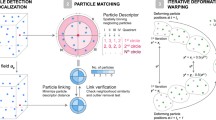
Abstract
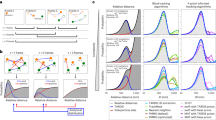
We introduce a new Lagrangian particle tracking algorithm that tracks particles in three dimensions to separations between trajectories approaching contact. The algorithm also detects low Weber number binary collisions that result in coalescence as well as droplet breakup. Particles are identified in two-dimensional high-resolution digital images by finding sets of circles to describe the edge of each body. This allows identification of particles that overlap in projection by over 80% even for noisy images and without invoking additional temporal data. The algorithm builds trajectories from three-dimensional particle coordinates by minimizing a penalty function that is a weighted sum of deviations from the expected particle coordinates using information from four moments in time. This new hybrid algorithm is validated against synthetic data and found to perfectly reproduce more trajectories than other commonly used methods. Collisions are detected with 95% accuracy for particles that move on average less than one tenth the distance to their nearest neighbor.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliseda A, Cartellier A, Hainaux F, Lasheras JC (2002) Effect of preferential concentration on the settling velocity of heavy particles in homogeneous isotropic turbulence. J Fluid Mech 468:77–105. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112002001593
Ayala O, Rosa B, Wang LP, Grabowski WW (2008) Effects of turbulence on the geometric collision rate of sedimenting droplets. Part 1: Results from direct numerical simulation. New J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/10/7/075015
Bateson CP, Aliseda A (2012) Wind tunnel measurements of the preferential concentration of inertial droplets in homogeneous isotropic turbulence. Exp Fluids 52(6):1373–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1252-6
Betelin VB, Smirnov NN, Nikitin VF, Dushin VR, Kushnirenko AG, Nerchenko VA (2012) Evaporation and ignition of droplets in combustion chambers modeling and simulation. Acta Astronaut 70:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2011.06.021
Bewley Gregory P, Saw Ewe-wei (2013) Observation of the sling effect. New J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/15/8/083051
Bordás R, Roloff C, Thévenin D, Shaw RA (2013) Experimental determination of droplet collision rates in turbulence. New J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/15/4/045010
Bourgeois F, Lassalle JC (1971) An extension of the Munkres algorithm for the assignment problem to rectangular matrices. Commun ACM 14(12):802–804. https://doi.org/10.1145/362919.362945
Canny J (1983) Finding edges and lines in images. PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Chen L, Goto S, Vassilicos JC (2006) Turbulent clustering of stagnation points and inertial particles. J Fluid Mech 553:143–154. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112006009177
Deriche R (1987) Using Canny’s criteria to derive a recursively implemented optimal edge detector. Int J Comput Vis 1(2):167–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123164
Devenish BJ, Bartello P, Brenguier JL, Collins LR, Grabowski WW, Ijzermans RH, Malinowski SP, Reeks MW, Vassilicos JC, Wang LP, Warhaft Z (2012) Droplet growth in warm turbulent clouds. Q J R Meteorol Soc 138(667):1401–1429. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.1897
Duru P, Koch DL, Cohen C (2007) Experimental study of turbulence-induced coalescence in aerosols. Int J Multiph Flow 33(9):987–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2007.03.006
Good GH, Ireland PJ, Bewley GP, Bodenschatz E, Collins LR, Warhaft Z (2014) Settling regimes of inertial particles in isotropic turbulence. J Fluid Mech 759:R3. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2014.602
Grabowski WW, Lp Wang (2013) Growth of cloud droplets in a turbulent environment. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45:293–326. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-011212-140750
Gülan U, Lüthi B, Holzner M, Liberzon A, Tsinober A, Kinzelbach W (2012) Experimental study of aortic flow in the ascending aorta via particle tracking velocimetry. Exp Fluids 53(5):1469–1485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-012-1371-8
Holzner M, Liberzon A, Nikitin N, Lüthi B, Kinzelbach W, Tsinober A (2008) A Lagrangian investigation of the small-scale features of turbulent entrainment through particle tracking and direct numerical simulation. J Fluid Mech 598:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112008000141
Hoyer K, Holzner M, Lüthi B, Guala M, Liberzon A, Kinzelbach W (2005) 3D scanning particle tracking velocimetry. Exp Fluids 39(5):923–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-005-0031-7
Ireland PJ, Collins LR (2012) Direct numerical simulation of inertial particle entrainment in a shearless mixing layer. J Fluid Mech 704:301–332. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2012.241
Ireland PJ, Vaithianathan T, Sukheswalla PS, Ray B, Collins LR (2013) Highly parallel particle-laden flow solver for turbulence research. Comput Fluids 76:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2013.01.020
Ireland PJ, Bragg AD, Collins LR (2016) The effect of Reynolds number on inertial particle dynamics in isotropic turbulence. Part 1. Simulations without gravitational effects. J Fluid Mech 796:617–658. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.238
