2015) TLR2 and AP-1/NF-kappaB are involved in the regulation of MMP-9 elicited by heat killed Listeria monocytogenes in human monocytic THP-1 cells. J Inflamm (Lond) 12:32
Sivamaruthi BS, Madhumita R, Balamurugan K, Rajan KE (2015) Cronobacter sakazakii infection alters serotonin transporter and improved fear memory retention in the rat. Front Pharmacol 6:188
Song KY, Hyeon JY, Shin HC, Park CK, Choi IS, Seo KH (2008) Evaluation of a chromogenic medium supplemented with glucose for detecting Enterobacter sakazakii. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18(3):579–584
Song J, Cho KJ, Cheon SY, Kim SH, Park KA, Lee WT, Lee JE (2013) Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is linked to neural stem cell differentiation after ischemic brain injury. Exp Mol Med 45(12):e69. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2013.134
Sorensen L, Stromgaard K, Kristensen AS (2014) Characterization of intracellular regions in the human serotonin transporter for phosphorylation sites. ACS Chem Biol 9(4):935–944
Sury MD, Agarinis C, Widmer HR, Leib SL, Christen S (2008) NK is activated but does not mediate hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in experimental neonatal Pneumococcal meningitis. Neurobiol Dis. 32(1):142–150
Takeda K, Naguro I, Nishitoh H, Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2011) Apoptosis signalling kinases: from stress response to health outcomes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 15(3):719–761. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3392
Wang KC, Fan LW, Kaizaki A, Pang Y, Cai Z, Tien LT (2013) Neonatal lipopolysaccharide exposure induces long-lasting learning impairment, less anxiety-like response and hippocampal injury in adult rats. Neuroscience 234:146–157
Ward PA (2004) The dark side of C5a in sepsis. Immunology 4:133–142
Ward PA (2010) Role of C5 activation products in sepsis. Sci World J 10:2395–2402
Ward PA (2012) The harmful role of c5a on innate immunity in sepsis. J Innate Immun 2(5):439–445
Warner-Schmidt JL, Vanover KE, Chen EY, Marshell JJ, Greengar P (2011) Antidepressant effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are attenuated by antiinflammatory drugs in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:9262–9267
Woehrl B, Brouwer MC, Murr C, Heckenberg SG, Baas F, Pfister HW, Zwinderman AH, Morgan BP, Barnum SR, van der Ende A, Koedel U, van de Beek D (2011) Complement component 5 contributes to poor disease outcome in humans and mice with pneumococcal meningitis. J Clin Invest. 121(10):3943–3953
Yan C, Gao H (2012) New insights for C5a and C5a receptors in sepsis. Front Immunol 10(3):368
Yoon Y, McKenna MC, Rollins DA, Song M, Nuriel T, Gross SS et al (2013) Anxiety-associated alternative polyadenylation of the serotonin transporter mRNA confers translational regulation by hnRNPK. PNAS 110(28):11624–11629
Zhu CB, LindLer LM, Owens AN, Daws LC, Blakely RD, Hewlett WA (2010) Interleukin-1 receptor activation by systemic lipopolysaccharide induces behavioral despair linked to MAPK regulation of CNS serotonin transporters. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:2510–2520
Acknowledgements
We thank the reviewers for their comments to improve the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, through major project (BT/PR17367/MED/122/44/2016) to KER and KB, and Department of Animal Science Instrumentation facility supported by UGC-SAP-DRS-II and DST-FIST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was duly approved by bio-safety committee and Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) (BDU/IAEC/2015/NE/34 Dt. 17/03.2015).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary 1
Working model: Overview of the inflammatory signalling pathway that possibly alter the synaptic plasticity, learning and memory. Cronobacter sakazakii infection induced activation of Tol-like receptors (TLRs)/ pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) further activate complement system complement anaphylatoxin (C5a). Subsequently, different stimuli activate tiers of protein kinases, which phosphorylate different proteins involving in signalling pathway that regulates/ cause defects in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory depend on the activation of proteins. The molecules marked with asterisk examined in the present study (PNG 975 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinay, P., Karen, C., Balamurugan, K. et al. Cronobacter sakazakii Infection in Early Postnatal Rats Impaired Contextual-Associated Learning: a Putative Role of C5a-Mediated NF-κβ and ASK1 Pathways. J Mol Neurosci 71, 28–41 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01622-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01622-8