Ireland PJ, Bragg AD, Collins LR (2016) The effect of Reynolds number on inertial particle dynamics in isotropic turbulence. Part 2. Simulations with gravitational effects. J Fluid Mech 796:659–711. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.227
Kawanisi K, Shiozaki R (2008) Turbulent effects on the settling velocity of suspended sediment. J Hydraul Eng 134(2):261–266. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134
Kobayashi H, White JL, Abidi AA (1991) An active resistor network for Gaussian filtering of images. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 26(5):738–748. https://doi.org/10.1109/4.78244
Lapp T, Rohloff M, Vollmer J, Hof B (2012) Particle tracking for polydisperse sedimenting droplets in phase separation. Exp Fluids 52(5):1187–1200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1243-7
Li Sing How M, Collins LR (2020) Direct numerical simulation of near contact motion and coalescence of inertial droplets in turbulence (Manuscript in preparation)
Maxey Corrsin (1986) Gravitation settling of aerosol particles in randomly oriented cellular flow fields. J Atmos Sci 43(11):1112–1134
Obligado M, Teitelbaum T, Cartellier A (2014) Preferential concentration of heavy particles in turbulence. J Turbul 15(5):293–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/14685248.2014.897710
Olivieri S, Picano F, Sardina G, Iudicone D, Brandt L (2014) The effect of the Basset history force on particle clustering in homogeneous and isotropic turbulence. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4871480
Ott S, Mann J (2000) An experimental investigation of the relative diffusion of particle pairs in three-dimensional turbulent flow. J Fluid Mech 422:207–223. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112000001658
Ouellette NT, Xu H, Bodenschatz E (2006) A quantitative study of three-dimensional Lagrangian particle tracking algorithms. Exp Fluids 40(2):301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-005-0068-7
Pratt V (1987) Direct least-squares fitting of algebraic surfaces. Comput Graph 21(4):145–152
Qian J, Law CK (1997) Regimes of coalescence and separation in droplet collision. J Fluid Mech 331:59–80. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112096003722
Reade WC, Collins LR (2000) Effect of preferential concentration on turbulent collision rates. Phys Fluids 12(10):2530–2540. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1288515
Saffman PG, Turner JS (1956) On the collision of drops in turbulent clouds. J Fluid Mech 1(1):16–30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112056000020
Salazar JP, De Jong J, Cao L, Woodward SH, Meng H, Collins LR (2008) Experimental and numerical investigation of inertial particle clustering in isotropic turbulence. J Fluid Mech 600:245–256. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112008000372
Schanz D, Gesemann S, Schröder A (2016) Shake-The-Box: Lagrangian particle tracking at high particle image densities. Exp Fluids 57(5):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-016-2157-1
Siewert C, Kunnen RPJ, Meinke M, Schröder W (2014) Orientation statistics and settling velocity of ellipsoids in decaying turbulence. Atmos Res 142:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.08.011
Smoluchowski M (1916) Drei vortrage uber diffusion, brownsche bewegungund koagulation von kolloidteilchen. Int J Res Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:557–585
Sobel I (1968) A 3 \(\times\) 3 isotropic gradient operator for image processing. In: Stanford artificial intelligence project
Sumbekova S, Cartellier A, Aliseda A, Bourgoin M (2017) Preferential concentration of inertial sub-Kolmogorov particles. The roles of mass loading of particles, St and Re. Phys Rev Fluids 2(2):1–18 arXiv:1607.01256v1
Trujillo-Pino A, Krissian K, Alemán-Flores M, Santana-Cedrés D (2013) Accurate subpixel edge location based on partial area effect. Image Vis Comput 31(1):72–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2012.10.005
Veenman CJ, Reinders MJT, Backer E (2003) Establishing motion correspondence using extended temporal scope. Artif Intell 145(1–2):227–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0004-3702(02)00380-6
Virant M, Dracos T (1997) 3D PTV and its application on Lagrangian motion. Meas Sci Technol 8(12):1539–1552. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/8/12/017
Wang LP, Wexler AS, Zhou Y (2000) Statistical mechanical description and modelling of turbulent collision of inertial particles. J Fluid Mech 415:117–153. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112000008661
Xue Y, Wang LP, Grabowski WW (2008) Growth of cloud droplets by turbulent collision-coalescence. J Atmos Sci 65(2):331–356. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007jas2406.1
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Melanie Li Sing How and Lance Collins of Cornell University for providing DNS data of inertial coalescing particles in turbulence for testing the tracking algorithm presented here.
Funding
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1605195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kearney, R.V., Bewley, G.P. Lagrangian tracking of colliding droplets. Exp Fluids 61, 155 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-020-02991-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-020-02991-x